标签:访问 识别 cin com 指定 counter tac 通过 title
大量的JavaWeb应用做的是IO密集型任务, 数据库的压力较大, 需要分流
大量的应用场景, 是读多写少, 数据库读取的压力更大
一个很自然的思路是使用一主多从的数据库集群: 一个是主库,负责写入数据;其它都是从库,负责读取数据. 主从库数据同步.
mysql原生支持主从复制
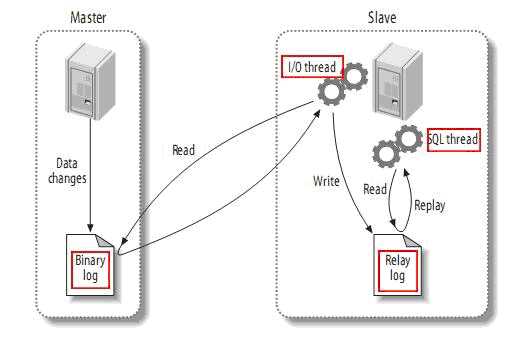
mysql主(称master)从(称slave)复制的原理:
1、master将数据改变记录到二进制日志(bin log)中, 这些记录叫binary log events
2、slave将master的binary log events拷贝到它的中继日志(relay log)
3、slave重做中继日志中的事件, 将改变反映它自己的数据(数据重演)
解决读写分离的方案大致有两种:
1)在应用层给读/写分别指定数据库
好处是数据源切换方便, 不用引入其他组件. 但是不能动态添加数据源.
2)使用中间件解决
好处是源程序不需要做任何改动, 还可以动态添加数据源. 但中间件会带来一定的性能损失.
目前有mysql-proxy, mycat, altas等
主库配置
修改my.ini:
#开启主从复制,主库的配置
log-bin = mysql3306-bin
#指定主库serverid
server-id=101
#指定同步的数据库,如果不指定则同步全部数据库
binlog-do-db=mydb
执行以下SQL:
SHOW MASTER STATUS;
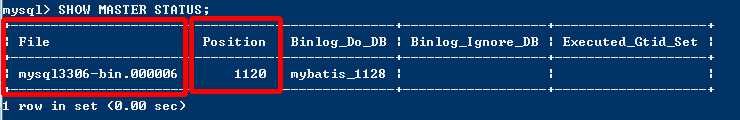
记录下Position值,需要在从库中设置同步起始值。
#授权从库用户slave01使用123456密码登录本库
grant replication slave on *.* to ‘slave01‘@‘127.0.0.1‘ identified by ‘123456‘;
flush privileges;
从库配置
修改my.ini:
#指定serverid
server-id=102
执行以下SQL:
CHANGE MASTER TO
master_host=‘127.0.0.1‘,
master_user=‘slave01‘,
master_password=‘123456‘,
master_port=3306,
master_log_file=‘mysql3306-bin.000006‘, #设置主库时记下的Position
master_log_pos=1120;
#启动slave同步
START SLAVE;
#查看同步状态 Slave_IO_Running和Slave_SQL_Running都为Yes说明同步成功
SHOW SLAVE STATUS;
这里采用的是应用层的读写分离方案
使用AOP, 在执行Service方法前判断,是使用写库还是读库
可以根据方法名作为依据判断,比如说以query、find、get等开头的就走读库,其他的走写库
切面类:
/**
* 如果在spring配置了事务的策略,则标记了ReadOnly的方法用从库Slave, 其它使用主库Master。
* 如果没有配置事务策略, 则采用方法名匹配, 以query、find、get开头的方法用Slave,其它用Master。
*/
public class DataSourceAspect {
private List<String> slaveMethodPattern = new ArrayList<String>(); //保存有readonly属性的带通配符方法名
private static final String[] defaultSlaveMethodStartWith = new String[]{"query", "find", "get" };
private String[] slaveMethodStartWith; //保存有slaveMethodStartWith属性的方法名头部
//注入
public void setTxAdvice(TransactionInterceptor txAdvice) throws Exception {
if (txAdvice == null) {
// 没有配置事务策略
return;
}
//从txAdvice获取策略配置信息
TransactionAttributeSource transactionAttributeSource = txAdvice.getTransactionAttributeSource();
if (!(transactionAttributeSource instanceof NameMatchTransactionAttributeSource)) {
return;
}
//使用反射技术获取到NameMatchTransactionAttributeSource对象中的nameMap属性值
NameMatchTransactionAttributeSource matchTransactionAttributeSource = (NameMatchTransactionAttributeSource) transactionAttributeSource;
Field nameMapField = ReflectionUtils.findField(NameMatchTransactionAttributeSource.class, "nameMap");
nameMapField.setAccessible(true); //设置该字段可访问
//获取nameMap的值
Map<String, TransactionAttribute> map = (Map<String, TransactionAttribute>) nameMapField.get(matchTransactionAttributeSource);
//遍历nameMap
for (Map.Entry<String, TransactionAttribute> entry : map.entrySet()) {
if (!entry.getValue().isReadOnly()) { // 定义了ReadOnly的策略才加入到slaveMethodPattern
continue;
}
slaveMethodPattern.add(entry.getKey());
}
}
// 切面 before方法
public void before(JoinPoint point) {
// 获取到当前执行的方法名
String methodName = point.getSignature().getName();
boolean isSlave = false;
if (slaveMethodPattern.isEmpty()) {
// 没有配置read-only属性,采用方法名匹配方式
isSlave = isSlaveByMethodName(methodName);
} else {
// 配置read-only属性, 采用通配符匹配
for (String mappedName : slaveMethodPattern) {
if (isSlaveByConfigWildcard(methodName, mappedName)) {
isSlave = true;
break;
}
}
}
if (isSlave) {
// 标记为读库
DynamicDataSource.markMaster(true);
} else {
// 标记为写库
DynamicDataSource.markMaster(false);
}
}
// 匹配以指定名称开头的方法名, 配置了slaveMethodStartWith属性, 或使用默认
private Boolean isSlaveByMethodName(String methodName) {
return StringUtils.startsWithAny(methodName, getSlaveMethodStartWith());
}
// 匹配带通配符"xxx*", "*xxx" 和 "*xxx*"的方法名, 源自配置了readonly属性的方法名
