标签:and nap hash 4.0 free spring trade any ppc
承接前文springboot情操陶冶-@Configuration注解解析,近期笔者接触的项目中有使用到了jmx的协议框架,遂在前文的基础上讲解下springboot中是如何整合jmx的
JMX:Java Management Extension(Java管理应用扩展),这种机制可以方便的管理、监控正在运行的Java程序。常用于监控管理线程、内存、日志Level、服务重启、系统环境等等。
更多的知识点参考此篇文献:https://blog.csdn.net/u013256816/article/details/52800742。笔者此处引用其中的框架图方便理解
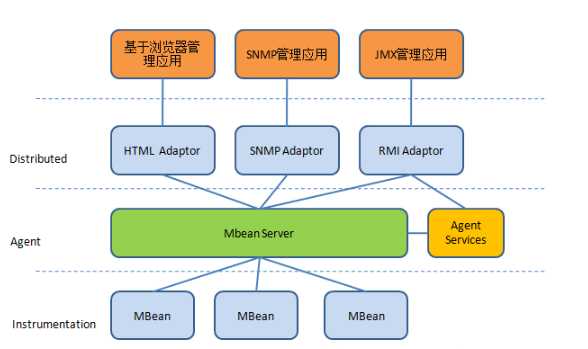
springboot通过在META-INF\spring.factories文件指定EnableAutoConfiguration属性值为JmxAutoConfiguration,便基本搭建了jmx的框架模子。听起来挺神奇的,笔者这就分析源码来一窥究竟
首先看下JmxAutoConfiguration头上的注解
@Configuration
@ConditionalOnClass({ MBeanExporter.class })
@ConditionalOnProperty(prefix = "spring.jmx", name = "enabled", havingValue = "true", matchIfMissing = true)
public class JmxAutoConfiguration implements EnvironmentAware, BeanFactoryAware {
}由上可知,要想使jmx环境生效,前提为
classpath环境得存在org.springframework.jmx.export.MBeanExporter类
环境变量spring.jmx.enabled设置为true,默认为true
一般引入springboot上述条件均是满足的,只是用户可通过spring.jmx.enabled属性来开关启jmx环境
其下有三个方法,分别被@Bean和@Conditional注解所修饰。笔者依次来进行解读
JmxAutoConfiguration#objectNamingStrategy()-获取ObjectName的生成策略
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(value = ObjectNamingStrategy.class, search = SearchStrategy.CURRENT)
public ParentAwareNamingStrategy objectNamingStrategy() {
// create namingStrategy
ParentAwareNamingStrategy namingStrategy = new ParentAwareNamingStrategy(
new AnnotationJmxAttributeSource());
// have a try to read environment property 'spring.jmx.default-domain'
String defaultDomain = this.environment.getProperty("spring.jmx.default-domain");
if (StringUtils.hasLength(defaultDomain)) {
namingStrategy.setDefaultDomain(defaultDomain);
}
return namingStrategy;
}上述代码也很简单,其中环境变量spring.jmx.default-domain代表jmx默认的域挂载。
JmxAutoConfiguration#mbeanServer()-创建MBeanServer
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
public MBeanServer mbeanServer() {
// 1.first to search classpath exsit 'weblogic.management.Helper'/'com.ibm.websphere.management.AdminServiceFactory' class if or not
SpecificPlatform platform = SpecificPlatform.get();
if (platform != null) {
return platform.getMBeanServer();
}
// 2.via MBeanServerFactoryBean to create MBeanServer
MBeanServerFactoryBean factory = new MBeanServerFactoryBean();
factory.setLocateExistingServerIfPossible(true);
factory.afterPropertiesSet();
return factory.getObject();
}笔者此处只关注MBeanServerFactoryBean是如何创建mbeanserver的,直接去看下其实现的afterPropertiesSet()方法
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() throws MBeanServerNotFoundException {
// 1.尝试去找寻已存在的mbeanserver
if (this.locateExistingServerIfPossible || this.agentId != null) {
try {
this.server = locateMBeanServer(this.agentId);
}
catch (MBeanServerNotFoundException ex) {
if (this.agentId != null) {
throw ex;
}
logger.info("No existing MBeanServer found - creating new one");
}
}
// 2.如果上述不存在mbeanserver,则调用jmx api生成mbeanserver
if (this.server == null) {
this.server = createMBeanServer(this.defaultDomain, this.registerWithFactory);
