标签:c# and web 下划线 int 方案 closed 解释型 设计
一、内容概要
1、Python 介绍
2、Python 版本
3、编写Hello World
4、编码
5、输入输出
6、变量
7、数据类型
8、条件语句
9、循环语句
10、常用数据类型
二、内容详细
1、Python 介绍
Python, 是一种面向对象的解释型计算机程序设计语言,由荷兰人Guido van Rossum于1989年发明,第一个公开发行版发行于1991年。
最新的TIOBE排行榜,Python赶超PHP占据第五!!!
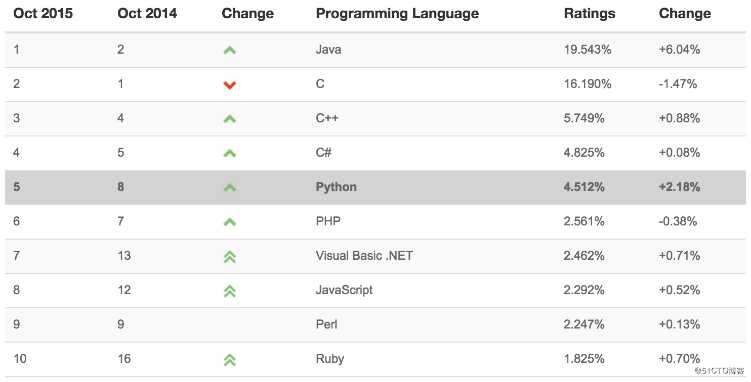
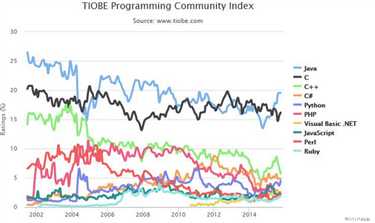
由上图可见,Python整体呈上升趋势,反映出Python应用越来越广泛并且也逐渐得到业内的认可!!!
Python可以应用于众多领域,如:数据分析、组件集成、网络服务、图像处理、数值计算和科学计算等众多领域。目前业内几乎所有大中型互联网企业 都在使用Python,如:Youtube、Dropbox、BT、Quora(中国知乎)、豆瓣、知乎、Google、Yahoo!、 Facebook、NASA、百度、腾讯、汽车之家、美团等。互联网公司广泛使用Python来做的事一般有:自动化运维、自动化测试、大数据分析、爬虫、Web 等。
1.1、为什么是Python而不是其他语言?
C 和 Python、Java、C#等
C语言: 代码编译得到 机器码 ,机器码在处理器上直接执行,每一条指令控制CPU工作
其他语言: 代码编译得到 字节码 ,虚拟机执行字节码并转换成机器码再后在处理器上执行
Python 和 C Python这门语言是由C开发而来
对于使用:Python的类库齐全并且使用简洁,如果要实现同样的功能,Python 10行代码可以解决,C可能就需要100行甚至更多.
对于速度:Python的运行速度相较与C,绝逼是慢了
Python 和 Java、C#等
对于使用:Linux原装Python,其他语言没有;以上几门语言都有非常丰富的类库支持
对于速度:Python在速度上可能稍显逊色
所以,Python和其他语言没有什么本质区别,其他区别在于:擅长某领域、人才丰富、先入为主。
1.2、Python的种类
Cpython
Python的官方版本,使用C语言实现,使用最为广泛,CPython实现会将源文件(py文件)转换成字节码文件(pyc文件),然后运行在Python虚拟机上。
Jyhton
Python的Java实现,Jython会将Python代码动态编译成Java字节码,然后在JVM上运行。
IronPython
Python的C#实现,IronPython将Python代码编译成C#字节码,然后在CLR上运行。(与Jython类似)
PyPy(特殊)
Python实现的Python,将Python的字节码字节码再编译成机器码。
RubyPython、Brython ...
