标签:return any 3.2 size dimens bsp normal bubuko isp
Interpolation and Curve Fitting
给定n+1个数据点(xi,yi), i = 0,1,2,…,n,评估y(x).
离散数据集,或者形如下面的表格,常常在技术计算中用到,数据源可能来自于实验观察或者数值计算。
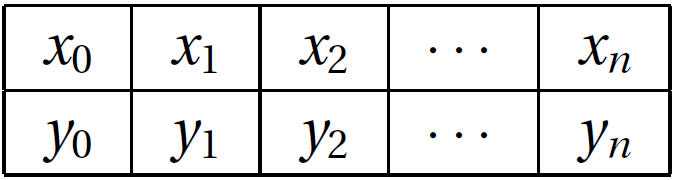
3.2 多项式插值(Polynomial Interpolation)
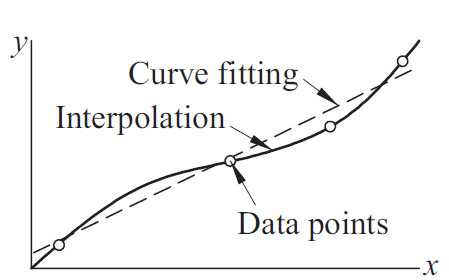
插值和曲线拟合存在差别。对于插值,我们通过数据拟合一条曲线,在拟合过程中,我们潜在假设数据是精确的和独特的;对于曲线拟合,使用的数据通常存在测量误差而引入了噪声,在某种程度上,我们想发现一条光滑的曲线近似数据点,进而,曲线不必穿过每个数据点。插值和曲线拟合的区别如下图:
Lagrange’s Method拉格朗如方法
插值最简单的形式是多项式,经过n+1个明确的数据点,构建一个自由度为n的特定多项式总是可以实现的。包含这个多项式的方法就是朗格朗日方程:
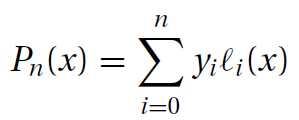
其中基函数(cardinal function)li(x)如下:
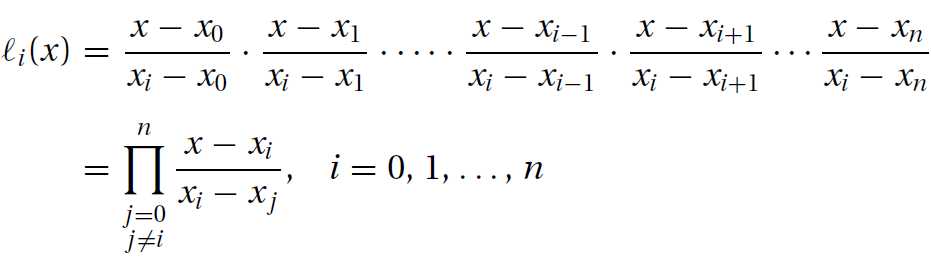
通过观察,基函数具有如下性质
牛顿方法Newton’s Method
牛顿方法的插值多项式如下:
![]()
对于有四个数据点n=3,多项式如下:
![]()
n=3,利于编程,定义如下形式:
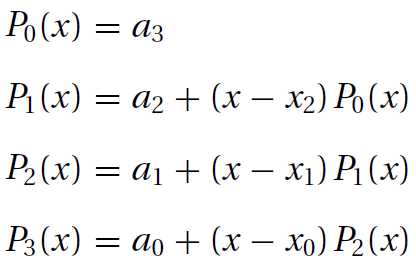
Denoting the x-coordinate array of the data points by xData and the degree of the polynomial by n, we have the following algorithm for computing Pn(x):
p = a[n]
for k in range(1, n+1):
p = a[n-k] + (x - xData[n-k])*p系数Pn迫使多项式通过每一个数据点:yi=Pn(xi), i=0,1,...,n。则下面的方程同时发生:
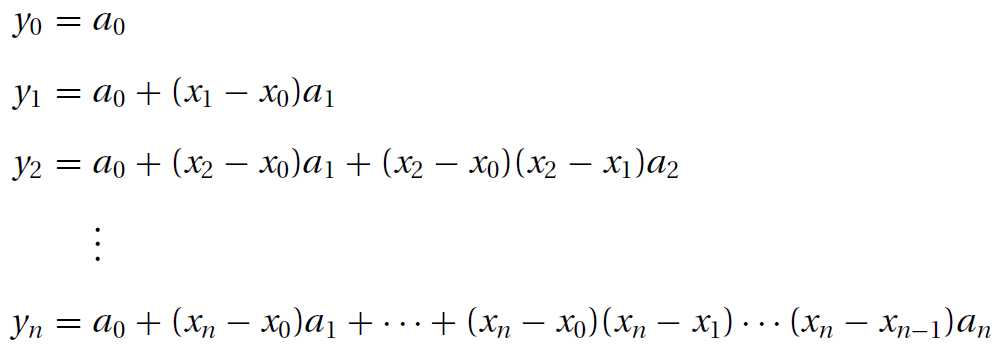
引入均差概念(divided differences)
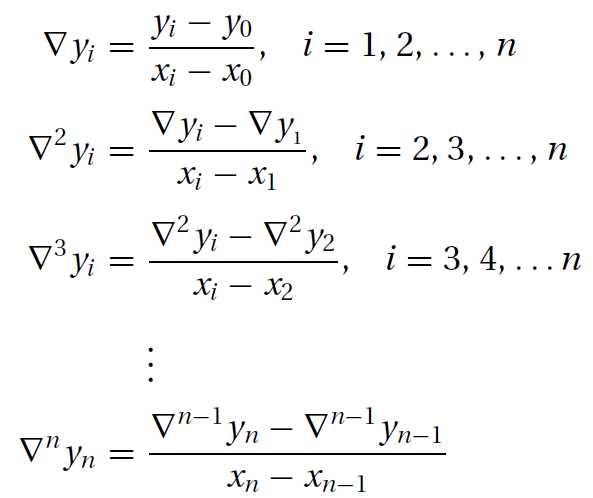
