目录
初衷
swagger介绍
在dropwizard中使用
在spring-boot中使用
配置
4.设定访问API doc的路由
6. 设置在生产环境关闭swagger
参考:
初衷
记得以前写接口,写完后会整理一份API接口文档,而文档的格式如果没有具体要求的话,最终展示的文档则完全决定于开发者的心情。也许多点,也许少点。甚至,接口总是需要适应新需求的,修改了,增加了,这份文档维护起来就很困难了。于是发现了swagger,自动生成文档的工具。
swagger介绍
首先,官网这样写的:
Swagger – The World‘s Most Popular Framework for APIs.
因为自强所以自信。swagger官方更新很给力,各种版本的更新都有。swagger会扫描配置的API文档格式自动生成一份json数据,而swagger官方也提供了ui来做通常的展示,当然也支持自定义ui的。不过对后端开发者来说,能用就可以了,官方就可以了。
最强的是,不仅展示API,而且可以调用访问,只要输入参数既可以try it out.
效果为先,最终展示doc界面,也可以设置为中文: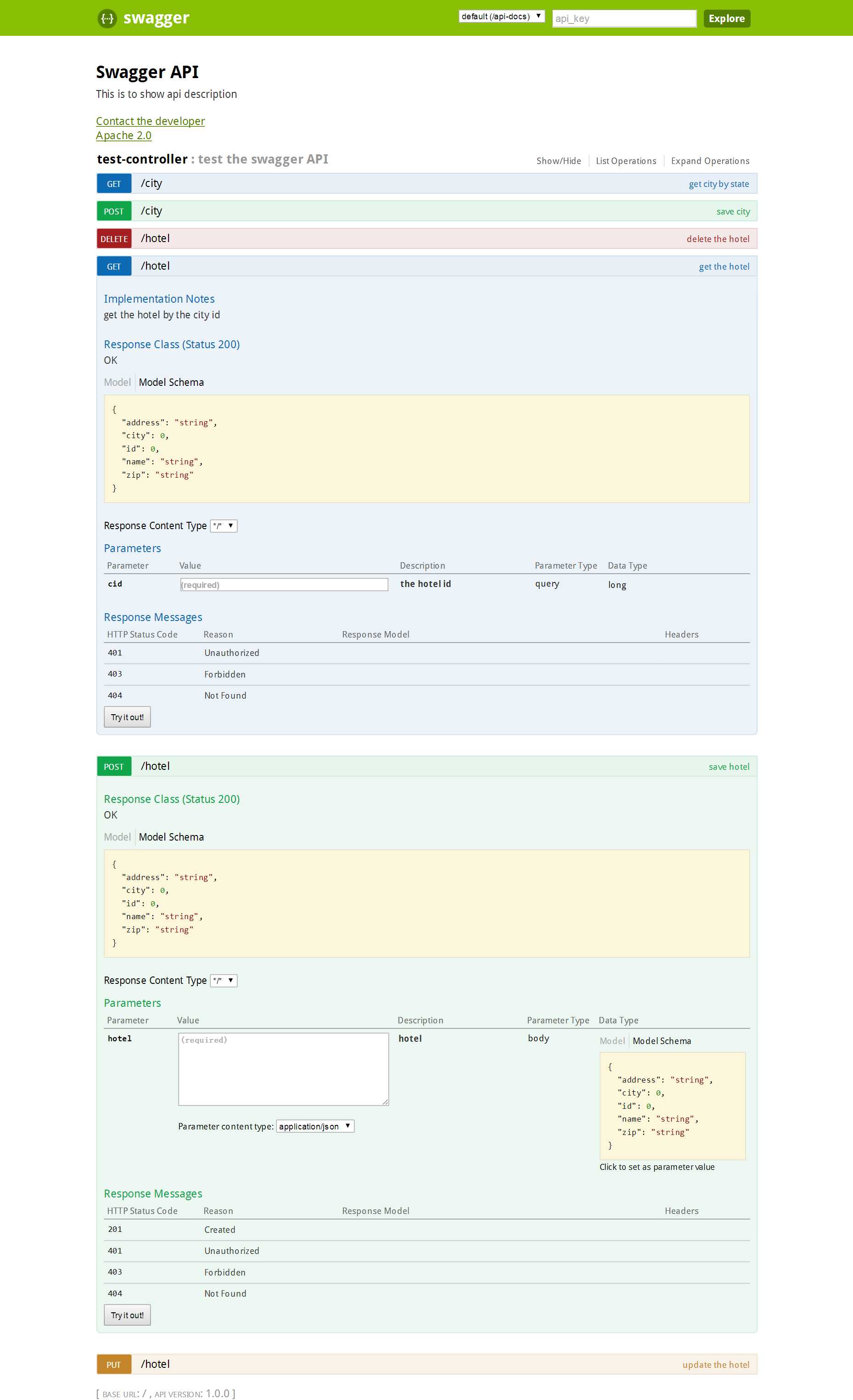
在dropwizard中使用
详细信息见另一篇在dropwizard中使用Swagger
在spring-boot中使用
以前总是看各种博客来配置,这次也不例外。百度了千篇一律却又各有细微的差别,甚至时间上、版本上各有不同。最终还是去看官方文档,终于发现了官方的sample。针对于各种option的操作完全在demo中了,所以clone照抄就可以用了。
github sample源码
配置
1.需要依赖两个包:
<dependency>
<groupId>io.springfox</groupId>
<artifactId>springfox-swagger2</artifactId>
<version>${springfox-version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>io.springfox</groupId>
<artifactId>springfox-swagger-ui</artifactId>
<version>${springfox-version}</version>
</dependency>第一个是API获取的包,第二是官方给出的一个ui界面。这个界面可以自定义,默认是官方的,对于安全问题,以及ui路由设置需要着重思考。
2.swagger的configuration
需要特别注意的是swagger scan base package,这是扫描注解的配置,即你的API接口位置。
@Configuration
@EnableSwagger2
public class SwaggerConfig {
public static final String SWAGGER_SCAN_BASE_PACKAGE = "com.test.web.controllers";
public static final String VERSION = "1.0.0";
ApiInfo apiInfo() {
return new ApiInfoBuilder()
.title("Swagger API")
.description("This is to show api description")
.license("Apache 2.0")
.licenseUrl("http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0.html")
.termsOfServiceUrl("")
.version(VERSION)
.contact(new Contact("","", "miaorf@outlook.com"))
.build();
}
@Bean
public Docket customImplementation(){
return new Docket(DocumentationType.SWAGGER_2)
.select()
.apis(RequestHandlerSelectors.basePackage(SWAGGER_SCAN_BASE_PACKAGE))
.build()
.directModelSubstitute(org.joda.time.LocalDate.class, java.sql.Date.class)
.directModelSubstitute(org.joda.time.DateTime.class, java.util.Date.class)
.apiInfo(apiInfo());
}
}当然,scan package 也可以换成别的条件,比如:
@Bean
public Docket api() {
return new Docket(DocumentationType.SWAGGER_2)
.apiInfo(apiInfo())
.select()
.apis(RequestHandlerSelectors.withMethodAnnotation(ApiOperation.class))
.build();
}3.在API上做一些声明
//本controller的功能描述
@Api(value = "pet", description = "the pet API")
public interface PetApi {
//option的value的内容是这个method的描述,notes是详细描述,response是最终返回的json model。其他可以忽略
@ApiOperation(value = "Add a new pet to the store", notes = "", response = Void.class, authorizations = {
@Authorization(value = "petstore_auth", scopes = {
@AuthorizationScope(scope = "write:pets", description = "modify pets in your account"),
@AuthorizationScope(scope = "read:pets", description = "read your pets")
})
}, tags={ "pet", })
//这里是显示你可能返回的http状态,以及原因。比如404 not found, 303 see other
@ApiResponses(value = {
@ApiResponse(code = 405, message = "Invalid input", response = Void.class) })
@RequestMapping(value = "/pet",
produces = { "application/xml", "application/json" },
consumes = { "application/json", "application/xml" },
method = RequestMethod.POST)
