标签:div 14. nbsp cat 创建 new 成功 util 检测
我想判断一个集合里面有没有"world"这个元素,如果有,我就添加一个"javaee"元素,
当时的做法是:
public class ListIteratorDemo1 { public static void main(String[] args) { // 创建List集合对象 List list = new ArrayList(); // 添加元素 list.add("hello"); list.add("world"); list.add("java"); // 迭代器遍历 Iterator it = list.iterator(); while (it.hasNext()) { String s = (String) it.next(); if ("world".equals(s)) { list.add("javaee"); } }
System.out.println("list:" + list); } }
但是报了错误Exception in thread "main" java.util.ConcurrentModificationException错误
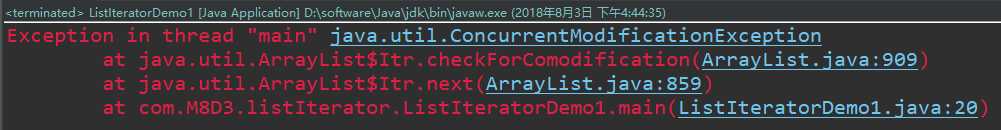
查阅API知道:
ConcurrentModificationException:当方法检测到对象的并发修改,但不允许这种修改时,抛出此异常。
产生此种的原因是:
迭代器是依赖于集合而存在的,在判断成功后,集合的中新添加了元素,而迭代器却不知道,所以就报错了,这个错叫并发修改异常。
其实这个问题简单的描述是:迭代器遍历元素的时候,通过集合是不能修改元素的。
如何解决呢?
A:迭代器迭代元素,迭代器修改元素
元素是跟在刚才迭代的元素后面的。
B:集合遍历元素,集合修改元素(普通for)
元素在最后添加的。
A的解决方案:
public class ListIteratorDemo1 { public static void main(String[] args) { // 创建List集合对象 List list = new ArrayList(); // 添加元素 list.add("hello"); list.add("world"); list.add("java"); // 方式1:迭代器迭代元素,迭代器修改元素 // 而Iterator迭代器却没有添加功能,所以我们使用其子接口ListIterator ListIterator lit = list.listIterator(); while (lit.hasNext()) { String s = (String) lit.next(); if ("world".equals(s)) { lit.add("javaee"); } } System.out.println("list:" + list); } }
执行结果:
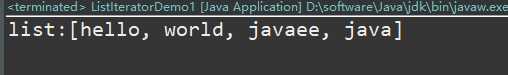
从结果看出:元素是跟在刚才迭代的元素后面的。
B的解决方案:
public class ListIteratorDemo1 { public static void main(String[] args) { // 创建List集合对象 List list = new ArrayList(); // 添加元素 list.add("hello"); list.add("world"); list.add("java"); // 方式2:集合遍历元素,集合修改元素(普通for) for (int x = 0; x < list.size(); x++) { String s = (String) list.get(x); if ("world".equals(s)) { list.add("javaee"); } } System.out.println("list:" + list); } }
执行结果:
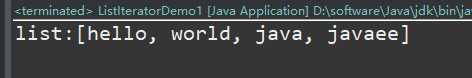
从结果看出:元素在最后添加的。
Exception in thread "main" java.util.ConcurrentModificationException解决方案
标签:div 14. nbsp cat 创建 new 成功 util 检测
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/whu-2017/p/9415126.html