标签:The 图片 redo stat str att 强制 指定 .com
流是一组有序的数据序列,根据操作的类型,可以分为输入流和输出流。
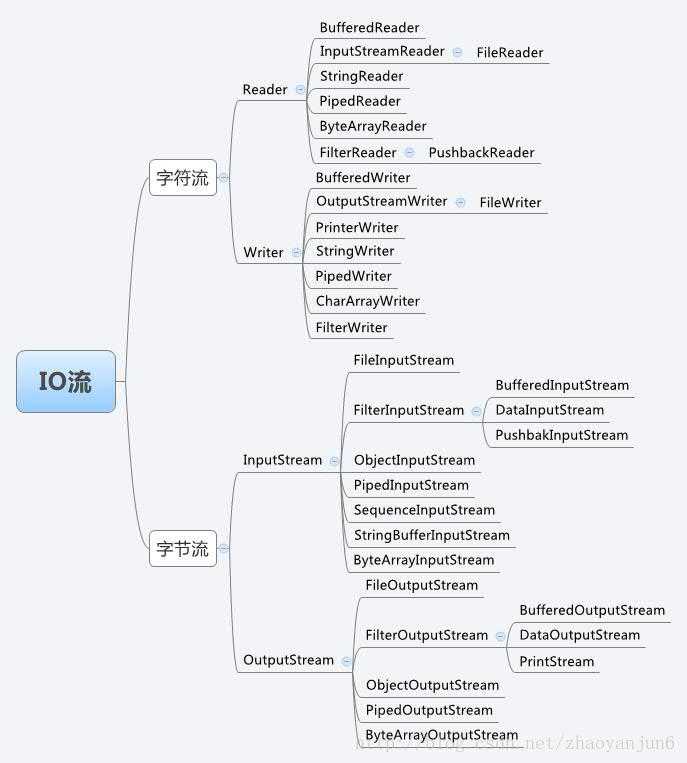
根据处理数据类型的不同,流又可分为字节流和字符流。相关类位于java.io包中,以下是相关类
1、文件输入\输出流
字节流:FileInputStream和FileOutputStream
FileInputStream和FileOutputStream分别继承自InputStream和OutputStream
/** * 写入文件 */ public static void testFileOutputStream(){ try { File file=new File("D:\\test.txt"); if(!file.exists()){ file.createNewFile(); } FileOutputStream fileOutputStream=new FileOutputStream(file); String str="this is the content"; byte[] b=str.getBytes(); fileOutputStream.write(b); fileOutputStream.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } /** * 读文件 */ public static void testFileInputStream(){ try { File file=new File("D:\\test.txt"); if(!file.exists()){ file.createNewFile(); } FileInputStream fileInputStream=new FileInputStream(file); byte[] b=new byte[1024]; System.out.println("b before:"+new String(b)); int len=fileInputStream.read(b);//Reads up to b.length bytes of data from this input stream into an array of bytes. System.out.println("b after:"+new String(b,0,len)); fileInputStream.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } }
输出:
b before: b after:this is the content
可见,FileInputStream的read(byte[] b)方法是从流中读取b中(Reads up to b.length bytes of data from this input stream into an array of bytes. )
字符流:FileReader和FileWriter
FileReader和FileWriter分别继承自Reader和Writer
/** * 写入文件 */ public static void testFileWriter(){ try { File file=new File("D:\\test.txt"); if(!file.exists()){ file.createNewFile(); } FileWriter fileWriter=new FileWriter(file); String str="this is the content2"; fileWriter.write(str); fileWriter.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } /** * 读文件 */ public static void testFileReader(){ try { File file=new File("D:\\test.txt"); if(!file.exists()){ file.createNewFile(); } FileReader fileReader=new FileReader(file); char[] cbuf=new char[1024]; System.out.println("cbuf before:"+new String(cbuf)); int len=fileReader.read(cbuf);//Attempts to read characters into the specified character buffer. System.out.println("cbuf after:"+new String(cbuf,0,len)); fileReader.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } }
输出:
cbuf before: cbuf after:this is the content2
FileReader的read(char[] cbuf)方法,是将流的内容读取到cbuf中
2、带缓存的输入/输出流
缓存是I/O的一种性能优化,缓存流为I/O流增加了内存缓存区。有了缓存区,使得在流上执行skip()、mark()和reset()方法成为可能。
字节流:BufferedInputStream和BufferedOutputStream
BufferedInputStream对所有InputStream类进行带缓存区的包装以达到性能的优化。BufferedInputStream有两个构造方法:
(1) BufferedInputStream(InputStream in)
(2) BufferedInputStream(InputStream in,int size)
第一个构造方法创建了一个带有32字节的缓存流;第二个构造方法size参数指定了创建的缓存区的大小。
BufferedInputStream读取文件的流程如下:
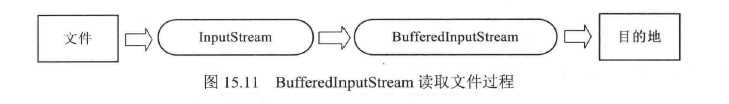
BufferedOutputStream与BufferedInputStream类似,也有两个构造方法,
