标签:filename history dde quit use back tor names white
1 将发布好的.net core 程序ftp上传到/home/netcore 目录 , 执行下面的命令
dotnet WebMVC.dll
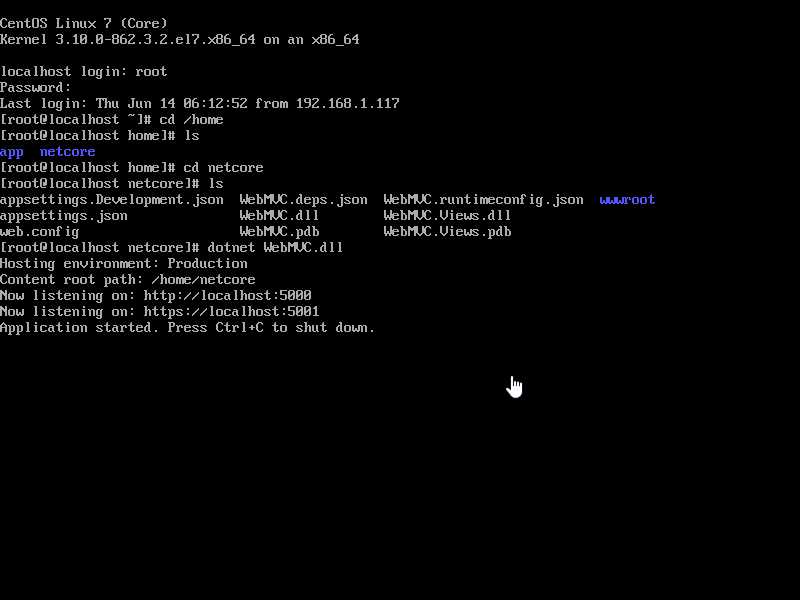
2.测试程序是否运行正常
curl http://localhost:5000
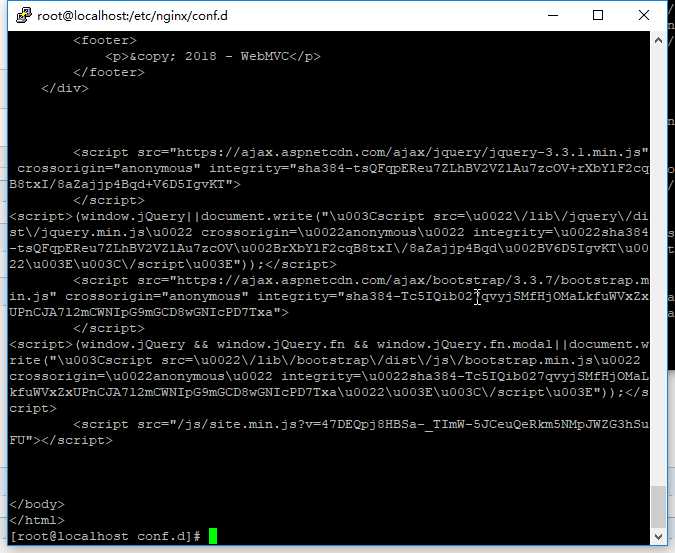
3.配置nginx
/etc/nginx/nginx.conf
user nginx;
worker_processes auto;
error_log /var/log/nginx/error.log;
pid /run/nginx.pid;
# Load dynamic modules. See /usr/share/nginx/README.dynamic.
include /usr/share/nginx/modules/*.conf;
events {
worker_connections 1024;
}
http {
log_format main ‘$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] "$request" ‘
‘$status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" ‘
‘"$http_user_agent" "$http_x_forwarded_for"‘;
access_log /var/log/nginx/access.log main;
sendfile on;
tcp_nopush on;
tcp_nodelay on;
keepalive_timeout 65;
types_hash_max_size 2048;
include /etc/nginx/mime.types;
default_type application/octet-stream;
# Load modular configuration files from the /etc/nginx/conf.d directory.
# See http://nginx.org/en/docs/ngx_core_module.html#include
# for more information.
include /etc/nginx/conf.d/*.conf;
