标签:陌陌 lse day 上下 windows 北京 基础学习 需要 组合
C语言基础学习PYTHON——基础学习D02
20180801内容纲要:
1 字符串的系列操作
2 集合
3 文件的读写
4 字符编码转换
5 小结
6 练习:三级菜单(有彩蛋)
1 字符串的系列操作
特性:不可修改。(‘str‘ object does not support item assignment)
支持运算:切片、索引、min()、max()、len()等
关于字符串的操作:

#关于字符串的一些操作 ‘‘‘ name = "zhang\tkanghui" print(name.capitalize()) #capitalize首字母大写 print(name.count("a")) #count计数 print(name.center(50,"-")) #center(50,“-”)表示总共50个字符,输出占中间位置 print(name.encode()) print(name.endswith("ui")) #判断是不是以ui结尾 print(name.expandtabs(tabsize=30)) #将tab在输出时转成相应数量的空格 print(name.find("kang")) #找到字符开头的索引 ‘‘‘ name ="my name is {name} and i am {year} old" print(name.format(name=‘zhangkanghui‘,year=23)) #格式化输出 print(name.format_map( {‘name‘:‘zhangkagnhui‘,‘year‘:23} )) #以字典形式格式化输出 print(name.isdigit()) #判断是否为数字 print(name.isalnum()) #判段是否为阿拉伯 print(‘abc12/‘.isalnum()) print(name.isalpha()) #判断是否为纯英语字母 print(‘Aa‘.isalpha()) print(name.isdecimal()) #判断是否为十进制 print(name.isidentifier()) #判断是否为合法标识符 print(‘ ab‘.isidentifier()) print(name.islower()) print(name.isnumeric()) print(‘1.2‘.isnumeric()) #判断是否为纯数字,小数点也不行 print(name.isspace()) #判断是否为空格 print(name.istitle()) #判断是否为标题,即每个都是首字母大写开头 print(name.isprintable()) #判断是否可打印,tty file,drive file print(name.isupper()) #判断是否全部为大写 print(‘+‘.join([‘1‘,‘2‘,‘3‘])) print(name.ljust(50,‘*‘)) #总长为50,左侧开始 print(name.rjust(50,‘-‘)) #总长为50,右侧开始 print(name.lower()) #把大写变成小写 print(name.upper()) #把小写变成大写 print(name.lstrip()) print(name.strip()) #去掉两头的空格和回车 print(name.rstrip()) p =str.maketrans(‘abc‘,‘123‘) print("alex li".translate(p)) print("alex li".replace(‘l‘,‘L‘,1)) print("alex li".rfind(‘l‘)) #查找右侧的 print("alex li".split()) #把字符串以空格分离,以列表输出 print("alex li".split(‘l‘)) #把字符串以l分 print("1+\n2+3".splitlines()) #去除换行符 print("alex Li".swapcase()) #小写换大写,大写换小写 print("alex li".title()) #变成标题,即每个首字母大写 print(name.zfill(50))
2 集合(set)
集合是一个无序、不可重复的数据组合。(字符和元组属于不可变序列,而列表支持插入、删除和替换元素;所有的序列都支持迭代;字典dict是无序的,且key必须是唯一的)
用途:
(1)去重:把一个列表变成一个集合。

list_1 = [1,2,4,5,6,2,1,] list_1 =set(list_1) print(list_1,type(list_1)) #集合无序、不重复
(2)关系测试:交集、并集、差集、子集、父集、对称差集
运算符:
&交集
|并集
-差集 例:t-a 在t中不在a中
^对称差集(除去交集对称的部分)
<=子集 例:a<=t测试是否a中的每一个元素都在t中
>=父集

list_2 =set([0,66,222,4,6]) print(list_1,list_2) #交集intersection print(list_1.intersection(list_2)) #并集union print(list_1.union(list_2)) #差集differeence in list_1 but not in list_2 print(list_1.difference(list_2)) print(list_2.difference(list_1)) #子集issubset print(list_1.issubset(list_2)) #父集isupperset print(list_1.issubset(list_2)) #对称差集 print(list_1.symmetric_difference(list_2)) list_3 =set([1,2,3]) list_4 =set([4,5,6]) print(list_3.isdisjoint(list_4)) #没有交集返回True
集合的基本操作:

#基本操作 list_3.add(999) print(list_3) list_3.update([777,888,999]) print(list_3) print(list_3.pop()) print(list_3.pop()) print(list_3.pop()) print(list_3.pop())
还有一些不常用的,比如:
.remove Remove and return an arbitrary set element.
.discard Remove an element from a set if it is a menber. If the element is not a menber, do nothing.
3 文件(file)
现有如下文件(热爱生命——汪国真):

1 我不去想是否能够成功 2 既然选择了远方 3 便只顾风雨兼程 4 我不去想能否赢得爱情 既然钟情于玫瑰 5 就勇敢地吐露真诚 6 我不去想身后会不会袭来寒风冷雨 7 既然目标是地平线 8 留给世界的只能是背影 9 我不去想未来是平坦还是泥泞 10 只要热爱生命 一切,都在意料之中
(1)文件的打开模式

1 ‘‘‘ 2 data =open("yesterday",encoding="utf-8").read() 3 #1encoding:windows默认GBK 4 #2‘r‘只能读;‘w‘只能写,且是创建一个新的文件,如果文件名已存在,则会覆盖;‘a‘只能写,append追加补充不会覆盖源文件 5 print(data) 6 ‘‘‘ 7 #f =open("yesterday",‘r‘,encoding="utf-8") 8 #f =open("yesterday",‘w‘,encoding="utf-8") 9 #f =open("yesterday",‘a‘,encoding="utf-8") 10 ‘‘‘ 11 f =open("yesterday",encoding="utf-8") #赋给f一个内存对象,又叫文件件句柄 12 data =f.read() 13 print(data) 14 ‘‘‘

1 #读写‘r+‘读和追加,能读能写,但是写只能在尾部追加无论读取光标的位置在哪 2 f =open("yesterday2",‘r+‘,encoding="utf-8") 3 print(f.readline()) 4 print(f.readline()) 5 print(f.readline()) 6 print(f.tell()) 7 f.write("-------NB--------") 8 9 #写读‘w+‘能写能读,创建新文件写,读仍然是在为不追加,无论读取光标位置 10 f =open("yesterday2",‘w+‘,encoding="utf-8") 11 f.write("-------NB--------\n") 12 f.write("-------NB--------\n") 13 f.write("-------NB--------\n") 14 print(f.tell()) 15 f.seek(10) 16 print(f.readline()) 17 f.write("should be at the begining of the second line") 18 f.close() 19 ‘‘‘ 20 #追加读写‘a+‘
"U"表示在读取时,可以将 \r \n \r\n自动转换成 \n (与 r 或 r+ 模式同使用)
"b"表示处理二进制文件
二进制文件的读取:

1 #Author:ZhangKanghui 2 3 ‘‘‘ 4 #‘rb‘二进制。视频以二进制读取。 5 f =open("yesterday2",‘rb‘) 6 print(f.readline()) 7 ‘‘‘ 8 f =open("yesterday2",‘wb‘) 9 f.write("Hello world\n".encode()) #二进制便把文件str转换成byte用encode()
等等,还有~with语句
为了避免打开文件后忘记关闭,可以通过管理上下文,即:
with open(‘log‘,‘r‘) as f:
....
如此方式,当with代码块执行完毕时,内部会自动关闭并释放文件资源。
(2)文件的读取
读取前五行:

1 #读取前五行 2 ‘‘‘ 3 f =open("yesterday",encoding="utf-8") 4 5 for i in range(5): 6 print(f.readline()) 7 8 print(f.readline()) 9 print(f.readline()) 10 print(f.readline()) 11 print(f.readline()) 12 print(f.readline())
不读取第十行:

