标签:items 分享图片 打开 span import develop font 实时 gic
https://developer.mozilla.org/zh-CN/docs/Web/CSS/@font-face
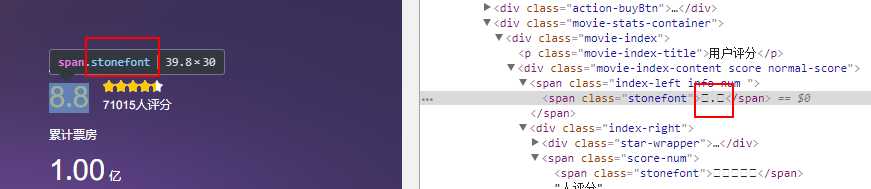
这是一个叫做@font-face 的CSS @规则 ,它允许网页开发者为其网页指定在线字体。 通过这种作者自备字体的方式,@font-face 可以消除对用户电脑字体的依赖。
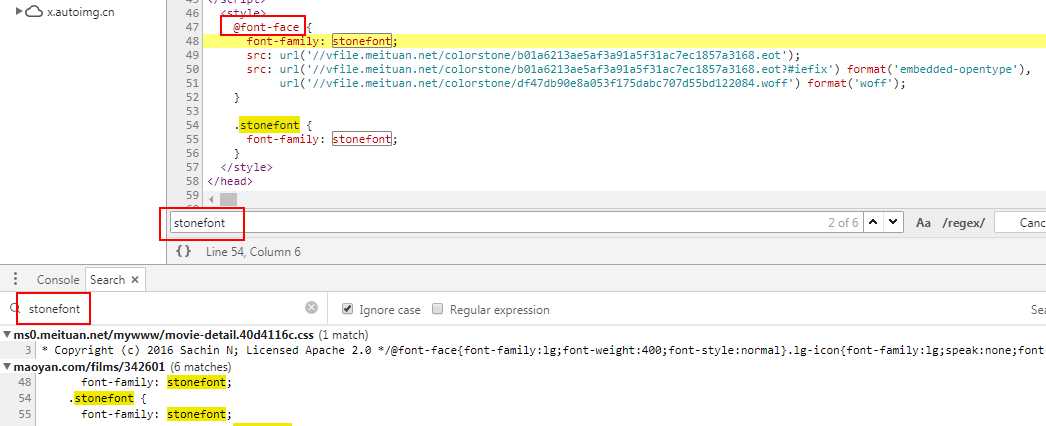
汽车之家字体反爬破解实践 https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/32087297
猫眼破解数字反爬获取实时票房 https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/33112359

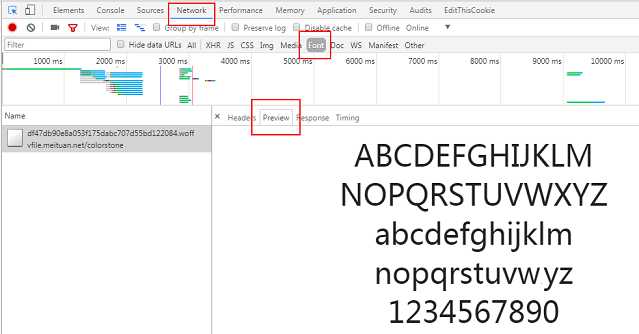
https://github.com/hanikesn/woff2otf
(py3) G:\>python woff2otf.py df47db90e8a053f175dabc707d55bd122084.woff df47db90e8a053f175dabc707d55bd122084.otf
http://www.high-logic.com/font-editor/fontcreator.html
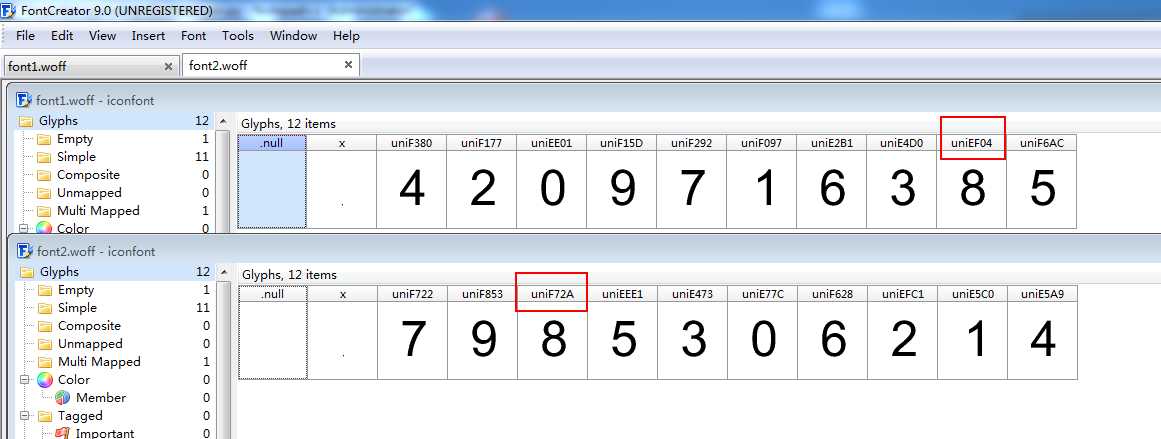
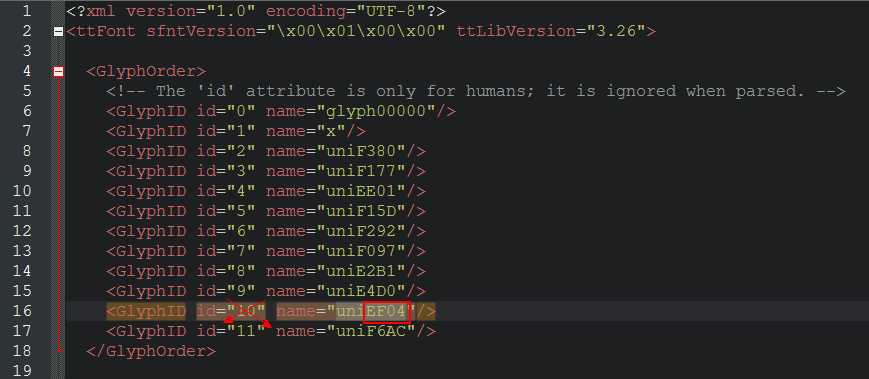
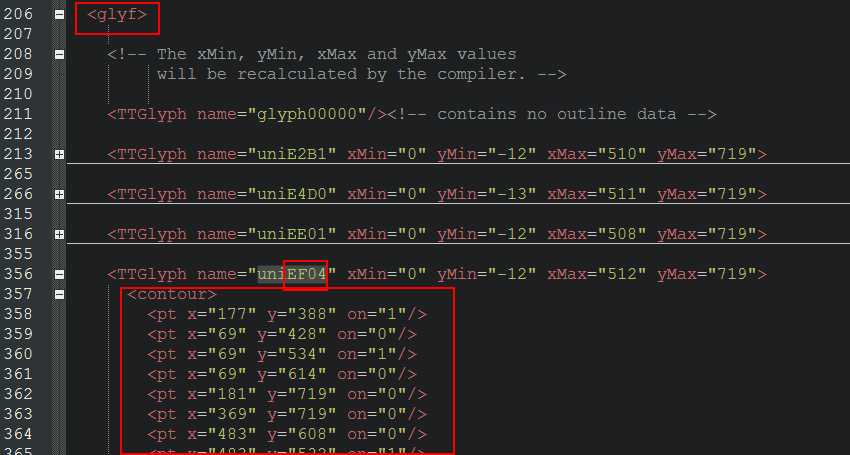
下图可见字符8的上方编号uniEF04与网页源代码  存在对应关系
新标签打开相同的页面,硬性刷新可见字体文件名称发生变化,另存字体文件为 font2.woff, 使用软件打开可见字符8的上方编号发生变化,即每次解析网页需要同时下载相应的字体文件。
pip install fontTools
from fontTools.ttLib import TTFont font1 = TTFont(‘font1.woff‘) font1.saveXML(‘font1.xml‘) font2 = TTFont(‘font2.woff‘) font2.saveXML(‘font2.xml‘)
