标签:byte tput 过程 logs 二进制 pac off 图片 tst
|
1
2
|
System.out.println(File.separator);//输出 \
System.out.println(File.pathSeparator);//输出 ;
|
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
|
//不使用 Java 提供的分隔符字段,注意:这样写只能在 Windows 平台有效
File f1 = new File("D:\\IO\\a.txt");
//使用 Java 提供的分隔符
File f2 = new File("D:"+File.separator+"IO"+File.separator+"a.txt");
System.out.println(f1);//输出 D:\IO\a.txt
System.out.println(f2);//输出 D:\IO\a.txt
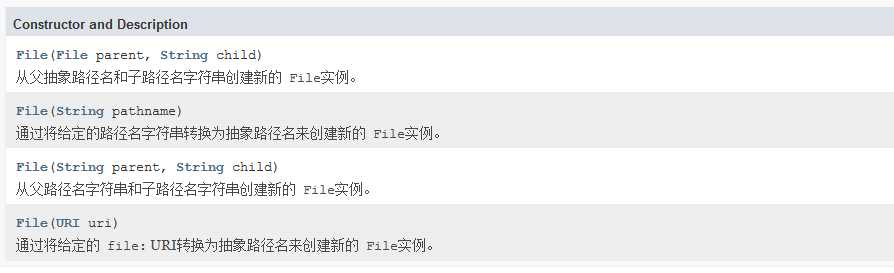
//File(File parent, String child)
//从父抽象路径名和子路径名字符串创建新的 File实例。
File f3 = new File("D:");
File f4 = new File(f3,"IO");
System.out.println(f4); //D:\IO
//File(String pathname)
//通过将给定的路径名字符串转换为抽象路径名来创建新的 File实例。
File f5 = new File("D:"+File.separator+"IO"+File.separator+"a.txt");
System.out.println(f5); //D:\IO\a.txt
//File(String parent, String child)
//从父路径名字符串和子路径名字符串创建新的 File实例。
File f6 = new File("D:","IO\\a.txt");
System.out.println(f6); //D:\IO\a.txt
|
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
|
//1、创建目标对象,输出流表示把数据保存到哪个文件。不写盘符,默认该文件是在该项目的根目录下
File target = new File("io"+File.separator+"a.txt");
//2、创建文件的字节输出流对象,第二个参数是 Boolean 类型,true 表示后面写入的文件追加到数据后面,false 表示覆盖
OutputStream out = new FileOutputStream(target,true);
//3、具体的 IO 操作(将数据写入到文件 a.txt 中)
/**
* void write(int b):把一个字节写入到文件中
* void write(byte[] b):把数组b 中的所有字节写入到文件中
* void write(byte[] b,int off,int len):把数组b 中的从 off 索引开始的 len 个字节写入到文件中
*/
out.write(65); //将 A 写入到文件中
out.write("Aa".getBytes()); //将 Aa 写入到文件中
out.write("ABCDEFG".getBytes(), 1, 5); //将 BCDEF 写入到文件中
//经过上面的操作,a.txt 文件中数据为 AAaBCDEF
//4、关闭流资源
out.close();
System.out.println(target.getAbsolutePath());
|
标签:byte tput 过程 logs 二进制 pac off 图片 tst
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/ribite/p/9384606.html