2、python解释器版本
→Python2.7
→Python3.6
2.1、python安装
windows:
2.1.1、下载安装包
https://www.python.org/downloads/
2.1.2、安装
默认安装路径:C:\python36
2.1.3、配置环境变量
【右键计算机】--》【属性】--》【高级系统设置】--》【高级】--》【环境变量】--》【在第二个内容框中找到 变量名为Path 的一行,双击】 --> 【Python安装目录追加到变值值中,用 ; 分割】
如:原来的值;C:\python36,切记前面有分号
环境变量:
Python配置:
;C:\Python36;
终端:python
pip配置:
;C:\Python36\Scripts
终端:pip3 install xxxx
;C:\Python36;C:\Python36\Scripts;
linux:
无需安装,原装Python环境
3. 编写程序
创建任意文件.py
print(‘hello world‘)
4. 编码
ascii:用1个字节=8位来表示计算机能表达的所有东西。
ASCII(American Standard Code for Information Interchange,美国标准信息交换代码)是基于拉丁字母的一套电脑编码系统,主要用于显示现代英语和其他西欧语言,其最多只能用 8 位来表示(一个字节),即:28 = 256,所以,ASCII码最多只能表示 256 个符号。
00000000 -> A
00000001 -> B
00000010 -> C
00000011
00000100
unicode: 万国码,用4个字节=32位来做对应关系
Unicode(统一码、万国码、单一码)是一种在计算机上使用的字符编码。Unicode 是为了解决传统的字符编码方案的局限而产生的,它为每种语言中的每个字符设定了统一并且唯一的二进制编码,规定虽有的字符和符号最少由 16 位来表示(2个字节),即:2 16 = 65536,
00000000 00000000 00000000 00000000 -> A
00000000 00000000 00000000 00000001 -> B
00000000 00000000 00000000 00000010 -> C
00000000 10000000 00010000 00011010 -> 紫
utf-8: 对万国码进行压缩,至少使用1个字节表示
UTF-8,是对Unicode编码的压缩和优化,他不再使用最少使用2个字节,而是将所有的字符和符号进行分类:ascii码中的内容用1个字节保存、欧洲的字符用2个字节保存,东亚的字符用3个字节保存...
00000000
00000001
00000010
10000000 00010000 00011010
PS: 中文3个字节=24位
gbk:对亚洲国家的文字做的对应关系
PS: 中文2个字节=16位
注意:
py2: 解释器默认编码ascii
#解释器默认编码utf-8
print(‘王紫薇‘)
py3:解释器默认编码utf-8
print(‘要睡觉‘)
py2/py3:#-- coding:gbk --
print(‘要睡觉‘)
4.1. IDE
→pycharm
→vim
使用:
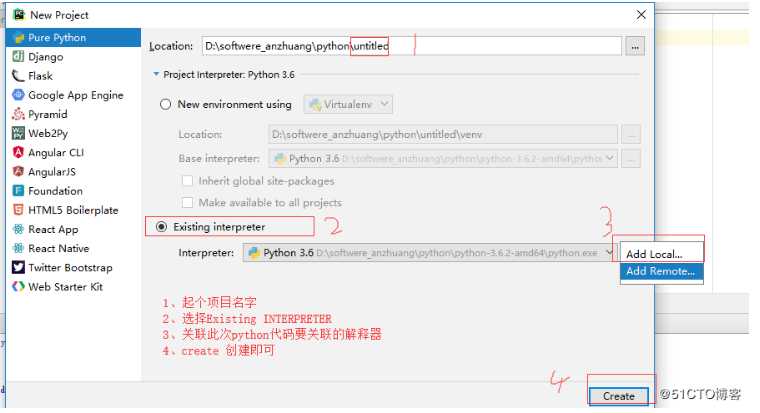
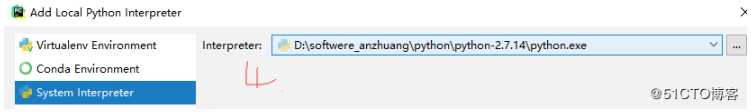
5. 输入输出
输出:
print("你是风儿我是沙")
输入:
user = input("请输入用户名:")
密码加密:
import getpass
pwd = getpass.getpass("请输入密码:") #需要在终端进行密码验证(密文)

6.变量
变量的作用:昵称,其代指内存里某个地址中保存的内容
变量定义的规则:
以下关键字不能声明为变量名
[‘and‘, ‘as‘, ‘assert‘, ‘break‘, ‘class‘, ‘continue‘, ‘def‘, ‘del‘, ‘elif‘, ‘else‘, ‘except‘, ‘exec‘, ‘finally‘, ‘for‘, ‘from‘, ‘global‘, ‘if‘, ‘import‘, ‘in‘, ‘is‘, ‘lambda‘, ‘not‘, ‘or‘, ‘pass‘, ‘print‘, ‘raise‘, ‘return‘, ‘try‘, ‘while‘, ‘with‘, ‘yield‘]
建议:见名知意; user_pwd = "xxx"
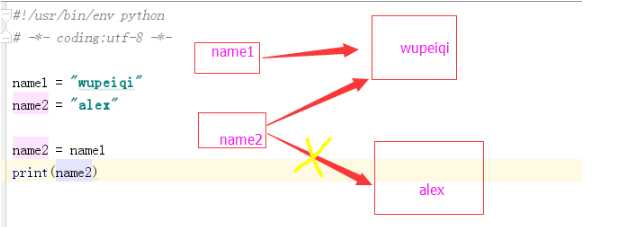
6.1、示例
7. 数据类型
age = 18 # 整数类型
name = "alex" # 字符串类型
