标签:little lib ring out short 情况 dmi show 使用
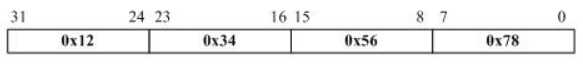
字节序是指多字节数据在计算机内存中存储或者网络传输时各字节的存储顺序。常见的主要有以下2种:
常见的还一种是网络序,即网络字节顺序,它是TCP/IP中规定好的一种数据表示格式,它与具体的CPU类型、操作系统等无关,从而可以保证数据在不同主机之间传输时能够被正确解释,网络字节顺序采用big endian排序方式。

1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <WinSock.h> 3 #pragma comment(lib, "ws2_32") 4 using namespace std; 5 6 void main() 7 { 8 int a = 0x12345678; 9 cout<<"a = "<<showbase<<hex<<a<<endl; 10 cout<<"Little Endian: ["; 11 for (int i=0; i<4; i++) 12 { 13 cout<<int(*((char*)&a+i))<<" "; 14 } 15 cout<<"]"<<endl; 16 17 int b = htonl(a); 18 cout<<"Big Endian: ["; 19 for (int i=0; i<4; i++) 20 { 21 cout<<int(*((char*)&b+i))<<" "; 22 } 23 cout<<"]"<<endl; 24 25 getchar(); 26 }
其运行结果为:

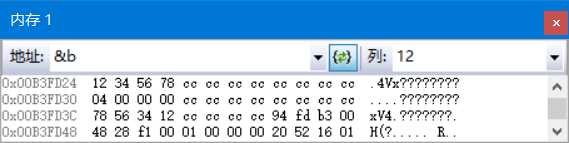
在调试状态下,在内存窗口中查看变量a和变量b的地址,也可以清晰的看到两种字节序的不同存储情况。本例中变量a和变量b的地址分别为0x00B3FD3C和0x00B3FD24:
(2)Python语言程序:
1 # -*- coding: utf-8 -*-# 2 3 #------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 4 # Name: LittleAndBigEndianTest 5 # Description: 6 # Author: Administrator 7 # Date: 2018/7/8 8 #------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 9 10 import sys 11 from struct import * 12 from ctypes import * 13 import numpy as np 14 15 a = 0x12345678 16 print(‘a: ‘ + hex(a)) 17 for name, fmt in zip([‘LittleEndian: ‘, ‘BigEndian: ‘, ‘Network: ‘], [Struct(‘<1i‘), Struct(‘>1i‘), Struct(‘!1i‘)]): 18 buffer = create_string_buffer(fmt.size) 19 fmt.pack_into(buffer, 0, a) 20 data = np.frombuffer(buffer, dtype=np.uint8) 21 print(name + str(map(lambda x: hex(x), data)))
其运行结果为:

结果同C语言版本一致,同时也验证了网络字节序同大端序结果完全相同。
标签:little lib ring out short 情况 dmi show 使用
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/luke0011/p/9280704.html