# server {
# listen 80 default_server;
# listen [::]:80 default_server;
# server_name _;
# root /usr/share/nginx/html;
# Load configuration files for the default server block.
# include /etc/nginx/default.d/*.conf;
# location / {
# proxy_pass http://localhost:5000;
# proxy_http_version 1.1;
# }
# error_page 404 /404.html;
# location = /40x.html {
# }
# error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html;
# location = /50x.html {
# }
# }
# Settings for a TLS enabled server.
#
# server {
# listen 443 ssl http2 default_server;
# listen [::]:443 ssl http2 default_server;
# server_name _;
# root /usr/share/nginx/html;
#
# ssl_certificate "/etc/pki/nginx/server.crt";
# ssl_certificate_key "/etc/pki/nginx/private/server.key";
# ssl_session_cache shared:SSL:1m;
# ssl_session_timeout 10m;
# ssl_ciphers HIGH:!aNULL:!MD5;
# ssl_prefer_server_ciphers on;
#
# # Load configuration files for the default server block.
# include /etc/nginx/default.d/*.conf;
#
# location / {
# }
#
# error_page 404 /404.html;
# location = /40x.html {
# }
#
# error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html;
# location = /50x.html {
# }
# }
}
/etc/nginx/conf.d/default.conf
server {
listen 80;
location / {
proxy_pass http://localhost:5000;
proxy_http_version 1.1;
proxy_set_header Upgrade $http_upgrade;
proxy_set_header Connection keep-alive;
proxy_set_header Host $host;
proxy_cache_bypass $http_upgrade;
}
}
执行:nginx –s reload 使其即时生效, 访问http://192.168.1.107
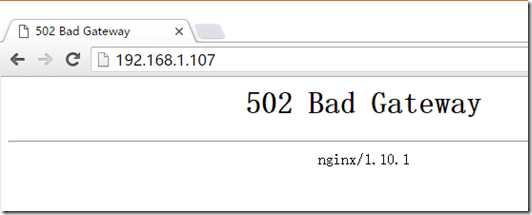
这个问题是由于SELinux保护机制所导致,我们需要将nginx添加至SELinux的白名单。
接下来我们通过一些命令解决这个问题。。
yum install policycoreutils-python sudo cat /var/log/audit/audit.log | grep nginx | grep denied | audit2allow -M mynginx sudo semodule -i mynginx.pp
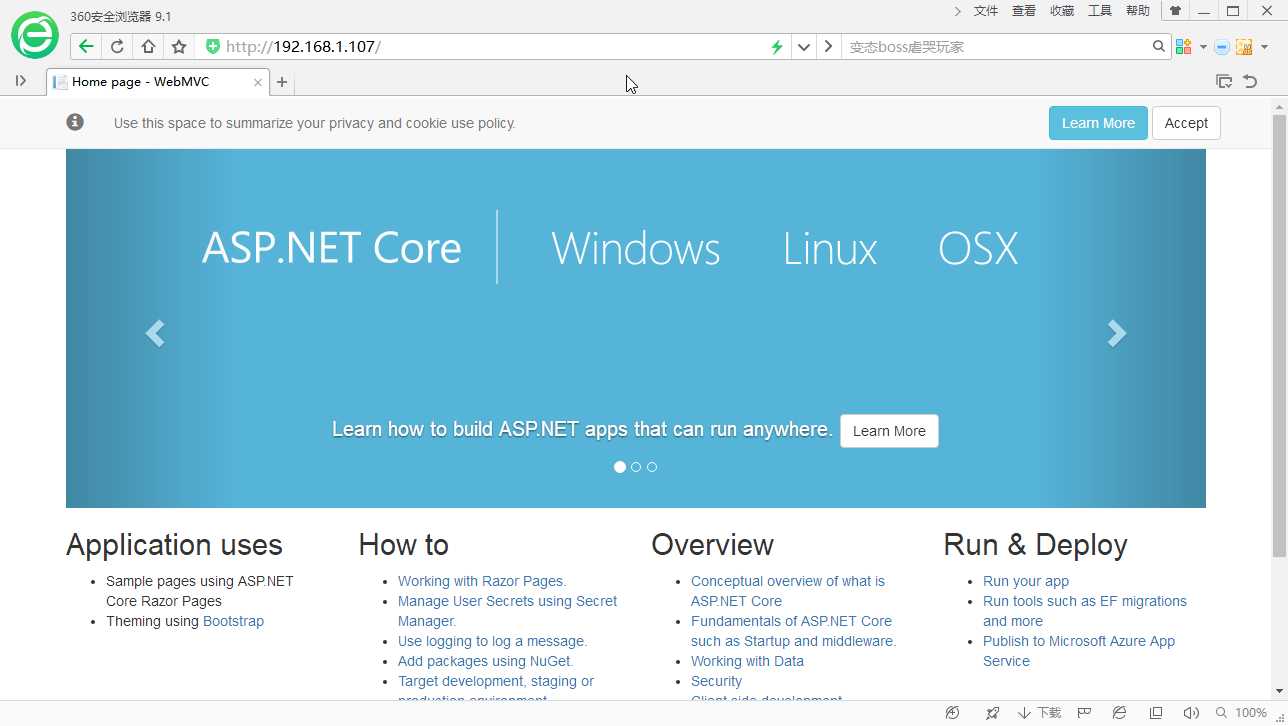
再次尝试访问。
安装
yum install python-setuptools
easy_install supervisor
配置
mkdir /etc/supervisor echo_supervisord_conf > /etc/supervisor/supervisord.conf
重启supervisor服务
$ supervisorctl reread