xx = "18"
xx = ‘18‘
xx = ‘‘‘18‘‘‘
xx = """18"""
xx = "123‘
8. 条件语句
格式一:
if 条件:
成功之后走这里
格式二:
if 条件:
成功之后走这里
else:
失败之后走这里
格式三:
if 条件:
成功之后走这里
elif 条件:
成功之后走这里
elif 条件:
成功之后走这里
else:
上述都失败
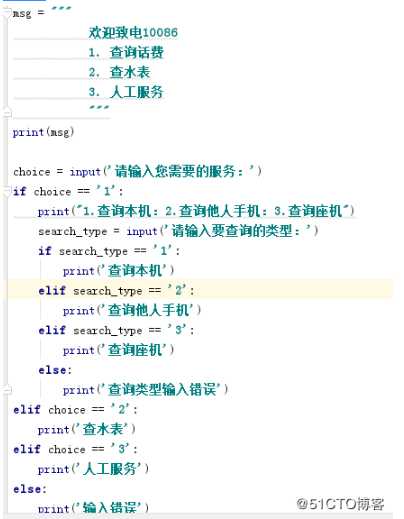
示例:
9. 循环语句
while 条件: 条件成立执行 while True: print(‘钓鱼要钓刀鱼,刀鱼要到岛上钓‘) while 1==1 and 2==2: print(‘钓鱼要钓刀鱼,刀鱼要到岛上钓‘)
timer = 0 while timer < 3: print(‘钓鱼要钓刀鱼,刀鱼要到岛上钓‘) timer = timer + 1 print(‘完成‘) 示例: 练习1: 页面上输出 1 - 10 count = 1 while count < 11: print(count) count = count + 1 break,强制终止当前所在循环 while True: print(‘钓鱼要钓刀鱼,刀鱼要到岛上钓‘) break 练习2: 页面上输出 1 - 10 (使用break) count = 1 while True: print(count) count = count + 1 if count == 11: break count = 1 while True: print(count) if count == 10: break count = count + 1 continue,跳出本次循环,继续下一次循环 练习题3:页面上输出 1 - 10,排除7 count = 1 while count < 11: if count == 7: count = count + 1 continue print(count) count = count + 1 第二种: count = 1 while count < 11: if count == 7: pass else: print(count) count = count + 1
10.常用数据类型
整数:
age = 18
字符串:
name = "紫薇"
n1 = name[0] #获取紫
n2 = name[1] #获取薇
列表:
user_list = ["紫薇","尔康","18","海量","小鸡"]
n3 = user_list[0] #紫薇
n4 = user_list[1] # "尔康"
user_list = ["紫薇","尔康","18","海量","小鸡"]
for xxx in user_list:
print(xxx)
if xxx == ‘18‘:
break
字典:
user_info = {"name":"紫薇","age":18}
n5 = user_info["name"] #获取紫薇
n6 = user_info["age"] #获取18

user_info[‘count‘] = 666 #{"name":"紫薇","age":18,"count":666} 数据类型嵌套: n7 = ["alex","eric",[11,22,33]] n7[1] # 获取 eric n7[2][1] #获取 11 n8 = [ "alex", {‘name‘:‘日天‘,‘age‘:18}, [11,22,33] ] n8[1]["age"] = 19 #修改键值对 问题1: 循环用户列表,打印用户姓名和密码 user_list = [ {‘username‘:‘alex‘, ‘password‘:‘123‘, ‘count‘:0 }, {‘username‘:‘eric‘, ‘password‘:‘123‘, ‘count‘:0 }, {‘username‘:‘tony‘, ‘password‘:‘123‘, ‘count‘:0 }, {‘username‘:‘oldboy‘, ‘password‘:‘123‘, ‘count‘:0 }, ] for item in user_list: print(item[‘username‘],item[‘password‘],item[‘count‘]) 问题2: 将每个用户的count改成1 user_list = [ {‘username‘:‘alex‘, ‘password‘:‘123‘, ‘count‘:0 }, {‘username‘:‘eric‘, ‘password‘:‘123‘, ‘count‘:0 }, {‘username‘:‘tony‘, ‘password‘:‘123‘, ‘count‘:0 }, {‘username‘:‘oldboy‘, ‘password‘:‘123‘, ‘count‘:0 }, ] for item in user_list: if item[‘username‘] == ‘alex‘ and item[‘password‘] == ‘123‘: item[‘count‘] = 1 print(item) 问题3: 用户输入用户名和密码,在user_list中进行校验 user_list = [ {‘username‘:‘alex‘, ‘password‘:‘123‘ }, {‘username‘:‘eric‘, ‘password‘:‘123‘}, {‘username‘:‘tony‘, ‘password‘:‘123‘}, {‘username‘:‘oldboy‘, ‘password‘:‘123‘}, ] user = input("请输入用户名:") pwd = input("请输入密码:") flag = False for item in user_list: if item[‘username‘] == user and item[‘password‘] == pwd: flag = True break else: pass if flag: print("登录成功") else: print("登录失败")
11、课后练习题
11.1 求1-100所有数的和
#!/usr/bin/env python # -*- coding:utf-8 -*- value = 0 i = 1 while i < 101: value = value + i i = i + 1 print(value)
11.2 求1-100内的所有奇数
#!/usr/bin/env python # -*- coding:utf-8 -*- i = 1 while i < 101: if i % 2 == 1: print(i) i = i + 1
11.3 求1-100内所有偶数
#!/usr/bin/env python # -*- coding:utf-8 -*- i = 1 while i < 101: if i % 2 == 0: print(i) i = i + 1
11.4 求1-2+3-4+5 ... 99的所有数的和
#!/usr/bin/env python #-*- coding:utf-8 -*- i = 1 n = 2 while n < 100: i = i - n n = n + 1 i = i + n n = n + 1 print(i) 第二种 i =1 sum = 0 while True : if i % 2 ==0 : i = -i sum = sum + i i = abs(i) + 1 if i == 100 : break print(sum)
11.5 用户登录(3次机会)

#!/usr/bin/env python # -*- coding:utf-8 -*- # 用户登录三次失败并直接退出 # i = 0 # while i < 3: # username = input(‘请输入用户名:‘) # password = input(‘请输入密码:‘) # if username == ‘oldboy‘ and password == ‘boss‘: # print(‘登录成功‘) # break # else: # print(‘用户名或密码失败‘) # i = i + 1 #用户登录三次失败并退出 user_list = [ {‘username‘:‘alex‘, ‘password‘:‘123‘ }, {‘username‘:‘eric‘, ‘password‘:‘123‘}, {‘username‘:‘tony‘, ‘password‘:‘123‘}, {‘username‘:‘oldboy‘, ‘password‘:‘123‘} ] i = 1 while True: user = input("请输入用户名:") passwd = input("请输入密码:") flag = False for item in user_list: if item[‘username‘] == user and item[‘password‘] == passwd: print("登录成功") flag = True break if flag: break else: print("用户名或密码有误") if i < 3: pass else: print("登录失败") break i += 1
标签:c# and web 下划线 int 方案 closed 解释型 设计
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/bowen-li/p/s920927.html