1 #不读取第十行 2 #f =open("yesterday",encoding="utf-8") 3 #low bige loop 4 ‘‘‘ 5 #print(f.readlines()) #把文件读取成一个列表,但这种方法只适合小文件读取 6 #for line in f.readlines(): 7 for index,line in enumerate(f.readlines()): 8 if index == 9: 9 print("-----我是分割线-----") 10 continue 11 print(line.strip()) #若不换行, .strip去除换行符 12 ‘‘‘ 13 #high bige loop 14 ‘‘‘ 15 count = 0 16 for line in f: 17 if count ==9: 18 print("------我是分割线-------") 19 count += 1 20 continue 21 print(line) #这种文件的读取方式效率最高,一行一行的读,内存对象一直都只有一行 22 count +=1
重新读取文件:
f.read()读取文件时,从头到尾。再次读取文件时需要先将读取位置光标调到开头。
f.tell() 文件读取位置,打印当前读取光标位置
f.seek() 寻找当前读取光标位置

1 #重新读取文件 2 print(f.tell()) #文件读取光标位置 3 #print(f.read(50)) 4 #print(f.tell()) 5 print(f.readline()) 6 print(f.readline()) 7 print(f.readline()) 8 print(f.tell()) 9 f.seek(0) #文件读取光标移到0,经常与.tell联合使用,以便再次读取文件 10 11 print(f.encoding) #数据编码
(3)文件的操作
a 截取
1 #截取truncate 2 f =open("yesterday",‘a‘,encoding="utf-8") 3 f.truncate(10) #无论读取光标在哪都是从头开始截取
b 修改

1 #Author:ZhangKanghui 2 3 f =open("热爱生命",‘r‘,encoding="utf-8") 4 f_new =open("热爱生命.bak",‘w‘,encoding="utf-8") 5 6 for line in f: 7 if "我不去想能否赢得爱情" in line: 8 line =line.replace("我","你") 9 f_new.write(line) 10 f.close() 11 f_new.close()
(4)文件关闭
f.close()
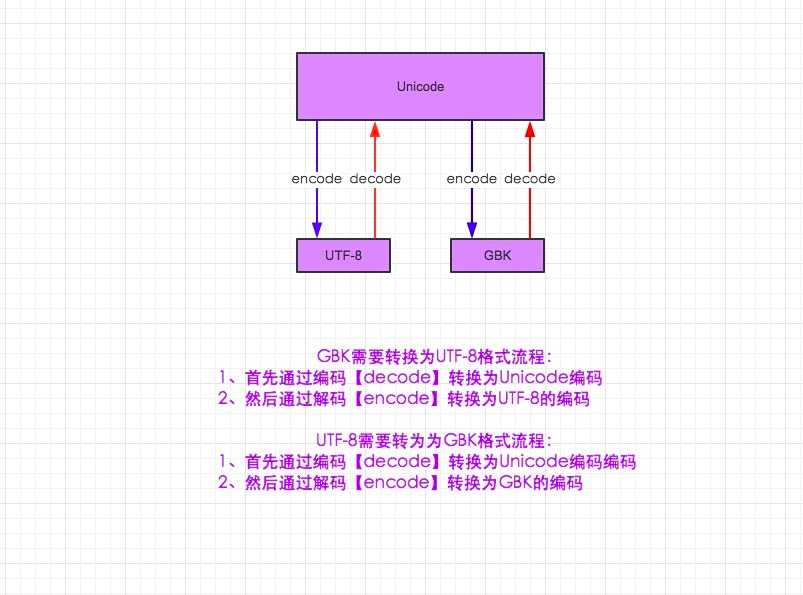
4 字符编码的转换
核心:Unicode,默认中英文都是2个字节16位
Utf-8可变长的字符编码,所有英文字符按ASCII码1个字节8位,中文3个字节。中国有钱~
详细文章:
http://www.cnblogs.com/yuanchenqi/articles/5956943.html
http://www.diveintopython3.net/strings.html
5 小结
字符编码的理解很关键~
发现插入代码折叠功能~
编程真的是和很难!
6 练习
多级菜单
要求:
两种答案:

