标签:factor 验证 obj except 种类 doc processor ble tca
在Spring Boot官方介绍中,首一段话是这样的(如下图)。我们可以大概了解到其所表达的含义:我们可以利用Spring Boot写很少的配置来创建一个非常方便的基于Spring整合第三方类库的单体企业级应用。相信使用过Spring Boot的人都知道,她在这方面从前到后的一系列整合。本篇文字将带你进入具体的实现细节。

首先我们写一段Spring Boot应用启动类的代码如下:
1 package com.springTest; 2 3 import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication; 4 import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication; 5 6 @SpringBootApplication //定义Spring Boot应用启动类 7 public class DemoApplication { 8 9 public static void main(String[] args) { 10 SpringApplication.run(DemoApplication.class, args);//启动spring容器等处理 11 } 12 }
跟人@SpringBootApplication注解实现我们可以看到它的源码:
1 @Target(ElementType.TYPE) 2 @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) 3 @Documented 4 @Inherited 5 @SpringBootConfiguration 6 @EnableAutoConfiguration //自动配置关键位置 7 @ComponentScan(excludeFilters = { 8 @Filter(type = FilterType.CUSTOM, classes = TypeExcludeFilter.class), 9 @Filter(type = FilterType.CUSTOM, classes = AutoConfigurationExcludeFilter.class) }) 10 public @interface SpringBootApplication {
通过名称我们就可以注意到第6行@EnableAutoConfiguration 自动配置,点进去看它的源码:
1 @Target(ElementType.TYPE) 2 @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) 3 @Documented 4 @Inherited 5 @AutoConfigurationPackage //自动扫描包路径配置 6 @Import(AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class) //自动配置导入 7 public @interface EnableAutoConfiguration {
上面的代码我们可以看到EnableAutoConfiguration利用@Import导入配置组件。 跟踪源码其org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.AutoConfigurationImportSelector#selectImports方法返回的是StringUtils.toStringArray(configurations)。
具体方法代码如下:
public String[] selectImports(AnnotationMetadata annotationMetadata) { if (!isEnabled(annotationMetadata)) { return NO_IMPORTS; } AutoConfigurationMetadata autoConfigurationMetadata = AutoConfigurationMetadataLoader .loadMetadata(this.beanClassLoader); AnnotationAttributes attributes = getAttributes(annotationMetadata); List<String> configurations = getCandidateConfigurations(annotationMetadata, attributes); //获取配置类的集合 configurations = removeDuplicates(configurations); Set<String> exclusions = getExclusions(annotationMetadata, attributes); checkExcludedClasses(configurations, exclusions); configurations.removeAll(exclusions); configurations = filter(configurations, autoConfigurationMetadata); fireAutoConfigurationImportEvents(configurations, exclusions); return StringUtils.toStringArray(configurations); }
上面代码,我们是通过第8行代码获取所需要的配置类的集合,所以我们继续跟代码,找到如下代码信息:
1 List<String> configurations = SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames(getSpringFactoriesLoaderFactoryClass(), getBeanClassLoader());