protected boolean isSlaveByConfigWildcard(String methodName, String mappedName) {
return PatternMatchUtils.simpleMatch(mappedName, methodName);
}
// 注入
public void setSlaveMethodStartWith(String[] slaveMethodStartWith) {
this.slaveMethodStartWith = slaveMethodStartWith;
}
public String[] getSlaveMethodStartWith() {
if(this.slaveMethodStartWith == null){
// 没有配置slaveMethodStartWith属性,使用默认
return defaultSlaveMethodStartWith;
}
return slaveMethodStartWith;
}
}
Spring的RoutingDataSource
/**
* 使用Spring的动态数据源,需要实现AbstractRoutingDataSource
* 通过determineCurrentLookupKey方法拿到识别key来判断选择读/写数据源
* token显然是多例的, 所以引入ThreadLocal保存
*/
public class DynamicDataSource extends AbstractRoutingDataSource {
// 读库总数
private Integer slaveCount;
// 读库轮询计数, 初始为-1, 本类为单例, AtomicInteger线程安全
private AtomicInteger counter = new AtomicInteger(-1);
// 存储读库的识别key sl1ve01, slave02... 写库识别key为master
private List<Object> slaveDataSources = new ArrayList<Object>();
//当前线程的写库/读库token
private static final ThreadLocal<Boolean> tokenHolder = new ThreadLocal<>();
public static void markMaster(boolean isMaster){
tokenHolder.set(isMaster);
}
@Override
protected Object determineCurrentLookupKey() {
if (tokenHolder.get()) {
return "master"; // 写库
}
// 轮询读库, 得到的下标为:0、1、2...
Integer index = counter.incrementAndGet() % slaveCount;
if (counter.get() > 99999) { // 以免超出Integer范围
counter.set(-1);
}
return slaveDataSources.get(index);
}
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() {
super.afterPropertiesSet();
// 父类的resolvedDataSources属性是private, 需要使用反射获取
Field field = ReflectionUtils.findField(AbstractRoutingDataSource.class, "resolvedDataSources");
field.setAccessible(true); // 设置可访问
try {
Map<Object, DataSource> resolvedDataSources = (Map<Object, DataSource>) field.get(this);
// 读库数等于dataSource总数减写库数
this.slaveCount = resolvedDataSources.size() - 1;
for (Map.Entry<Object, DataSource> entry : resolvedDataSources.entrySet()) {
if ("master".equals(entry.getKey())) {
continue;
}
slaveDataSources.add(entry.getKey());
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
spring配置文件
<!-- 定义事务策略 -->
<tx:advice id="txAdvice" transaction-manager="transactionManager">
<tx:attributes>
<!--所有以query开头的方法都是只读的 -->
<tx:method name="query*" read-only="true" /> <!-- readonly属性 -->
<!--其他方法使用默认事务策略 -->
<tx:method name="*" />
</tx:attributes>
</tx:advice>
<!-- 定义AOP切面处理器 -->
<bean class="com.zx.DataSourceAspect" id="dataSourceAspect">
<!-- 注入事务策略 -->
<property name="txAdvice" ref="txAdvice"/>
<!-- 指定slave方法的前缀(非必须) -->
<property name="slaveMethodStartWith" value="query,find,get"/>
</bean>
<aop:config>
<aop:pointcut id="myPointcut" expression="execution(* com.zx.service.*.*(..))" />
<!-- 将切面应用到自定义的切面处理器上,-9999保证该切面优先级最高执行 -->
<aop:aspect ref="dataSourceAspect" order="-9999">
<aop:before method="before" pointcut-ref="myPointcut" />
</aop:aspect>
</aop:config>
<!-- 定义数据源,继承了spring的动态数据源 -->
<bean id="dataSource" class="com.zx.DynamicDataSource">
<!-- 设置多个数据源 -->
<property name="targetDataSources">
<map key-type="java.lang.String">
<!-- 这些设置的key和determineCurrentLookupKey方法拿到的key相比对, 根据匹配选择数据源 -->
<entry key="master" value-ref="masterDataSource"/> <!-- value-ref指向数据源 -->
<entry key="slave01" value-ref="slave01DataSource"/>
<entry key="slave02" value-ref="slave02DataSource"/>
<entry key="slave03" value-ref="slave03DataSource"/>
</map>
</property>
<!-- 设置默认的数据源,这里默认走写库 -->
<property name="defaultTargetDataSource" ref="masterDataSource"/>
</bean>
标签:访问 识别 cin com 指定 counter tac 通过 title
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/jswang/p/9054815.html