标签:.com 演示 system his tac throws 代码 需要 唤醒
1. 这里我推荐下Java代码质量改进之:同步对象的选择这篇博文。
2. 以上推荐的博文是以卖火车票为例,引出了非同步会导致的错误以及同步锁(监视器)应该如果选择,应该能够帮助大家理解同步锁。
1. 这里我推荐下Java中synchronized同步锁用法及作用范围这篇博文。
2. 以上的博文将静态锁(字节码文件锁)和非静态锁(this)进行了对比,以及将线程非同步和线程同步下进行了对比,对大家了解线程锁的用法和作用范围有很大的帮助。
1. 这里我推荐下java中线程同步的理解(非常通俗易懂)这篇博文。
2. 以上推荐的博文以非常通俗易懂的观点解释了到时什么同步,将同步理解成了线程同步就是线程排队,而且举了一些日常生活中的例子来让大家理解到底什么是同伴。
1. 并不是说同步在什么情况下都是好的,因为线程的同步会带来较低效率,因为线程同步就代表着线程要排队,即线程同步锁会带来的同步阻塞状态。
2. 因为CPU是随意切换线程的,当我们想让当前线程执行之后CPU不随意切换到其他线程,或者我们想要让某个线程的代码能够在完全执行之前不会被抢夺执行权,不会导致从而无法连续执行,那么我们就需要线程的帮助。
1.sleep方法的基本用法
Thread.sleep(long millis),传入毫秒数(1秒 = 1000毫秒),在指定的毫秒数内让当前正在执行的线程休眠(暂停执行),此操作受到系统计时器和调度程序精度和准确性的影响。该线程不丢失任何监视器的所属权。
(~注:Java技术文档的意思就是让线程休眠指定的毫秒数,而且休眠状态暂时失去CPU执行权,而且线程醒来后,该线程不会释放锁,还有执行权。)
1 /** 2 * 3 * Thread.sleep的计时器用法 4 * 5 */ 6 public class ThreadSleepTest { 7 8 public static void main(String[] args) { 9 new Thread() { 10 @Override 11 public void run() { 12 int timeCount = 10; 13 while (timeCount >= 0) { 14 if (timeCount == 0) { 15 System.out.println("新年快乐!~"); 16 break; 17 } 18 System.out.println("还剩" + timeCount-- + "秒"); 19 try { 20 Thread.sleep(1000); 21 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 22 e.printStackTrace(); 23 } 24 } 25 } 26 }.start(); 27 } 28 29 }
2.sleep方法使用的位置选择
我在使用sleep方法时发现,当sleep的位置不一致所放的位置不同时,线程所运行的结果也是大不相同的,以下是代码是为了举例子,并不是说这个同步代码块就是应这样写(其实这段代码这么写是有很大的问题的,因为同步资源的选择不准确),至于同步资源的选择我在第二个大问题会讲到。
1 package javase.week4; 2 3 public class SellTrainTickets { 4 5 public static void main(String[] args) { 6 new MyThread("窗口1").start(); 7 new MyThread("窗口2").start(); 8 new MyThread("窗口3").start(); 9 new MyThread("窗口4").start(); 10 } 11 12 } 13 14 class MyThread extends Thread { 15 16 static int tickets = 100; 17 18 public MyThread(String name) { 19 super(name); 20 } 21 22 @Override 23 public void run() { 24 while (tickets > 0) {//假设这已经减到了1 1>0 然后窗口1 窗口2 窗口3 窗口4 都进入循环 25 try { 26 Thread.sleep(20); 27 28 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 29 e.printStackTrace(); 30 } 31 synchronized (MyThread.class) { 32 System.out.println(getName() + "卖出了第" + tickets-- + "张票!");//然后0 -1 -2 -3,这时就出现了负票 33 } 34 } 35 } 36 }

1 public class SellTrainTickets { 2 3 public static void main(String[] args) { 4 new MyThread("窗口1").start(); 5 new MyThread("窗口2").start(); 6 new MyThread("窗口3").start(); 7 new MyThread("窗口4").start(); 8 } 9 10 } 11 12 class MyThread extends Thread { 13 14 static int tickets = 100; 15 16 public MyThread(String name) { 17 super(name); 18 } 19 20 @Override 21 public void run() { 22 while (tickets > 0) {//假设这已经减到了0 5>0 然后窗口1 窗口2 窗口3 窗口4 都进入循环 23 synchronized (MyThread.class) { 24 System.out.println(getName() + "卖出了第" + tickets-- + "张票!");//然后 3 2 1 0 25 } 26 try { 27 Thread.sleep(20);//此时票数等于0,这时窗口1 窗口2 窗口3 窗口4 都处于休眠,然后如果这里的时间合理的话,再次判断的话,正好在等于0的时候,都没有线程再次进入循环,也就不会出现负票了 28 29 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 30 e.printStackTrace(); 31 } 32 } 33 } 34 }