则有:
![]()
对于n=4,手工计算系数,可以通过如下表格快速解决:
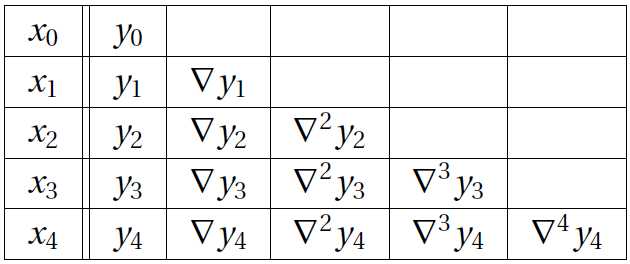
Machine computations can be carried out within a one-dimensional array a employing the following algorithm (we use the notation m = n + 1 = number of data points):
Python 计算流程如下:
a = yData.copy()
for k in range(1,m):
for i in range(k, m):
a[i] = (a[i] - a[k-1])/(xData[i] - xData[k-1])最初,a包含数据的y坐标,因此它与上表中的第二列相同。 每次通过外部循环时,都会在下一列中生成条目,这会覆盖a的相应元素。 因此,结束包含上表中的对角项(即多项式的系数)。
牛顿多项式插值方法的Python代码
Newton’s method. Given the data point arrays xData and yData, the function coeffts returns the coefficient array a. After the coefficients are found, the interpolant Pn(x) can be evaluated at any value of x with the function evalPoly.
def evalPoly(a, xData, x):
n = len(xData) - 1
p = a[n]
for k in range(1, n+1):
p = a[n-k] + (x - xData[n-k])*p
return p
def coeffts(xData, yData):
m = len(xData)
a = yData.copy()
for k in range(1,m):
a[k:m] = (a[k:m] - a[k-1]) / (xData[k:m] - xData[k-1])
return a参考翻译《Numerical Methods in Engineering with Python 3》
标签:return any 3.2 size dimens bsp normal bubuko isp
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/brightyuxl/p/9058353.html