标签:输出 第一个字符 file pre 编码 文本文件 整数 cep 选项
od命令用于将指定文件内容以八进制、十进制、十六进制、浮点格式或ASCII编码字符方式显示,通常用于显示或查看文件中不能直接显示在终端的字符。
常见的文件为文本文件和二进制文件。od命令主要用来查看保存在二进制文件中的值,按照指定格式解释文件中的数据并输出。
od [<选项><参数>] [<文件名>]
-t<TYPE>:指定输出格式,格式包括a、c、d、f、o、u和x,各含义如下:
od -tx File是以十六进制输出File的内容,默认以四字节为一组显示。
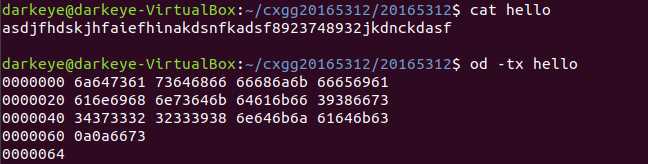
od -tc File输出字节对应的ASCII值
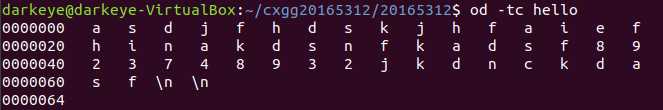
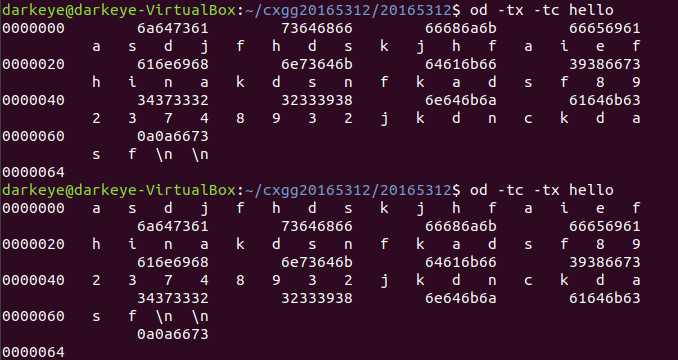
题目中od -tx -tc File是先在以十六进制输出File文件内容的同时,输出字节对应的ASCII值,它与od -tc -tx File的区别在于输出的次序
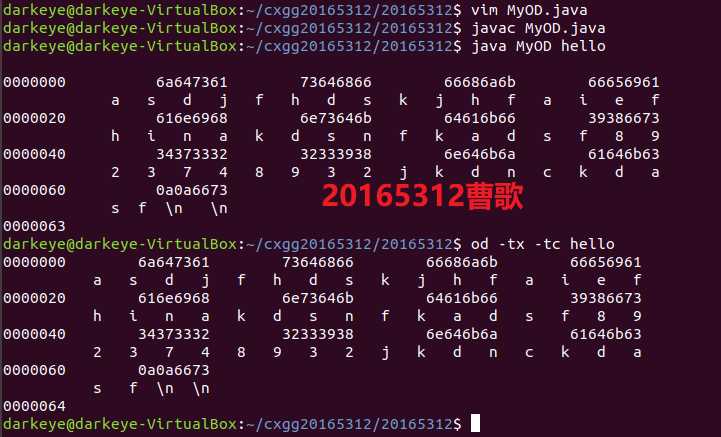
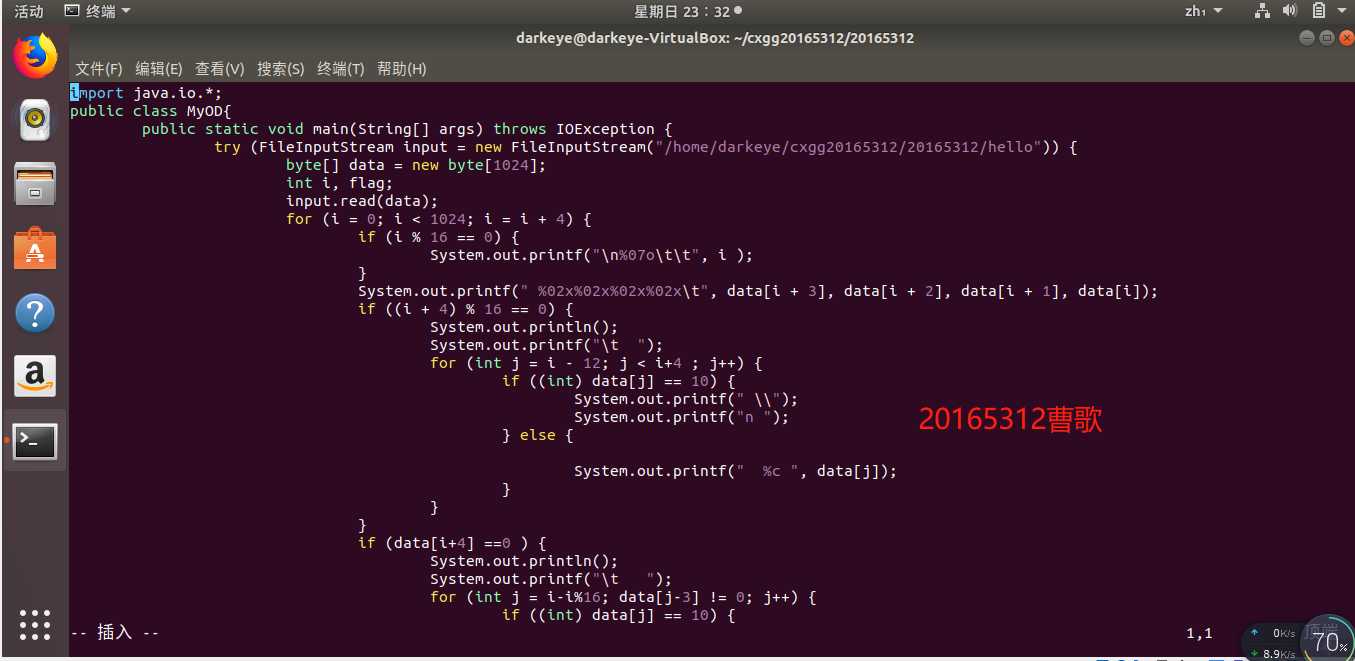
import java.io.*;
public class MyOD{
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
try (FileInputStream input = new FileInputStream("/home/darkeye/cxgg20165312/20165312/hello")) {
byte[] data = new byte[1024];
int i, flag;
input.read(data);
for (i = 0; i < 1024; i = i + 4) {
if (i % 16 == 0) {
System.out.printf("\n%07o\t\t", i );
} //四个字节为一组,一行四组。i=16时为左侧第一列(默认的地址),格式为七位八进制。
// 通过找规律,其数值是该行第一个字符的序号值(从0到length-1)对应的的八进制数
System.out.printf(" %02x%02x%02x%02x\t", data[i + 3], data[i + 2], data[i + 1], data[i]);
if ((i + 4) % 16 == 0) {
System.out.println();
System.out.printf("\t ");
for (int j = i - 12; j < i+4 ; j++) {
if ((int) data[j] == 10) {
System.out.printf(" \\");
System.out.printf("n ");
} else {
System.out.printf(" %c ", data[j]);
}
}
}
if (data[i+4] ==0 ) {
System.out.println();
System.out.printf("\t ");
for (int j = i-i%16; data[j-3] != 0; j++) {
if ((int) data[j] == 10) {
System.out.printf(" \\");
System.out.printf("n ");
} else {
System.out.printf(" %c ", data[j]);
}
}
break;
}
}
System.out.printf("\n%07o\n", i+3 );
}
}
}
标签:输出 第一个字符 file pre 编码 文本文件 整数 cep 选项
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/cxgg/p/9165062.html