3.sleep方法的传入参数的选择
sleep方法的传入的毫秒数对于线程的运行结果是有较大的影响的,最直接简单的影响就是让运行延迟了,但是除了这个以外其实也让线程的运行结果发生了变化,顺便分享一篇一篇高质量的博文Sleep(0)的妙用。
1 public class TicketsThreadTest { 2 3 public static void main(String[] args) { 4 new TicketThread("窗口1").start(); 5 new TicketThread("窗口2").start(); 6 new TicketThread("窗口3").start(); 7 new TicketThread("窗口4").start(); 8 } 9 10 } 11 12 class TicketThread extends Thread { 13 14 public TicketThread(String name) { 15 super(name); 16 } 17 18 private static int ticket = 100; 19 20 public void run() { 21 while (true) { 22 synchronized (TicketThread.class) { 23 if (ticket <= 0) { 24 break; 25 } 26 System.out.println(getName() + "卖出了第" + ticket-- + "张票!"); 27 try { 28 Thread.sleep(100); 29 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 30 e.printStackTrace(); 31 } 32 } 33 } 34 } 35 }
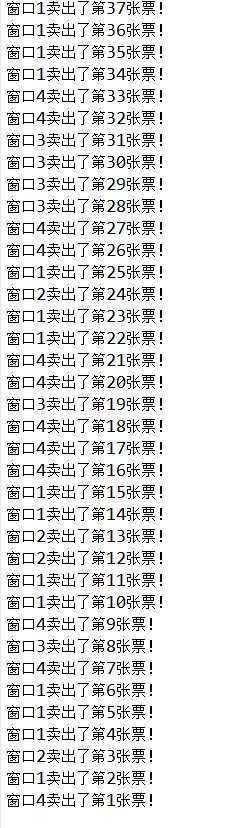
1 public class TicketsThreadTest { 2 3 public static void main(String[] args) { 4 new TicketThread("窗口1").start(); 5 new TicketThread("窗口2").start(); 6 new TicketThread("窗口3").start(); 7 new TicketThread("窗口4").start(); 8 } 9 10 } 11 12 class TicketThread extends Thread { 13 14 public TicketThread(String name) { 15 super(name); 16 } 17 18 private static int ticket = 100; 19 20 public void run() { 21 while (true) { 22 synchronized (TicketThread.class) { 23 if (ticket <= 0) { 24 break; 25 } 26 System.out.println(getName() + "卖出了第" + ticket-- + "张票!"); 27 try { 28 Thread.sleep(1); 29 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 30 e.printStackTrace(); 31 } 32 } 33 } 34 } 35 }

如果这里同步的是代码块不是代码方法,那么这里需要对要同步的共享资源的选择要准确,如果选择得不准确会导致结果不理想。
1 public class TicketsThreadTest { 2 3 public static void main(String[] args) { 4 new TicketThread("窗口1").start(); 5 new TicketThread("窗口2").start(); 6 new TicketThread("窗口3").start(); 7 new TicketThread("窗口4").start(); 8 } 9 10 } 11 12 class TicketThread extends Thread { 13 14 public TicketThread(String name) { 15 super(name); 16 } 17 18 private static int ticket = 100; 19 20 public void run() { 21 while (true) { 22 if (ticket <= 0) { 23 break; 24 } 25 synchronized (TicketThread.class) { 26 System.out.println(getName() + "卖出了第" + ticket-- + "张票!"); 27 } 28 try { 29 Thread.sleep(0); 30 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 31 e.printStackTrace(); 32 } 33 } 34 } 35 }

1 public class TicketsThreadTest { 2 3 public static void main(String[] args) { 4 new TicketThread("窗口1").start(); 5 new TicketThread("窗口2").start(); 6 new TicketThread("窗口3").start(); 7 new TicketThread("窗口4").start(); 8 } 9 10 } 11 12 class TicketThread extends Thread { 13 14 public TicketThread(String name) { 15 super(name); 16 } 17 18 private static int ticket = 100; 19 20 public void run() { 21 while (true) { 22 synchronized (TicketThread.class) { 23 if (ticket <= 0) { 24 break; 25 } 26 System.out.println(getName() + "卖出了第" + ticket-- + "张票!"); 27 try { 28 Thread.sleep(0); 29 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 30 e.printStackTrace(); 31 } 32 } 33 } 34 } 35 }