如果重启的时候报错: error: <class ‘socket.error‘>, [Errno 111] Connection refused: file: /usr/lib64/python2.6/socket.py line: 567
则说明服务尚未启动,先启动即可:
sudo supervisord -c /etc/supervisor/supervisord.conf
sudo supervisorctl -c /etc/supervisor/supervisord.conf
如果修改了 /etc/supervisor/supervisord.conf ,需要执行 supervisorctl reload 来重新加载配置文件,否则不会生效。
配置Supervisor开机启动:
file=/tmp/supervisor.sock ; socket文件的路径,supervisorctl用XML_RPC和supervisord通信就是通过它进行
; 的。如果不设置的话,supervisorctl也就不能用了 不设置的话,默认为none。 非必须设置
;chmod=0700 ; 修改上面的那个socket文件的权限为0700
;不设置的话,默认为0700。 非必须设置
;chown=nobody:nogroup ; 修改上面的那个socket文件的属组为user.group
; 不设置的话,默认为启动supervisord进程的用户及属组。非必须设置
;username=user ; 使用supervisorctl连接的时候,认证的用户。不设置的话,默认为不需要用户。 非必须设置
;password=123 ; 和上面的用户名对应的密码,可以直接使用明码,也可以使用SHA加密
; 如:{SHA}82ab876d1387bfafe46cc1c8a2ef074eae50cb1d
;默认不设置。。。非必须设置
;[inet_http_server] ; 侦听在TCP上的socket,Web Server和远程的supervisorctl都要用到他
; 不设置的话,默认为不开启。非必须设置
;port=127.0.0.1:9001 ; 这个是侦听的IP和端口,侦听所有IP用 :9001或*:9001。
; 这个必须设置,只要上面的[inet_http_server]开启了,就必须设置它
;username=user ; 这个和上面的uinx_http_server一个样。非必须设置
;password=123 ; 这个也一个样。非必须设置
[supervisord] ;这个主要是定义supervisord这个服务端进程的一些参数的
;这个必须设置
logfile=/tmp/supervisord.log ;这个是supervisord这个主进程的日志路径,注意和子进程的日志不搭嘎。
; 默认路径$CWD/supervisord.log,$CWD是当前目录。。非必须设置
logfile_maxbytes=50MB ;这个是上面那个日志文件的最大的大小,当超过50M的时候,会生成一个新的日志文件。当设置为0时,表示不限制文件大小
;默认值是50M,非必须设置。
logfile_backups=10 ;日志文件保持的数量,上面的日志文件大于50M时,就会生成一个新文件。文件
;数量大于10时,最初的老文件被新文件覆盖,文件数量将保持为10
;当设置为0时,表示不限制文件的数量。
;默认情况下为10。。。非必须设置
loglevel=info ; 日志级别,有critical, error, warn, info, debug, trace, or blather等
;默认为info,非必须设置项
pidfile=/tmp/supervisord.pid ;supervisord的pid文件路径。默认为$CWD/supervisord.pid。。。非必须设置
nodaemon=false ; 如果是true,supervisord进程将在前台运行
; 默认为false,也就是后台以守护进程运行。。。非必须设置
minfds=1024 ;这个是最少系统空闲的文件描述符,低于这个值supervisor将不会启动。
;系统的文件描述符在这里设置cat /proc/sys/fs/file-max
;默认情况下为1024。。。非必须设置
minprocs=200 ;最小可用的进程描述符,低于这个值supervisor也将不会正常启动。
;ulimit -u这个命令,可以查看linux下面用户的最大进程数
;默认为200。非必须设置
;umask=022 ;进程创建文件的掩码默认为022。。非必须设置项
;user=chrism ;这个参数可以设置一个非root用户,当我们以root用户启动supervisord之后。