name 对应的 id 没有实际意义
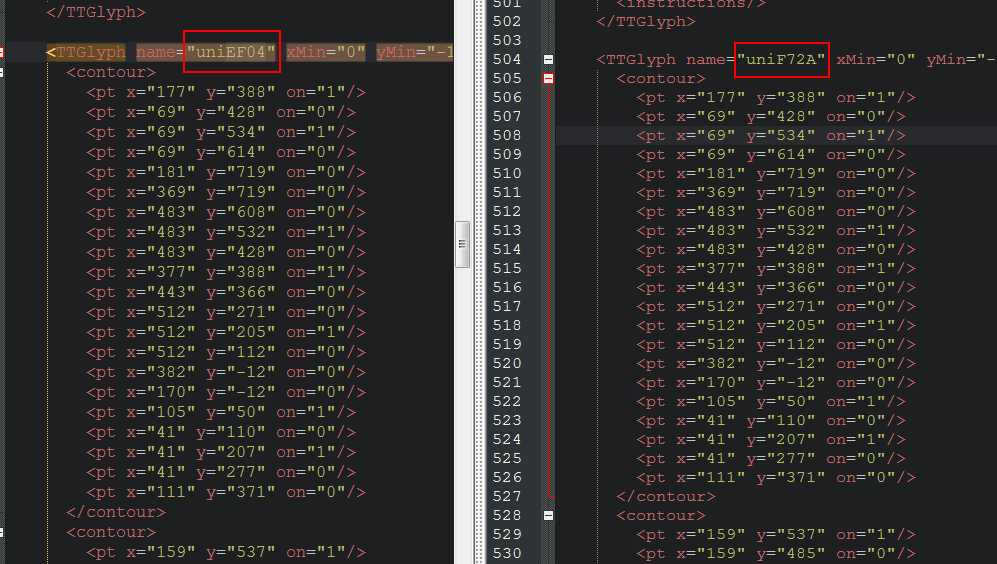
font1.woff 字符8 >>> name1 >>> 字形定义 == 字形定义 <<< name2 <<< 字符8 font2.woff
In [26]: font1[‘glyf‘].keys() Out[26]: dict_keys([‘glyph00000‘, ‘x‘, ‘uniF380‘, ‘uniF177‘, ‘uniEE01‘, ‘uniF15D‘, ‘uniF292‘, ‘uniF097‘, ‘uniE2B1‘, ‘uniE4D0‘, ‘uniEF04‘, ‘uniF6AC‘]) In [27]: font2[‘glyf‘].keys() Out[27]: dict_keys([‘glyph00000‘, ‘x‘, ‘uniF722‘, ‘uniF853‘, ‘uniF72A‘, ‘uniEEE1‘, ‘uniE473‘, ‘uniE77C‘, ‘uniF628‘, ‘uniEFC1‘, ‘uniE5C0‘, ‘uniE5A9‘])
In [38]: font1_8 = font1[‘glyf‘][‘uniEF04‘] In [39]: font2_8 = font2[‘glyf‘][‘uniF72A‘] In [40]: font1_8? Type: Glyph String form: <fontTools.ttLib.tables._g_l_y_f.Glyph object at 0x000000000787CE80> File: e:\programdata\anaconda3\envs\py3\lib\site-packages\fonttools\ttlib\tables\_g_l_y_f.py Docstring: <no docstring> In [41]: font1_8 == font2_8 Out[41]: True In [47]: font1_4 = font1[‘glyf‘][‘uniF380‘] In [48]: font2_7 = font2[‘glyf‘][‘uniF722‘] In [49]: font1_4 == font2_7 Out[49]: False
