标签:没有 else 代码 ict 转换 exit IV color inpu
这里我只实现了员工信息的查询功能,其它的增删改没有实现。
关于员工信息的画了一个简单的流程图
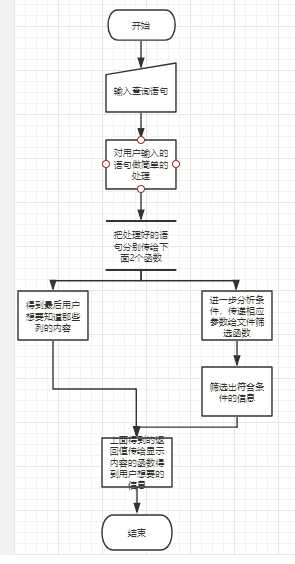
1、我们得到要查询的语句先把这个语句做简单的处理得到我们想要的数据
condition = input(">>>:").lower().replace(‘ ‘, ‘‘) # 不区分大小写 "selectname,agewhereage>20" ret = condition.split(‘where‘) # [‘selectage,name‘, ‘age>2‘]
上面可以简单的得到我们从用户输入的地方想要的2个信息
2、把从用户得到的2个数据分别传入一个为处理用户想要显示那些列的函数中一个传入从员工信息筛选的函数中得到符合条件的员工信息。
处理得到想要查询的内容列表
def get_show_lst(col_condition): """ 解析传进来的参数得到我们要显示的列名 :param col_condition: 用户输入后解析的条件 :return:列表组成的字典 """ # ‘select age,name‘ col_info_lst = col_condition.split(‘select‘) # [‘‘, ‘age,name‘] col_info = [col_info_item for col_info_item in col_info_lst if col_info_item.strip()] # [‘age,name‘] if "*" in col_info: # 查询所有信息 return column_dic.keys() # dict_keys([‘id‘, ‘name‘, ‘age‘, ‘phone‘, ‘job‘]) else: ret = col_info[0].split(‘,‘) # [‘age‘, ‘name‘] for i in ret: if i not in column_dic.keys(): # 判断要显示的列的有没有 print(‘您输入的查询条件不正确‘) sys.exit(0) return ret # [‘age‘, ‘name‘]
筛选到符合条件的信息
def filter_handler(operate, con): """ 把文件中符合条件的筛选出来作为一个列表当成元素加入到一个列表中 :param operate: 用户进行的操作 > | < | = | like :param con:用户输入的where条件 :return:被筛选出来的行按条件转换成列表加入到一个列表中的元素 """ # ‘>‘,‘age>2‘ selected_lst = [] col, val = con.split(operate) # age 2 judge = ‘int(line_lst[column_dic[col]]) %s int(val)‘% operate if operate==‘<‘ or operate==‘>‘ else ‘line_lst[column_dic[col]]‘ f = open(‘users‘, encoding=‘utf8‘) for line in f: line_lst = line.strip().split(‘,‘) # [‘1‘,‘alex‘,‘28‘,‘18765789854‘,‘python‘] if eval(judge): selected_lst.append(line_lst) f.close() return selected_lst def get_selected_line(con): """ 获取符合该条件的每一行,并将符合条件的每一行作为一个列表项存储在selected_lst中 :param con: :return: 存储符合条件的行列表 """ # ‘age>2‘ if ‘>‘ in con: selected_lst = filter_handler(‘>‘,con) elif ‘<‘ in con: selected_lst = filter_handler(‘<‘, con) elif ‘=‘ in con: selected_lst = filter_handler(‘==‘, con.replace(‘=‘,‘==‘)) elif ‘like‘ in con: selected_lst = filter_handler(‘in‘, con) return selected_lst
3、把得到的处理后的参数传给显示最后结果的函数
def show(selected_lst, show_lst): """ 把符合要求的内容显示出来 :param selected_lst: [[‘1‘,‘alex‘,‘28‘,‘18765789854‘,‘python‘],[],] :param show_lst: [‘age‘, ‘name‘] :return: """ if not selected_lst: print(‘您要查询信息不存在‘) for i in selected_lst: # [[‘1‘,‘alex‘,‘28‘,‘18765789854‘,‘python‘],[],] for j in show_lst: # [‘age‘, ‘name‘] print(i[column_dic[j]],end=‘ ‘) # 把同一个人的信息显示在同一行 print() # 第二个人换一行输出
下面就是完整的程序代码,不过这里面实现了查询得功能。