;我这里面设置的这个用户,也可以对supervisord进行管理
;默认情况是不设置。非必须设置项
;identifier=supervisor ;这个参数是supervisord的标识符,主要是给XML_RPC用的。当你有多个
;supervisor的时候,而且想调用XML_RPC统一管理,就需要为每个
;supervisor设置不同的标识符了默认是supervisord。非必需设置
;directory=/tmp ; 这个参数是当supervisord作为守护进程运行的时候,设置这个参数的话,启动
; supervisord进程之前,会先切换到这个目录
; 默认不设置。。。非必须设置
;nocleanup=true ; 这个参数当为false的时候,会在supervisord进程启动的时候,把以前子进程
; 产生的日志文件(路径为AUTO的情况下)清除掉。有时候咱们想要看历史日志,当
; 然不想日志被清除了。所以可以设置为true
; 默认是false,有调试需求的同学可以设置为true。。。非必须设置
;childlogdir=/tmp ; 当子进程日志路径为AUTO的时候,子进程日志文件的存放路径。
; 默认路径是这个东西,执行下面的这个命令看看就OK了,处理的东西就默认路径
; python -c "import tempfile;print tempfile.gettempdir()",非必须设置
;environment=KEY="value" ; 这个是用来设置环境变量的,supervisord在linux中启动默认继承了linux的
; 环境变量,在这里可以设置supervisord进程特有的其他环境变量。
; supervisord启动子进程时,子进程会拷贝父进程的内存空间内容。 所以设置的
; 这些环境变量也会被子进程继承。
; 默认为不设置。。。非必须设置
;strip_ansi=false ;这个选项如果设置为true,会清除子进程日志中的所有ANSI 序列。默认为false。。。非必须设置
; the below section must remain in the config file for RPC
; (supervisorctl/web interface) to work, additional interfaces may be
; added by defining them in separate rpcinterface: sections
[rpcinterface:supervisor] ;这个选项是给XML_RPC用的,当然你如果想使用supervisord或者web server 这个选项必须要开启的
supervisor.rpcinterface_factory = supervisor.rpcinterface:make_main_rpcinterface
[supervisorctl] ;这个主要是针对supervisorctl的一些配置
serverurl=unix:///tmp/supervisor.sock ; 这个是supervisorctl本地连接supervisord的时候,本地UNIX socket路径,注意这个是和前面的[unix_http_server]对应的
; 默认值就是unix:///tmp/supervisor.sock。。非必须设置
;serverurl=http://127.0.0.1:9001 ; 这个是supervisorctl远程连接supervisord的时候,用到的TCP socket路径
; 注意这个和前面的[inet_http_server]对应.默认就是http://127.0.0.1:9001。。。非必须项
;username=chris ; 用户名,默认空。。非必须设置
;password=123 ; 密码默认空。。非必须设置
;prompt=mysupervisor ; 输入用户名密码时候的提示符默认supervisor。。非必须设置
;history_file=~/.sc_history ; 这个参数和shell中的history类似,我们可以用上下键来查找前面执行过的命令
;默认是no file的。。所以我们想要有这种功能,必须指定一个文件。。。非必须设置
; The below sample program section shows all possible program subsection values,
; create one or more ‘real‘ program: sections to be able to control them under
; supervisor.