上面的代码通过传入getSpringFactoriesLoaderFactoryClass()和 getBeanClassLoader()的返回值获取配置信息集合。通过跟踪代码,我们可以知道getSpringFactoriesLoaderFactoryClass()方法返回的值为固定的EnableAutoConfiguration.class。 getBeanClassLoader()方法则返回的是this.beanClassLoader对象。深入loadFactoryNames(Class<?> factoryClass, @Nullable ClassLoader classLoader)方法得知,其返回值的代码为:
return loadSpringFactories(classLoader).getOrDefault(factoryClassName, Collections.emptyList());
这段代码明显是将loadSpringFactories(classLoader)返回的集合进行过滤获取key为“EnableAutoConfiguration”的List类型的value值。那么我们继续检查loadSpringFactories的源码:
1 private static Map<String, List<String>> loadSpringFactories(@Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) { 2 MultiValueMap<String, String> result = cache.get(classLoader); 3 if (result != null) { 4 return result; 5 } 6 7 try { 8 Enumeration<URL> urls = (classLoader != null ? 9 classLoader.getResources(FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION) : 10 ClassLoader.getSystemResources(FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION)); // 找到关于FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION的定义:public static final String FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION = "META-INF/spring.factories"; 11 result = new LinkedMultiValueMap<>(); 12 while (urls.hasMoreElements()) { 13 URL url = urls.nextElement(); 14 UrlResource resource = new UrlResource(url); 15 Properties properties = PropertiesLoaderUtils.loadProperties(resource); 16 for (Map.Entry<?, ?> entry : properties.entrySet()) { 17 List<String> factoryClassNames = Arrays.asList( 18 StringUtils.commaDelimitedListToStringArray((String) entry.getValue())); 19 result.addAll((String) entry.getKey(), factoryClassNames); 20 } 21 } 22 cache.put(classLoader, result); 23 return result; 24 } 25 catch (IOException ex) { 26 throw new IllegalArgumentException("Unable to load factories from location [" + 27 FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION + "]", ex); 28 } 29 }
上面的代码我们能够很容易的看出它所实现的功能为:加载所有jar包中META-INF/spring.factories文件并解析返回其数据集。到这里,我们不得不对META-INF/spring.factories这个文件产生浓厚的兴趣。通过对Spring Boot所引入的jar包的查找中我们找到了这么一个配置文件如下图(注意箭头指示的内容):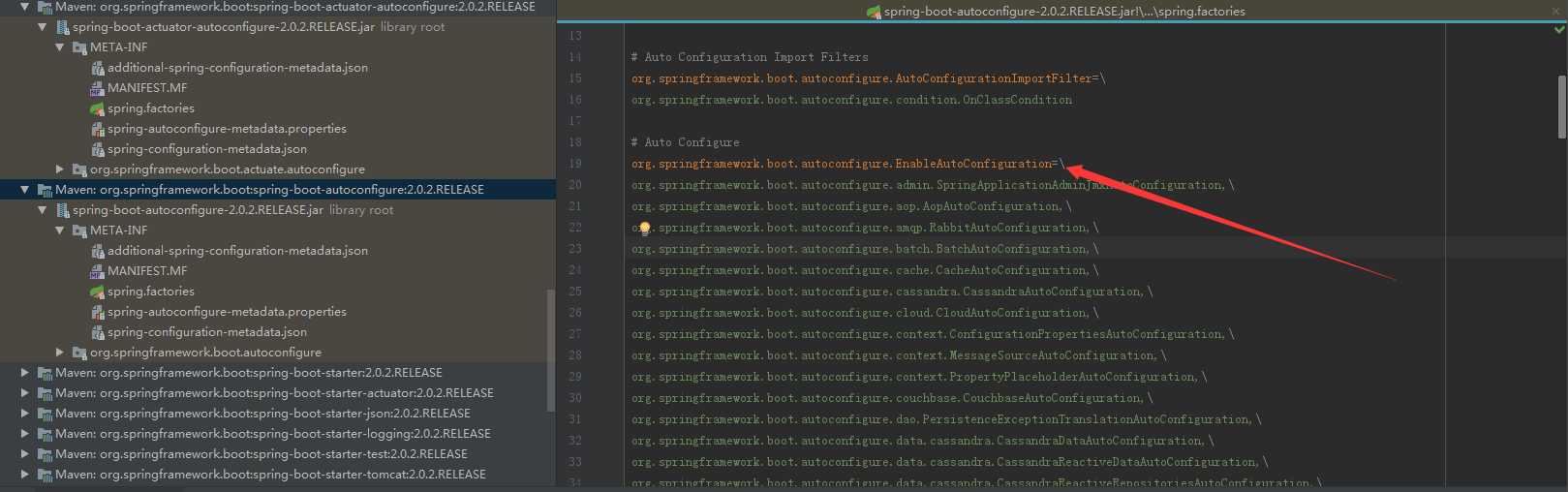
这不正是我们取到多有META-INF/spring.factories文件中定义的数据之后过滤出来所需要的内容吗?忍着激动,我们继续进行分析。
我们应该很容易的猜想到这里面定义的全类名对应的内容应该跟我们所要找的自动配置有关系,所以我们随便先找一个Configuration来验证一下我们的猜想。以org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache.CacheAutoConfiguration为例,我们分析一下它的底层实现:
1 @Configuration //Spring配置文件注解,表明这是一个配置类 2 @ConditionalOnClass(CacheManager.class) //底层实现为@Condition 代表CacheManager.class这个类必须存在,否则这个配置文件配置的类将不生效 3 @ConditionalOnBean(CacheAspectSupport.class) 4 @ConditionalOnMissingBean(value = CacheManager.class, name = "cacheResolver") 5 @EnableConfigurationProperties(CacheProperties.class) //对应配置文件的配置 6 @AutoConfigureBefore(HibernateJpaAutoConfiguration.class) 7 @AutoConfigureAfter({ CouchbaseAutoConfiguration.class, HazelcastAutoConfiguration.class, 8 RedisAutoConfiguration.class }) 9 @Import(CacheConfigurationImportSelector.class) //导入种类的缓存配置 10 public class CacheAutoConfiguration { 11 12 @Bean 13 @ConditionalOnMissingBean 14 public CacheManagerCustomizers cacheManagerCustomizers( 15 ObjectProvider<List<CacheManagerCustomizer<?