标签:响应式 简写 strong parent 有趣的 import == hover txt
<p style=‘backgroud-color:red">hellow</p>
嵌入式是将CSS样式集中写在网页的<head></head>标签对的<style></style>标签对中。格式如下:
<head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> <style> p{ background-color: #2b99ff; } </style> </head>
将一个.css文件引入到HTML文件中
<link href="mystyle.css" rel="stylesheet" type="text/css"/>
将一个独立的.css文件引入HTML文件中,导入式使用CSS规则引入外部CSS文件,<style>标记也是写在<head>标记中,使用的语法如下:
<style type="text/css"> @import"mystyle.css"; 此处要注意.css文件的路径 </style>
文本颜色:color
颜色是通过CSS最经常的指定:
p { color: rebeccapurple; }
水平对齐方式
text-align 属性规定元素中的文本的水平对齐方式。

<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="utf-8"> <title>css</title> <style> h2 {text-align:center;} p.publish_time {text-align:right;} p.content {text-align:justify;} </style> </head> <body> <h1>CSS text-align 水平居中</h1> <p class="publish_time">2017 年 5 月 17 号</p> <p class="content"> 有个落拓不得志的中年人每隔三两天就到教堂祈祷,而且他的祷告词几乎每次都相同。第一次他到教堂时, 跪在圣坛前,虔诚地低语:“上帝啊,请念在我多年来敬畏您的份上。让我中一次彩票吧!阿门。” 几天后,他又垂头丧气回到教堂,同样跪着祈祷:“上帝啊,为何不让我中彩票?我愿意更谦卑地来 服侍你,求您让我中一次彩票吧!阿门。”又过了几天,他再次出现在教堂,同样重复他的祈祷。如此周而 复始,不间断地祈求着。到了最后一次,他跪着:“我的上帝,为何您不垂听我的祈求?让我中一次彩票吧! 只要一次,让我解决所有困难,我愿终身奉献,专心侍奉您……”就在这时,圣坛上发出一阵宏伟庄严的声 音:“我一直垂听你的祷告。可是最起码?你也该先去买一张彩票吧!”</p> <p><b>注意:</b> 重置浏览器窗口大小查看 "justify" 是如何工作的。</p> </body> </html>
/*
font-size: 10px;
line-height: 200px; 文本行高 通俗的讲,文字高度加上文字上下的空白区域的高度 50%:基于字体大小的百分比
vertical-align:-4px 设置元素内容的垂直对齐方式 ,只对行内元素有效,对块级元素无效
text-decoration:none text-decoration 属性用来设置或删除文本的装饰。主要是用来删除链接的下划线
font-family: ‘Lucida Bright‘
font-weight: lighter/bold/border/
font-style: oblique
text-indent: 150px; 首行缩进150px
letter-spacing: 10px; 字母间距
word-spacing: 20px; 单词间距
text-transform: capitalize/uppercase/lowercase ; 文本转换,用于所有字句变成大写或小写字母,或每个单词的首字母大写
*/
属性介绍
border-style: solid;
border-color: chartreuse;
border-width: 20px;
简写:
border-top-style:dotted;
border-right-style:solid;
border-bottom-style:dotted;
border-left-style:none;
list-style-type 设置列表项标志的类型。
list-style-image 将图象设置为列表项标志。
list-style-position 设置列表中列表项标志的位置。
list-style 简写属性。用于把所有用于列表的属性设置于一个声明中
ist-style-type属性指定列表项标记的类型:
ul { list-style-type: square; }
使用图像来替换列表项的标记:
ul {
list-style-image: url(‘‘); }noneblockinlinep{display:none;}
注意与visibility:hidden的区别:
visibility:hidden可以隐藏某个元素,但隐藏的元素仍需占用与未隐藏之前一样的空间。也就是说,该元素虽然被隐藏了,但仍然会影响布局。
display:none可以隐藏某个元素,且隐藏的元素不会占用任何空间。也就是说,该元素不但被隐藏了,而且该元素原本占用的空间也会从页面布局中消失。
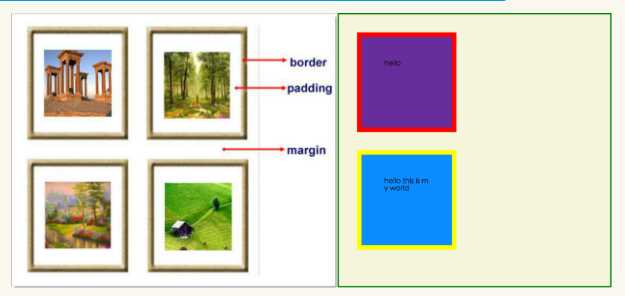
margin-top:100px;
margin-bottom:100px;
margin-right:50px;
margin-left:50px;

margin:10px 20px 20px 10px;
上边距为10px
右边距为20px
下边距为20px
左边距为10px
margin:10px 20px 10px;
上边距为10px
左右边距为20px
下边距为10px
margin:10px 20px;
上下边距为10px
左右边距为20px
margin:25px;
所有的4个边距都是25px
margin: 0 auto;单独使用填充属性可以改变上下左右的填充。缩写填充属性也可以使用,一旦改变一切都改变。
设置同margine;
页码实例:

<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> <style> .outer{ margin: 0 auto; width: 80%; } .content{ background-color: darkgrey; height: 500px; } a{ text-decoration: none; } .page-area{ text-align: center; padding-top: 30px; padding-bottom: 30px; background-color: #f0ad4e; } .page-area ul li{ display: inline-block; } .page-area ul li a ,.page-area ul li span{ display: inline-block; color: #369; height: 25px; width: 25px; text-align: center; line-height: 25px; padding: 8px; margin-left: 8px; border: 1px solid #e1e1e1; border-radius: 15%; } .page-area ul li .page-next{ width: 70px; border-radius:0 } .page-area ul li span.current_page{ border: none; color: black; font-weight:900; } .page-area ul li a:hover{ color: #fff; background-color: #2459a2; } </style> </head> <body> <div class="outer"> <div class="content"></div> <div class="page-area"> <ul> <li><span class="current_page">1</span></li> <li><a href="#" class="page-a">2</a></li> <li><a href="#" class="page-a">3</a></li> <li><a href="#" class="page-a">4</a></li> <li><a href="#" class="page-a">5</a></li> <li><a href="#" class="page-a">6</a></li> <li><a href="#" class="page-a">7</a></li> <li><a href="#" class="page-a">8</a></li> <li><a href="#" class="page-a">9</a></li> <li><a href="#" class="page-a">10</a></li> <li><a href="#" class="page-a page-next">下一页</a></li> </ul> </div> </div> </body> </html>
先来了解一下block元素和inline元素在文档流中的排列方式。
block元素通常被现实为独立的一块,独占一行,多个block元素会各自新起一行,默认block元素宽度自动填满其父元素宽度。block元素可以设置width、height、margin、padding属性;
inline元素不会独占一行,多个相邻的行内元素会排列在同一行里,直到一行排列不下,才会新换一行,其宽度随元素的内容而变化。inline元素设置width、height属性无效
所谓的文档流,指的是元素排版布局过程中,元素会自动从左往右,从上往下的流式排列。
脱离文档流,也就是将元素从普通的布局排版中拿走,其他盒子在定位的时候,会当做脱离文档流的元素不存在而进行定位。
假如某个div元素A是浮动的,如果A元素上一个元素也是浮动的,那么A元素会跟随在上一个元素的后边(如果一行放不下这两个元素,那么A元素会被挤到下一行);如果A元素上一个元素是标准流中的元素,那么A的相对垂直位置不会改变,也就是说A的顶部总是和上一个元素的底部对齐。此外,浮动的框之后的block元素元素会认为这个框不存在,但其中的文本依然会为这个元素让出位置。 浮动的框之后的inline元素,会为这个框空出位置,然后按顺序排列。
示例代码:

<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> <style> *{ margin: 0; } .r1{ width: 300px; height: 100px; background-color: #7A77C8; float: left; } .r2{ width: 200px; height: 200px; background-color: wheat; /*float: left;*/ } .r3{ width: 100px; height: 200px; background-color: darkgreen; float: left; } </style> </head> <body> <div class="r1"></div> <div class="r2"></div> <div class="r3"></div> </body> </html>
清除浮动
clear语法:
clear : none | left | right | both
取值:
none : 默认值。允许两边都可以有浮动对象
left : 不允许左边有浮动对象
right : 不允许右边有浮动对象
both : 不允许有浮动对象
但是需要注意的是:clear属性只会对自身起作用,而不会影响其他元素。