1 #Author:ZhangKanghui 2 3 data ={ 4 ‘北京‘:{ 5 "朝阳":{ 6 "望京":["奔驰","陌陌"], 7 "国贸":["CICC","HP"], 8 "东直门":["Advent","飞信"], 9 }, 10 "昌平":{ 11 "沙河":["old boy","test"], 12 "天通苑":["链家地产","我爱我家"], 13 }, 14 "海淀": {}, 15 }, 16 ‘山东‘:{ 17 "德州":{}, 18 "青岛":{}, 19 "济南":{}, 20 }, 21 ‘广东‘:{ 22 "常熟":{}, 23 "东莞":{}, 24 "惠州":{}, 25 }, 26 } 27 28 ‘‘‘ 29 while True: 30 for i1 in data: 31 print(i1) 32 choice =input("选择进入1>>:") 33 if choice in data: 34 while True: 35 for i2 in data[choice]: 36 print("\t\t",i2) 37 choice2 =input("选择进入2>>:") 38 if choice2 in data[choice]: 39 while True: 40 for i3 in data[choice][choice2]: 41 print("\t\t\t\t",i3) 42 choice3 =input("选择进入3>>:") 43 if choice3 in data[choice][choice2]: 44 for i4 in data[choice][choice2][choice3]: 45 print("\t\t\t\t\t\t",i4) 46 choice4 =input("最后一层,按b返回>>:") 47 if choice4 ==‘b‘: 48 pass 49 if choice3 == ‘b‘: 50 break 51 if choice2 == ‘b‘: 52 break 53 ‘‘‘ 54 #为了实现在每一级都能退出 将True换掉 55 exit_tag = False 56 57 while not exit_tag: 58 for i1 in data: 59 print(i1) 60 choice =input("选择进入1>>:") 61 if choice in data: 62 while not exit_tag: 63 for i2 in data[choice]: 64 print("\t\t",i2) 65 choice2 =input("选择进入2>>:") 66 if choice2 in data[choice]: 67 while not exit_tag: 68 for i3 in data[choice][choice2]: 69 print("\t\t\t\t",i3) 70 choice3 =input("选择进入3>>:") 71 if choice3 in data[choice][choice2]: 72 for i4 in data[choice][choice2][choice3]: 73 print("\t\t\t\t\t\t",i4) 74 choice4 =input("最后一层,按b返回>>:") 75 if choice4 ==‘b‘: 76 pass 77 elif choice4 ==‘q‘: 78 exit_tag =True 79 if choice3 == ‘b‘: 80 break 81 elif choice3 == ‘q‘: 82 exit_tag = True 83 if choice2 == ‘b‘: 84 break 85 elif choice2 == ‘q‘: 86 exit_tag = True

1 #Author:ZhangKanghui 2 3 data ={ 4 ‘北京‘:{ 5 "朝阳":{ 6 "望京":["奔驰","陌陌"], 7 "国贸":["CICC","HP"], 8 "东直门":["Advent","飞信"], 9 }, 10 "昌平":{ 11 "沙河":["old boy","test"], 12 "天通苑":["链家地产","我爱我家"], 13 }, 14 "海淀": {}, 15 }, 16 ‘山东‘:{ 17 "德州":{}, 18 "青岛":{}, 19 "济南":{}, 20 }, 21 ‘广东‘:{ 22 "常熟":{}, 23 "东莞":{}, 24 "惠州":{}, 25 }, 26 } 27 28 while True: 29 for i1 in data: 30 print(i1) 31 choice =input("选择进入1>>:") 32 if choice in data: 33 while True: 34 for i2 in data[choice]: 35 print("\t\t",i2) 36 choice2 =input("选择进入2>>:") 37 if choice2 == ‘b‘: 38 break 39 if choice2 in data[choice]: 40 while True: 41 for i3 in data[choice][choice2]: 42 print("\t\t\t\t",i3) 43 choice3 =input("选择进入3>>:") 44 if choice3 == ‘b‘: 45 break 46 if i3 in data[choice][choice2]: 47 while True: 48 for i4 in data[choice][choice2][choice3]: 49 print("\t\t\t\t\t\t",i4) 50 choice4 =input("最后一层,按b返回>>:") 51 if choice4 ==‘b‘: 52 break
这是尾巴:
最后推荐一个链接:我要自学网,不让打广告只能植入图片了。点击进入学习可以给我加V币。
内容丰富免费
这是随笔~
标签:陌陌 lse day 上下 windows 北京 基础学习 需要 组合
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/zhangkanghui/p/9399136.html