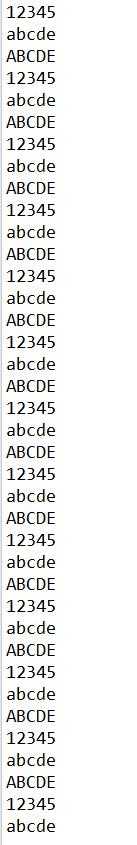
1 package javase.week4; 2 3 /** 4 * 5 * 三个线程之间的通信使用if选择语句 6 * 7 */ 8 public class ComunicatedThreadTest { 9 public static void main(String[] args) { 10 Printer1121 p = new Printer1121(); 11 new Thread() { 12 @Override 13 public void run() { 14 while (true) { 15 try { 16 p.print1(); 17 } catch (Exception e) { 18 e.printStackTrace(); 19 } 20 } 21 } 22 }.start(); 23 new Thread() { 24 @Override 25 public void run() { 26 while (true) { 27 try { 28 p.print2(); 29 } catch (Exception e) { 30 e.printStackTrace(); 31 } 32 } 33 } 34 }.start(); 35 36 new Thread() { 37 @Override 38 public void run() { 39 while (true) { 40 try { 41 p.print3(); 42 } catch (Exception e) { 43 e.printStackTrace(); 44 } 45 } 46 } 47 }.start(); 48 } 49 50 } 51 52 class Printer1121 { 53 private int flag = 1; 54 55 public void print1() throws Exception { 56 synchronized (this) { 57 if (flag != 1) { 58 this.wait(); 59 } 60 Thread.sleep(100); 61 System.out.print(1); 62 System.out.print(2); 63 System.out.print(3); 64 System.out.print(4); 65 System.out.print(5); 66 System.out.println(); 67 flag = 2; 68 this.notifyAll(); 69 } 70 } 71 72 public void print2() throws Exception { 73 synchronized (this) { 74 if (flag != 2) { 75 this.wait(); 76 } 77 Thread.sleep(100); 78 System.out.print("a"); 79 System.out.print("b"); 80 System.out.print("c"); 81 System.out.print("d"); 82 System.out.print("e"); 83 System.out.println(); 84 flag = 3; 85 this.notifyAll(); 86 } 87 } 88 89 public void print3() throws Exception { 90 synchronized (this) { 91 if (flag != 3) { 92 this.wait(); 93 } 94 Thread.sleep(100); 95 System.out.print("A"); 96 System.out.print("B"); 97 System.out.print("C"); 98 System.out.print("D"); 99 System.out.print("E"); 100 System.out.println(); 101 flag = 1; 102 this.notifyAll(); 103 } 104 } 105 }
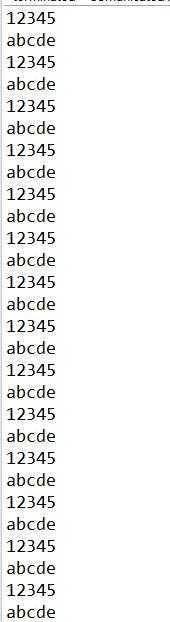
1 package javase.week4; 2 /** 3 * 4 * 三个线程之间的通信使用while循环判断语句 5 * 6 */ 7 public class ComunicatedThreadTest { 8 public static void main(String[] args) { 9 Printer1121 p = new Printer1121(); 10 new Thread() { 11 @Override 12 public void run() { 13 while (true) { 14 try { 15 p.print1(); 16 } catch (Exception e) { 17 e.printStackTrace(); 18 } 19 } 20 } 21 }.start(); 22 new Thread() { 23 @Override 24 public void run() { 25 while (true) { 26 try { 27 p.print2(); 28 } catch (Exception e) { 29 e.printStackTrace(); 30 } 31 } 32 } 33 }.start(); 34 35 new Thread() { 36 @Override 37 public void run() { 38 while (true) { 39 try { 40 p.print3(); 41 } catch (Exception e) { 42 e.printStackTrace(); 43 } 44 } 45 } 46 }.start(); 47 } 48 49 } 50 51 class Printer1121 { 52 private int flag = 1; 53 54 public void print1() throws Exception { 55 synchronized (this) { 56 while (flag != 1) { 57 this.wait(); 58 } 59 Thread.sleep(100); 60 System.out.print(1); 61 System.out.print(2); 62 System.out.print(3); 63 System.out.print(4); 64 System.out.print(5); 65 System.out.println(); 66 flag = 2; 67 this.notifyAll(); 68 } 69 } 70 71 public void print2() throws Exception { 72 synchronized (this) { 73 while (flag != 2) { 74 this.wait(); 75 } 76 Thread.sleep(100); 77 System.out.print("a"); 78 System.out.print("b"); 79 System.out.print("c"); 80 System.out.print("d"); 81 System.out.print("e"); 82 System.out.println(); 83 flag = 3; 84 this.notifyAll(); 85 } 86 } 87 88 public void print3() throws Exception { 89 synchronized (this) { 90 while (flag != 3) { 91 this.wait(); 92 } 93 Thread.sleep(100); 94 System.out.print("A"); 95 System.out.print("B"); 96 System.out.print("C"); 97 System.out.print("D"); 98 System.out.print("E"); 99 System.out.println(); 100 flag = 1; 101 this.notifyAll(); 102 } 103 } 104 }
关于Java多线程的线程同步和线程通信的一些小问题(顺便分享几篇质量高的博文)
标签:.com 演示 system his tac throws 代码 需要 唤醒
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/JNovice/p/9425361.html