<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> <style> *{ margin: 0; } .r1{ width: 300px; height: 100px; background-color: #7A77C8; float: left; } .r2{ width: 200px; height: 200px; background-color: wheat; float: left; clear: left; } .r3{ width: 100px; height: 200px; background-color: darkgreen; float: left; } </style> </head> <body> <div class="r1"></div> <div class="r2"></div> <div class="r3"></div> </body> </html>
把握住两点:1、元素是从上到下、从左到右依次加载的。
2、clear: left;对自身起作用,一旦左边有浮动元素,即切换到下一行来保证左边元素不是浮动的,依据这一点解决父级塌陷问题。
static 默认值,无定位,不能当作绝对定位的参照物,并且设置标签对象的left、top等值是不起作用的的。
relative: 相对定位。
相对定位是相对于该元素在文档流中的原始位置,即以自己原始位置为参照物。有趣的是,即使设定了元素的相对定位以及偏移值,元素还占有着原来的位置,即占据文档流空间。对象遵循正常文档流,但将依据top,right,bottom,left等属性在正常文档流中偏移位置。而其层叠通过z-index属性定义。
注意:position:relative的一个主要用法:方便绝对定位元素找到参照物。
定义:设置为绝对定位的元素框从文档流完全删除,并相对于最近的已定位祖先元素定位,如果元素没有已定位的祖先元素,那么它的位置相对于最初的包含块(即body元素)。元素原先在正常文档流中所占的空间会关闭,就好像该元素原来不存在一样。元素定位后生成一个块级框,而不论原来它在正常流中生成何种类型的框。
重点:如果父级设置了position属性,例如position:relative;,那么子元素就会以父级的左上角为原始点进行定位。这样能很好的解决自适应网站的标签偏离问题,即父级为自适应的,那我子元素就设置position:absolute;父元素设置position:relative;,然后Top、Right、Bottom、Left用百分比宽度表示。
另外,对象脱离正常文档流,使用top,right,bottom,left等属性进行绝对定位。而其层叠通过z-index属性定义。
示例代码:

<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> <style> *{ margin: 0; } .outet{ /*position: relative;*/ } .item{ width: 200px; height:200px ; } .r1{ background-color: #7A77C8; } .r2{ background-color: wheat; /*position: relative;*/ position: absolute; top: 200px; left: 200px; } .r3{ background-color: darkgreen; } </style> </head> <body> <div class="item r1"></div> <div class="outet"> <div class="item r2"></div> <div class="item r3"></div> </div> </body> </html>
总结:参照物用相对定位,子元素用绝对定位,并且保证相对定位参照物不会偏移即可。
fixed:对象脱离正常文档流,使用top,right,bottom,left等属性以窗口为参考点进行定位,当出现滚动条时,对象不会随着滚动。而其层叠通过z-index属性 定义。 注意点: 一个元素若设置了 position:absolute | fixed; 则该元素就不能设置float。这 是一个常识性的知识点,因为这是两个不同的流,一个是浮动流,另一个是“定位流”。但是 relative 却可以。因为它原本所占的空间仍然占据文档流。
在理论上,被设置为fixed的元素会被定位于浏览器窗口的一个指定坐标,不论窗口是否滚动,它都会固定在这个位置。
示例代码:

<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> <style> *{ margin: 0; } .back{ background-color: wheat; width: 100%; height: 1200px; } span{ display: inline-block; width: 80px; height: 50px; position: fixed; bottom: 20px; right: 20px; background-color: rebeccapurple; color: white; text-align: center; line-height: 50px; } </style> </head> <body> <div class="back"> <span>返回顶部</span> </div> </body> </html>
(1)父子都是块级元素

<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <title>fortest</title> <style> div.parent{ width: 500px; height: 300px; background: #ccc; } div.son{ width: 100%; height: 200px; background: green; } </style> </head> <body> <div class="parent"> <div class="son"></div> </div> </body> </html>
这时,子元素设置为了父元素width的100%,那么子元素的宽度也是500px;
但是如果我们把子元素的width去掉之后,就会发现子元素还是等于父元素的width。也就是说,对于块级元素,子元素的宽度默认为父元素的100%。
当我们给子元素添加padding和margin时,可以发现宽度width是父元素的宽度减去子元素的margin值和padding值。
毫无疑问,如果去掉子元素的height,就会发先子元素的高度为0,故height是不会为100%的,一般我们都是通过添加内容(子元素)将父元素撑起来。
(2)父:块级元素 子:内联元素
如果内联元素是不可替换元素(除img,input以外的一般元素),元素是没有办法设置宽度的,也就谈不上100%的问题了。 即内联元素必须依靠其内部的内容才能撑开。
如果内联元素是可替换元素(img,input,本身可以设置长和宽),不管怎么设置父元素的宽度和高度,而不设置img的宽和高时,img总是表现为其原始的宽和高。