this.newlyRegistered = this.registerWithFactory;
}
}主要调用jmx api的MBeanServerFactory.createMBeanServer()方法创建mbeanserver,具体的创建过程笔者就不深究了,感兴趣的读者可自行分析
JmxAutoConfiguration#mbeanExporter()-创建mbeanExporter
源码如下
@Bean
@Primary
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(value = MBeanExporter.class, search = SearchStrategy.CURRENT)
public AnnotationMBeanExporter mbeanExporter(ObjectNamingStrategy namingStrategy) {
// 1.创建注解类型的AnnotationMBeanExporter,表明采取注解方式加载mbean
AnnotationMBeanExporter exporter = new AnnotationMBeanExporter();
exporter.setRegistrationPolicy(RegistrationPolicy.FAIL_ON_EXISTING);
// 2.set above namingStrategy
exporter.setNamingStrategy(namingStrategy);
// 3.set mbeanserver via spring applicationContext
String serverBean = this.environment.getProperty("spring.jmx.server",
"mbeanServer");
if (StringUtils.hasLength(serverBean)) {
exporter.setServer(this.beanFactory.getBean(serverBean, MBeanServer.class));
}
return exporter;
}创建AnnotationMBeanExporter类来读取注解方式的mbean,并优先从spring上下文读取mbeanserver。
通过上述的分析可得,笔者发现最终暴露给外界调用jmx协议是通过AnnotationMBeanExporter来完成的,其里面也蕴含了解析mbean相关注解的玄机
其实现的常用接口有InitializingBean/SmartInitializingSingleton/DisposableBean以及MBeanExportOperations
public AnnotationMBeanExporter() {
setNamingStrategy(this.metadataNamingStrategy);
setAssembler(this.metadataAssembler);
setAutodetectMode(AUTODETECT_ALL);
}主要是设置基础的属性
InitializingBean接口实现类如下
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() {
// have a try to find exsiting mbeanserver
if (this.server == null) {
this.server = JmxUtils.locateMBeanServer();
}
}SmartInitializingSingleton接口实现类如下
@Override
public void afterSingletonsInstantiated() {
try {
logger.info("Registering beans for JMX exposure on startup");
registerBeans();
registerNotificationListeners();
}
catch (RuntimeException ex) {
// Unregister beans already registered by this exporter.
unregisterNotificationListeners();
unregisterBeans();
throw ex;
}
}此处的registerBeans()方法便是mbeanserver去注册mbean的过程,可以继续跟踪下
protected void registerBeans() {
// The beans property may be null, for example if we are relying solely on autodetection.
if (this.beans == null) {
this.beans = new HashMap<>();
// Use AUTODETECT_ALL as default in no beans specified explicitly.
if (this.autodetectMode == null) {
this.autodetectMode = AUTODETECT_ALL;
}
}
// Perform autodetection, if desired.
int mode = (this.autodetectMode != null ? this.autodetectMode : AUTODETECT_NONE);
if (mode != AUTODETECT_NONE) {
if (this.beanFactory == null) {
throw new MBeanExportException("Cannot autodetect MBeans if not running in a BeanFactory");
}
if (mode == AUTODETECT_MBEAN || mode == AUTODETECT_ALL) {
// Autodetect any beans that are already MBeans.
logger.debug("Autodetecting user-defined JMX MBeans");
autodetect(this.beans, (beanClass, beanName) -> isMBean(beanClass));
}
// Allow the assembler a chance to vote for bean inclusion.