;[program:theprogramname] ;这个就是咱们要管理的子进程了,":"后面的是名字,最好和实际进程有点关联最好。这样的program我们可以设置一个或多个,一个program就是要被管理的一个进程
;command=/bin/cat ; 这个就是我们的要启动进程的命令路径了,可以带参数
; 有一点需要注意的是,我们的command只能是那种在终端运行的进程,不能是
; 守护进程。比如说command=service httpd start。
; httpd这个进程被linux的service管理了,我们的supervisor再去启动这个命令
; 这已经不是严格意义的子进程了。这个是个必须设置的项
;process_name=%(program_name)s ; 这个是进程名,如果我们下面的numprocs参数为1的话,就不用管这个参数
; 了,它默认值%(program_name)s也就是上面的那个program冒号后面的名字,
; 但是如果numprocs为多个的话,那就不能这么干了。
;numprocs=1 ; 启动进程的数目。当不为1时,就是进程池的概念,注意process_name的设置默认为1 。。非必须设置
;directory=/tmp ; 进程运行前,会前切换到这个目录.默认不设置。。。非必须设置
;umask=022 ; 进程掩码,默认none,非必须
;priority=999 ; 子进程启动关闭优先级,优先级低的,最先启动,关闭的时候最后关闭.默认值为999 。。非必须设置
;autostart=true ; 如果是true的话,子进程将在supervisord启动后被自动启动.默认就是true 。。非必须设置
;autorestart=unexpected ; 这个是设置子进程挂掉后自动重启的情况,有三个选项,false,unexpected
; 和true。如果为false的时候,无论什么情况下,都不会被重新启动,
; 如果为unexpected,只有当进程的退出码不在下面的exitcodes里面定义的退
; 出码的时候,才会被自动重启。当为true的时候,只要子进程挂掉,将会被无条件的重启
;startsecs=1 ; 这个选项是子进程启动多少秒之后,此时状态如果是running,则我们认为启动成功了
; 默认值为1。非必须设置
;startretries=3 ; 当进程启动失败后,最大尝试启动的次数。。当超过3次后,supervisor将把此进程的状态置为FAIL
; 默认值为3。非必须设置
;exitcodes=0,2 ; 注意和上面的的autorestart=unexpected对应。。exitcodes里面的定义的
; 退出码是expected的。
;stopsignal=QUIT ; 进程停止信号,可以为TERM, HUP, INT, QUIT, KILL, USR1, or USR2等信号
; 默认为TERM 。。当用设定的信号去干掉进程,退出码会被认为是expected非必须设置
;stopwaitsecs=10 ; 这个是当我们向子进程发送stopsignal信号后,到系统返回信息
; 给supervisord,所等待的最大时间。 超过这个时间,supervisord会向该子进程发送一个强制kill的信号。
; 默认为10秒。。非必须设置
;stopasgroup=false ; 这个东西主要用于,supervisord管理的子进程,这个子进程本身还有
; 子进程。那么我们如果仅仅干掉supervisord的子进程的话,子进程的子进程
; 有可能会变成孤儿进程。所以咱们可以设置可个选项,把整个该子进程的
; 整个进程组都干掉。 设置为true的话,一般killasgroup也会被设置为true。
; 需要注意的是,该选项发送的是stop信号
; 默认为false。。非必须设置。。
;killasgroup=false ; 这个和上面的stopasgroup类似,不过发送的是kill信号
;user=chrism ; 如果supervisord是root启动,我们在这里设置这个非root用户,可以用来管理该program,默认不设置。。。非必须设置项
;redirect_stderr=true ; 如果为true,则stderr的日志会被写入stdout日志文件中默认为false,非必须设置
;stdout_logfile=/a/path ; 子进程的stdout的日志路径,可以指定路径,AUTO,none等三个选项。
; 设置为none的话,将没有日志产生。设置为AUTO的话,将随机找一个地方
; 生成日志文件,而且当supervisord重新启动的时候,以前的日志文件会被
; 清空。当 redirect_stderr=true的时候,sterr也会写进这个日志文件
;stdout_logfile_maxbytes=1MB ; 日志文件最大大小,和[supervisord]中定义的一样。默认为50
;stdout_logfile_backups=10 ; 和[supervisord]定义的一样。默认10
;stdout_capture_maxbytes=1MB ; 这个东西是设定capture管道的大小,当值不为0的时候,子进程可以从stdout发送信息,而supervisor可以根据信息,发送相应的event。默认为0,为0的时候表达关闭管道,非必须项
;stdout_events_enabled=false ; 当设置为ture的时候,当子进程由stdout向文件描述符中写日志的时候,将触发supervisord发送PROCESS_LOG_STDOUT类型的event默认为false。。。非必须设置
;stderr_logfile=/a/path ; 这个东西是设置stderr写的日志路径,当redirect_stderr=true。这个就不用设置了,设置了也是没用。因为它会被写入stdout_logfile的同一个文件中
; 默认为AUTO,也就是随便找个地存,supervisord重启被清空。。非必须设置
;stderr_logfile_maxbytes=1MB
;stderr_logfile_backups=10
;stderr_capture_maxbytes=1MB ;和stdout_capture一样。 默认为0,关闭状态
;stderr_events_enabled=false ; 默认为false
;environment=A="1",B="2" ; 为该子进程的环境变量,和别的子进程是不共享的
;serverurl=AUTO ;
; The below sample eventlistener section shows all possible
; eventlistener subsection values, create one or more ‘real‘
; eventlistener: sections to be able to handle event notifications
; sent by supervisor.