<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <title>...</title> <style> div.parent{ width: 500px; height: 300px; background: #ccc; } img{ height: 100px; background: green; } </style> </head> <body> <div class="parent"> <img class="son" src="s1.jpg"></img> </div> </body> </html>
由此我们可以发现,虽然没有设置宽度,但是表现在浏览器上为160px,它并没有继承父元素的100%得到500px,而是根据既定的高度来等比例缩小宽度。 同样, 如果只设置width,那么height也会等比例改变。 如果我们把img的width设置为100%,就可以发现其宽度这时就和父元素的宽度一致了。而我们一般的做法时,首先确定img的父元素的宽度和高度,然后再将img的宽度和高度设置位100%,这样,图片就能铺满父元素了。

<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> <style> .pg-header{ height: 48px; width: 100%; background-color: #2459a2; position: fixed; top:0; left: 0; } .left{ position:absolute; left:0; top:48px; bottom:0; width:200px; background-color: #ededed; } .right{ position:absolute; right:0; left:200px; top:48px; bottom:0; overflow:auto; } .content{ height: 2000px; width: 100%; } </style> </head> <body> <div class="pg-header"></div> <div> <div class="left"> </div> <div class="right"> <div class="content"></div> </div> </div> </body> </html>

<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> <style> /*======================================初始化=====================*/ *{ margin: 0; padding: 0; } body{ font-size: 12px; } a{ text-decoration: none; } /*======================================header区域设置=====================*/ .header{ height: 44px; width: 100%; background-color: #2459a2; position: fixed; top:0; left: 0; } .header_content{ width: 80%; height: 44px; background-color: #2459a2; margin: 0 auto; line-height: 44px; position: relative; } /*======header区part1:logo ===========*/ .logo{ float: left; width: 121px; height: 23px; margin-top: 9px; } /*======header区part2:action-menu =====*/ .action-menu{ float: left; margin-left: 30px; } .action-menu a.tb{ color: #c0cddf; padding: 0 10px; text-align: center; margin-left: -3px; display: inline-block; } .action-menu a.tb:hover { color: #fff; background-color: lightslategrey; } .action-menu a.active, .action-menu a.active:hover { color: #fff; background-color:#204982;; } /*======header区part3:key-search =====*/ .key-search{ margin-top: 5px; float: right; } .key-search a.search-icon-box, .search-txt { float: left; } .search-txt { color: #333; line-height: 25px; padding: 2px 2px 2px 5px; height: 25px; width: 91px; } .key-search a.search-icon-box { border: 1px solid #e0e0e0; background-color: #f4f4f4; width: 30px; height: 31px; border-left: 0; } .key-search a.search-icon-box span.search-icon{ background: url("images/icon.png") no-repeat 0 -197px; float: left; height: 12px; width: 11px; margin-left: 10px; margin-top: 9px; } /*======header区part4:action-nav =====*/ .action-nav { float: right; margin-right: 10px; } .action-nav a { color: white; padding: 14px 18px; } .action-nav a:hover{ background-color: lightslategrey; color: white; } /*======================================content区域设置=====================*/ .content-box { background-color: #ededed; padding-top: 44px; height: 100%; } .content { width: 960px; margin: 0 auto; height: auto!important; overflow: hidden; min-height: 713px; padding: 6px 28px; background-color: #fff; /*overflow: hidden;取消后看看效果*/ } /*===============================响应式布局=====================*/ @media(max-width:1050px) { .action-menu a.item{ display: none; background-color: gold; border: dashed 1px rebeccapurple; color: black; } .action-menu a.active{ padding: 0 25px; } .action-nav{ float: left; margin-left: 80px; } .key-search{ float: right; margin-right: 100px; } .action-menu:hover a.item{ display: block; } } @media(max-width:810px) { .key-search{ display: none; } .action-nav{ display: none; } } </style> </head> <body> <!--header结构--> <div class="header"> <div class="header_content"> <div class="logo"> <a href="/"><img src="images/logo.png" alt=""></a> </div> <div class="action-menu"> <a href="#" class="tb active">全部</a> <a href="#" class="tb item">42区</a> <a href="#" class="tb item">段子</a> <a href="#" class="tb item">图片</a> <a href="#" class="tb item">挨踢1024</a> <a href="#" class="tb item">你问我答</a> </div> <div class="key-search"> <form action="/" method="post"> <input type="text" class="search-txt"> <a href="#" class="search-icon-box" > <span class="search-icon"></span> </a> </form> </div> <div class="action-nav"> <a href="#" class="register-btn">注册</a> <a href="#" class="login-btn">登录</a> </div> </div> </div> <!--content结构--> <div class="content-box"> <div class="content"> </div> </div> </body> </html>
标签:响应式 简写 strong parent 有趣的 import == hover txt
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/lanyinhao/p/9280116.html