ResponseEntity<Void> addPet(
//这里是针对每个参数的描述
@ApiParam(value = "Pet object that needs to be added to the store" ,required=true ) @RequestBody Pet body);案例:
package com.test.mybatis.web.controllers;
import com.test.mybatis.domain.entity.City;
import com.test.mybatis.domain.entity.Hotel;
import com.test.mybatis.domain.mapper.CityMapper;
import com.test.mybatis.domain.mapper.HotelMapper;
import com.test.mybatis.domain.model.common.BaseResponse;
import io.swagger.annotations.*;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.http.HttpStatus;
import org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*;
import java.util.List;
/**
* Created by miaorf on 2016/9/10.
*/
@Api(value = "Test", description = "test the swagger API")
@RestController
public class TestController {
@Autowired
private CityMapper cityMapper;
@Autowired
private HotelMapper hotelMapper;
@ApiOperation(value = "get city by state", notes = "Get city by state", response = City.class)
@ApiResponses(value = {@ApiResponse(code = 405, message = "Invalid input", response = City.class) })
@RequestMapping(value = "/city", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public ResponseEntity<BaseResponse<City>> getCityByState(
@ApiParam(value = "The id of the city" ,required=true ) @RequestParam String state){
City city = cityMapper.findByState(state);
if (city!=null){
BaseResponse response = new BaseResponse(city,true,null);
return new ResponseEntity<>(response, HttpStatus.OK);
}
return new ResponseEntity<>(HttpStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR);
}
@ApiOperation(value = "save city", notes = "", response = City.class)
@RequestMapping(value = "/city", method = RequestMethod.POST)
public ResponseEntity<BaseResponse<City>> saveCity(
@ApiParam(value = "The id of the city" ,required=true ) @RequestBody City city){
int save = cityMapper.save(city);
if (save>0){
BaseResponse response = new BaseResponse(city,true,null);
return new ResponseEntity<>(response, HttpStatus.OK);
}
return new ResponseEntity<>(HttpStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR);
}
@ApiOperation(value = "save hotel", notes = "", response = Hotel.class)
@RequestMapping(value = "/hotel", method = RequestMethod.POST)
public ResponseEntity<BaseResponse<Hotel>> saveHotel(
@ApiParam(value = "hotel" ,required=true ) @RequestBody Hotel hotel){
int save = hotelMapper.save(hotel);
if (save>0){
BaseResponse response = new BaseResponse(hotel,true,null);
return new ResponseEntity<>(response, HttpStatus.OK);
}
return new ResponseEntity<>(HttpStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR);
}
@ApiOperation(value = "get the hotel", notes = "get the hotel by the city id", response = Hotel.class)
@RequestMapping(value = "/hotel", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public ResponseEntity<BaseResponse<Hotel>> getHotel(
@ApiParam(value = "the hotel id" ,required=true ) @RequestParam Long cid){
List<Hotel> hotels = hotelMapper.selectByCityId(cid);
return new ResponseEntity<>(new BaseResponse(hotels,true,null), HttpStatus.OK);
}
@ApiOperation(value = "update the hotel", notes = 