In [2]: from fontTools.ttLib import TTFont ...: font1 = TTFont(‘font1.woff‘) ...: ...: print(font1[‘glyf‘].keys()) ...: keys = font1[‘glyf‘].keys() ...: values = list(‘ .4209716385‘) ...: # 构建基准 {name: num} ...: dict1 = dict((k,v) for k,v in zip(keys, values)) ...: print(dict1) ...: ...: ...: font2 = TTFont(‘font2.woff‘) ...: dict2 = {} ...: for key in font2[‘glyf‘].keys(): ...: for k, v in dict1.items(): ...: # 通过比较 字形定义 填充新的name和num映射关系 ...: if font1[‘glyf‘][k] == font2[‘glyf‘][key]: ...: dict2[key] = v.strip() ...: break ...: print(dict2) ...: ...: dict_keys([‘glyph00000‘, ‘x‘, ‘uniF380‘, ‘uniF177‘, ‘uniEE01‘, ‘uniF15D‘, ‘uniF292‘, ‘uniF097‘, ‘uniE2B1‘, ‘uniE4D0‘, ‘uniEF04‘, ‘uniF6AC‘]) {‘glyph00000‘: ‘ ‘, ‘x‘: ‘.‘, ‘uniF380‘: ‘4‘, ‘uniF177‘: ‘2‘, ‘uniEE01‘: ‘0‘, ‘uniF15D‘: ‘9‘, ‘uniF292‘: ‘7‘, ‘uniF097‘: ‘1‘, ‘uniE2B1‘: ‘6‘, ‘uniE4D0‘: ‘3‘, ‘uniEF04‘: ‘8‘, ‘uniF6AC‘: ‘5‘} {‘glyph00000‘: ‘‘, ‘x‘: ‘.‘, ‘uniF722‘: ‘7‘, ‘uniF853‘: ‘9‘, ‘uniF72A‘: ‘8‘, ‘uniEEE1‘: ‘5‘, ‘uniE473‘: ‘3‘, ‘uniE77C‘: ‘0‘, ‘uniF628‘: ‘6‘, ‘uniEFC1‘: ‘2‘, ‘uniE5C0‘: ‘1‘, ‘uniE5A9‘: ‘4‘}

标签:items 分享图片 打开 span import develop font 实时 gic
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/my8100/p/js_maoyandianying.html