(1) BufferedOutputStream(OutputStream out)
(2) BufferedOutputStream(OutputStream out,int size)
第一个构造方法创建了一个带有32字节的缓存流;第二个构造方法size参数指定了创建的缓存区的大小。
BufferedOutputStream的flush()方法强制将缓存区的数据输出完。
以下是代码:
/** * 写入文件 */ public static void testBufferedOutputStream(){ try { File file=new File("D:\\test.txt"); if(!file.exists()){ file.createNewFile(); } FileOutputStream fileOutputStream=new FileOutputStream(file); BufferedOutputStream BufferedOutputStream=new BufferedOutputStream(fileOutputStream); String str="this is the content3"; byte[] b=str.getBytes(); BufferedOutputStream.write(b); BufferedOutputStream.close(); fileOutputStream.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } /** * 读文件 */ public static void testBufferedInputStream(){ try { File file=new File("D:\\test.txt"); if(!file.exists()){ file.createNewFile(); } FileInputStream fileInputStream=new FileInputStream(file); BufferedInputStream BufferedInputStream=new BufferedInputStream(fileInputStream); byte[] b=new byte[1024]; System.out.println("b before:"+new String(b)); int len=BufferedInputStream.read(b);//Reads up to byte.length bytes of data from this input stream into an array of bytes. System.out.println("b after:"+new String(b,0,len)); BufferedInputStream.close(); fileInputStream.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } }
字符流:BufferedReader和BufferedWriter
BufferedReader和BufferedWriter分别继承自Reader和Writer,具有内部缓存的机制,并可以以行为单位进行输入输出。下图是读取的过程
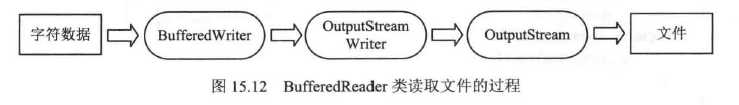
以下是代码示例:
/** * 写文件 */ public static void testBufferedWriter(){ try { File file=new File("D:\\test.txt"); if(!file.exists()){ file.createNewFile(); } FileOutputStream fileOutputStream=new FileOutputStream(file); OutputStreamWriter outputStreamWriter=new OutputStreamWriter(fileOutputStream); BufferedWriter bufferedWriter=new BufferedWriter(outputStreamWriter); String str="this is the content5\n thissssss"; bufferedWriter.write(str); bufferedWriter.close(); outputStreamWriter.close(); fileOutputStream.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } /** * 读文件 */ public static void testBufferedReader(){ try { File file=new File("D:\\test.txt"); if(!file.exists()){ file.createNewFile(); } FileInputStream fileInputStream=new FileInputStream(file); InputStreamReader inputStreamReader=new InputStreamReader(fileInputStream); BufferedReader bufferedReader=new BufferedReader(inputStreamReader); String str=bufferedReader.readLine(); System.out.println(str); int i=bufferedReader.read(); System.out.println(i); bufferedReader.close(); inputStreamReader.close(); fileInputStream.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } }
输出结果:
this is the content5 32
标签:The 图片 redo stat str att 强制 指定 .com
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/BonnieWss/p/9339056.html