import sys column_dic = {‘id‘: 0, ‘name‘: 1, ‘age‘: 2, ‘phone‘: 3, ‘job‘: 4} # 文件中每一列的名字和数字的对应关系 # select age,name where age>2 def filter_handler(operate, con): """ 把文件中符合条件的筛选出来作为一个列表当成元素加入到一个列表中 :param operate: 用户进行的操作 > | < | = | like :param con:用户输入的where条件 :return:被筛选出来的行按条件转换成列表加入到一个列表中的元素 """ # ‘>‘,‘age>2‘ selected_lst = [] col, val = con.split(operate) # age 2 judge = ‘int(line_lst[column_dic[col]]) %s int(val)‘% operate if operate==‘<‘ or operate==‘>‘ else ‘line_lst[column_dic[col]]‘ f = open(‘users‘, encoding=‘utf8‘) for line in f: line_lst = line.strip().split(‘,‘) # [‘1‘,‘alex‘,‘28‘,‘18765789854‘,‘python‘] if eval(judge): selected_lst.append(line_lst) f.close() return selected_lst def get_selected_line(con): """ 获取符合该条件的每一行,并将符合条件的每一行作为一个列表项存储在selected_lst中 :param con: :return: 存储符合条件的行列表 """ # ‘age>2‘ if ‘>‘ in con: selected_lst = filter_handler(‘>‘,con) elif ‘<‘ in con: selected_lst = filter_handler(‘<‘, con) elif ‘=‘ in con: selected_lst = filter_handler(‘==‘, con.replace(‘=‘,‘==‘)) elif ‘like‘ in con: selected_lst = filter_handler(‘in‘, con) return selected_lst def get_show_lst(col_condition): """ 解析传进来的参数得到我们要显示的列名 :param col_condition: 用户输入后解析的条件 :return:列表组成的字典 """ # ‘select age,name‘ col_info_lst = col_condition.split(‘select‘) # [‘‘, ‘age,name‘] col_info = [col_info_item for col_info_item in col_info_lst if col_info_item.strip()] # [‘age,name‘] if "*" in col_info: # 查询所有信息 return column_dic.keys() # dict_keys([‘id‘, ‘name‘, ‘age‘, ‘phone‘, ‘job‘]) else: ret = col_info[0].split(‘,‘) # [‘age‘, ‘name‘] for i in ret: if i not in column_dic.keys(): # 判断要显示的列的有没有 print(‘您输入的查询条件不正确‘) sys.exit(0) return ret # [‘age‘, ‘name‘] def show(selected_lst, show_lst): """ 把符合要求的内容显示出来 :param selected_lst: [[‘1‘,‘alex‘,‘28‘,‘18765789854‘,‘python‘],[],] :param show_lst: [‘age‘, ‘name‘] :return: """ if not selected_lst: print(‘您要查询信息不存在‘) for i in selected_lst: # [[‘1‘,‘alex‘,‘28‘,‘18765789854‘,‘python‘],[],] for j in show_lst: # [‘age‘, ‘name‘] print(i[column_dic[j]],end=‘ ‘) # 把同一个人的信息显示在同一行 print() # 第二个人换一行输出 def sele_search(): condition = input(">>>:").lower().replace(‘ ‘, ‘‘) # 不区分大小写 "selectname,agewhereage>20" ret = condition.split(‘where‘) # [‘selectage,name‘, ‘age>2‘] show_lst = get_show_lst(ret[0]) # ‘selectage,name‘ return: [‘age‘, ‘name‘] selected_lst = get_selected_line(ret[1]) # ‘age>2‘ return: [[‘1‘,‘alex‘,‘28‘,‘18765789854‘,‘python‘],[],] show(selected_lst,show_lst) # 在屏幕上打印查出来的结果 # sele_search() if __name__ == "__main__": di = { 1:‘查询‘, 2:‘修改‘, 3:‘增加‘, 4:‘删除‘ } li = [sele_search,] while True: for i in di: print(i, di[i]) num = int(input(‘>>>:‘)) li[num-1]()
标签:没有 else 代码 ict 转换 exit IV color inpu
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/yang-China/p/9229892.html