>>> customizers) { 16 return new CacheManagerCustomizers(customizers.getIfAvailable()); 17 } 18 19 @Bean 20 public CacheManagerValidator cacheAutoConfigurationValidator( 21 CacheProperties cacheProperties, ObjectProvider<CacheManager> cacheManager) { 22 return new CacheManagerValidator(cacheProperties, cacheManager); 23 } 24 25 @Configuration 26 @ConditionalOnClass(LocalContainerEntityManagerFactoryBean.class) 27 @ConditionalOnBean(AbstractEntityManagerFactoryBean.class) 28 protected static class CacheManagerJpaDependencyConfiguration 29 extends EntityManagerFactoryDependsOnPostProcessor { 30 31 public CacheManagerJpaDependencyConfiguration() { 32 super("cacheManager"); 33 } 34 35 } 36 37 /** 38 * Bean used to validate that a CacheManager exists and provide a more meaningful 39 * exception. 40 */ 41 static class CacheManagerValidator implements InitializingBean { 42 43 private final CacheProperties cacheProperties;//自动注入缓存配置 44 45 private final ObjectProvider<CacheManager> cacheManager; 46 47 CacheManagerValidator(CacheProperties cacheProperties, 48 ObjectProvider<CacheManager> cacheManager) { 49 this.cacheProperties = cacheProperties; 50 this.cacheManager = cacheManager; 51 } 52 53 @Override 54 public void afterPropertiesSet() { 55 Assert.notNull(this.cacheManager.getIfAvailable(), 56 () -> "No cache manager could " 57 + "be auto-configured, check your configuration (caching " 58 + "type is ‘" + this.cacheProperties.getType() + "‘)"); 59 } 60 61 } 62 63 /** 64 * {@link ImportSelector} to add {@link CacheType} configuration classes. 65 */ 66 static class CacheConfigurationImportSelector implements ImportSelector { 67 68 @Override 69 public String[] selectImports(AnnotationMetadata importingClassMetadata) { 70 CacheType[] types = CacheType.values(); 71 String[] imports = new String[types.length]; 72 for (int i = 0; i < types.length; i++) { 73 imports[i] = CacheConfigurations.getConfigurationClass(types[i]); 74 } 75 return imports; 76 } 77 78 } 79 80 }
再对应CacheProperties.class的的源码实现:
1 @ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.cache") //spring中自动导入配置注解 2 public class CacheProperties { 3 4 /** 5 * Cache type. By default, auto-detected according to the environment. 6 */ 7 private CacheType type; //spring.cache.type对应
其实分析到这里已经差不多通透了,还有一些实现细节由于篇(wo)幅(hao)原(lan)因(le),不便详叙。如果疑问,欢迎留言,我会认真作答。
Spring Boot自动配置源码解析(基于Spring Boot 2.0.2.RELEASE)
标签:factor 验证 obj except 种类 doc processor ble tca
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/HuaiyinMarquis/p/9078127.html