;[eventlistener:theeventlistenername] ;这个东西其实和program的地位是一样的,也是suopervisor启动的子进程,不过它干的活是订阅supervisord发送的event。他的名字就叫
;listener了。我们可以在listener里面做一系列处理,比如报警等等
;command=/bin/eventlistener ; 这个和上面的program一样,表示listener的可执行文件的路径
;process_name=%(program_name)s ; 这个也一样,进程名,当下面的numprocs为多个的时候,才需要。否则默认就可以
;numprocs=1 ; 相同的listener启动的个数
;events=EVENT ; event事件的类型,也就是说,只有写在这个地方的事件类型。才会被发送
;buffer_size=10 ; 这个是event队列缓存大小,单位不太清楚,楼主猜测应该是个吧。当buffer超过10的时候,最旧的event将会被清除,并把新的event放进去。默认值为10。。非必须选项
;directory=/tmp ; 进程执行前,会切换到这个目录下执行默认为不切换。。。非必须
;umask=022 ; 默认为none,不说了
;priority=-1 ; 启动优先级,默认-1,也不扯了
;autostart=true ; 是否随supervisord启动一起启动,默认true
;autorestart=unexpected ; 是否自动重启,和program一个样,分true,false,unexpected等,注意unexpected和exitcodes的关系
;startsecs=1 ; 也是一样,进程启动后跑了几秒钟,才被认定为成功启动,默认1
;startretries=3 ; 失败最大尝试次数,默认3
;exitcodes=0,2 ; 期望或者说预料中的进程退出码,
;stopsignal=QUIT ; 干掉进程的信号,默认为TERM,比如设置为QUIT,那么如果QUIT来干这个进程那么会被认为是正常维护,退出码也被认为是expected中的
;stopwaitsecs=10 ; max num secs to wait b4 SIGKILL (default 10)
;stopasgroup=false ; send stop signal to the UNIX process group (default false)
;killasgroup=false ; SIGKILL the UNIX process group (def false)
;user=chrism ;设置普通用户,可以用来管理该listener进程。默认为空。。非必须设置
;redirect_stderr=true ; 为true的话,stderr的log会并入stdout的log里面默认为false。。。非必须设置
;stdout_logfile=/a/path
;stdout_logfile_maxbytes=1MB
;stdout_logfile_backups=10
;stdout_events_enabled=false
;stderr_logfile=/a/path
;stderr_logfile_maxbytes=1MB
;stderr_logfile_backups
;stderr_events_enabled=false
;environment=A="1",B="2" ;这个是该子进程的环境变量默认为空。。。非必须设置
;serverurl=AUTO ; override serverurl computation (childutils)
; The below sample group section shows all possible group values,
; create one or more ‘real‘ group: sections to create "heterogeneous"
; process groups.
;[group:thegroupname] ;这个东西就是给programs分组,划分到组里面的program。我们就不用一个一个去操作了
;我们可以对组名进行统一的操作。 注意:program被划分到组里面之后,就相当于原来
;的配置从supervisor的配置文件里消失了。。。supervisor只会对组进行管理,而不再
;会对组里面的单个program进行管理了
;programs=progname1,progname2 ; 组成员,用逗号分开这个是个必须的设置项
;priority=999 ; 优先级,相对于组和组之间说的默认999。。非必须选项
; The [include] section can just contain the "files" setting. This
; setting can list multiple files (separated by whitespace or
; newlines). It can also contain wildcards. The filenames are
; interpreted as relative to this file. Included files *cannot*
; include files themselves.
;[include] ;这个东西挺有用的,当我们要管理的进程很多的时候,写在一个文件里面就有点大了。我们可以把配置信息写到多个文件中,然后include过来
;files = relative/directory/*.ini
标签:filename history dde quit use back tor names white
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/zuann301/p/9186758.html