标签:堆内存 技术 new java基础 分配 TE 冒泡 inf .com
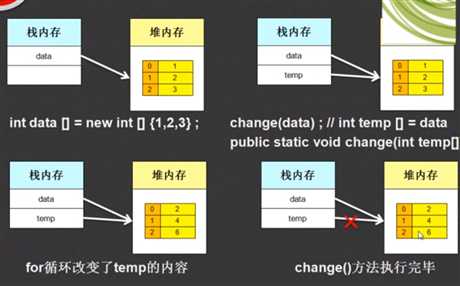
通常,向方法中传递的都是基本数据类型,而向方法中传递数组时,就需要考虑内存的分配
public class test2 { public static void main(String args[]) { int arr[] = new int[] {9, 1, 2, 3, 4, 7, 8, 6, 5 }; sort(arr); for(int i=0; i<arr.length; i++) { System.out.println(arr[i]); } } public static void sort(int arr[]) {//冒泡排序 for (int x= 0; x<arr.length; x++) { for (int y=0; y<arr.length-1; y++) { if (arr[y] > arr[y+1]) { int temp; temp = arr[y]; arr[y] = arr[y+1]; arr[y+1] = temp; } } } } }
向方法之中传递数组,或者将一个数组的值传给另一个数组,都会产生新的栈内存。引用之中对数组的改变会影响到原数组(其实就是在原数组的堆内存上操作)。当引用操作完成之后,引用产生的占内存不再只想原数组的堆内存。
标签:堆内存 技术 new java基础 分配 TE 冒泡 inf .com
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/xhnxhnu/p/9123910.html