if ((mode == AUTODETECT_ASSEMBLER || mode == AUTODETECT_ALL) &&
this.assembler instanceof AutodetectCapableMBeanInfoAssembler) {
autodetect(this.beans, ((AutodetectCapableMBeanInfoAssembler) this.assembler)::includeBean);
}
}
// mbeanserver register mbeans
if (!this.beans.isEmpty()) {
this.beans.forEach((beanName, instance) -> registerBeanNameOrInstance(instance, beanName));
}
}避免代码过长带来的视觉疲劳,笔者此处对关键方法作下总结
@MBean注解的类*MBean接口的实现类@ManagedResource注解的类@ManagedResource注解的属性objectName生成ObjectName对象@ManagedResource注解的,则生成ModelBean对象并读取@ManagedOperation、@ManagedAttribute等jmx注解通过上述的操作便可以将搜索到的mbean注册至mbeanserver上了,只要用户使用@ManagedOperation、@ManagedAttribute、@ManagedResource注解搭配即可
pom内容
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>com.example</groupId>
<artifactId>demo</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<packaging>jar</packaging>
<name>demo-springboot</name>
<description>Demo project for Spring Boot</description>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.0.3.RELEASE</version>
<relativePath/> <!-- lookup parent from repository -->
</parent>
<properties>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
<project.reporting.outputEncoding>UTF-8</project.reporting.outputEncoding>
<java.version>1.8</java.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>mbean创建
package com.hundsun.quote.server.monitor;
...
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
/**
* common monitor MBean for system and application
*
* @author nanco
* @create 2018/8/6
**/
@Configuration
@ManagedResource(value = "monitor:name=SystemCommonMonitor")
public class SysCommonMonitorMBean implements InitializingBean {
private static AbstractMonitorService commonMonitorService;
private Gson gson = new Gson();
@Autowired
private ApplicationContext springApplicationContext;
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {
Assert.notNull(springApplicationContext, "spring applicationContext is not autowired");
commonMonitorService = springApplicationContext.getAutowireCapableBeanFactory().createBean(CommonMonitorService.class);
}
@ManagedAttribute
public String getSystemCommonInfo() {
Map<String, String> systemMap = new HashMap<>(8);
systemMap.put("sysCpuRatio", commonMonitorService.getSysCpuRatio());
systemMap.put("sysCurrentTime", commonMonitorService.getSysCurrentTime());
systemMap.put("sysStartupTime", commonMonitorService.getSysStartupTime());
systemMap.put("sysMemoryRatio", commonMonitorService.getSysMemoryRatio());
systemMap.put("sysDiskTotal", commonMonitorService.getSysDiskTotal());
systemMap.put("sysDiskFree", commonMonitorService.getSysDiskFree());
return gson.toJson(systemMap);
}
@ManagedAttribute
public String getAppCommonInfo() {
Map<String, String> applicationMap = new HashMap<>(4);
applicationMap.put("appCpuRatio", commonMonitorService.getAppCpuRatio());
applicationMap.put("appMemoryRatio", commonMonitorService.getAppMemoryRatio());
applicationMap.put("appStartupTime", commonMonitorService.getAppStartupTime());
return gson.toJson(applicationMap);
}
}package com.jing.quote.server.monitor;
....
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.jmx.export.annotation.ManagedOperation;
import org.springframework.jmx.export.annotation.ManagedOperationParameter;
import org.springframework.jmx.export.annotation.ManagedOperationParameters;
import org.springframework.jmx.export.annotation.ManagedResource;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
import java.util.List;
/**
* trade date Mbean
*
* @author nanco
* @create 2018/8/6
**/
@Configuration
@ManagedResource(value = "monitor:name=TradeDateMonitor")
public class TradeDateMonitorMBean {
private static final String OK_RESP = "Execute Success!";
private static final String FAIL_RESP = "Execute Fail!";
private Gson gson = new Gson();
@Resource
private DsTradeDateService tradeDateService;
@Resource
private DsBaseService baseService;
@ManagedOperation(description = "select_all_trade_date_excl")
public String selectAllTradeDateExcl() {
List<TradeDateExcl> tradeDateExcls = tradeDateService.selectAllTradeDateExcl();
return gson.toJson(tradeDateExcls);
}
@ManagedOperation(description = "insert_trade_date_excl")
@ManagedOperationParameters(value = {
@ManagedOperationParameter(name = "financeMic", description = "financeMic"),
@ManagedOperationParameter(name = "exclDate", description = "exclDate"),
@ManagedOperationParameter(name = "dayOfWeek", description = "dayOfWeek"),
@ManagedOperationParameter(name = "exclDesc", description = "exclDesc")
})
public String insertTradeDateExcl(String financeMic, int exclDate, int dayOfWeek, String exclDesc) {
TradeDateExcl tradeDateExcl = new TradeDateExcl();
tradeDateExcl.setFinanceMic(financeMic);
tradeDateExcl.setExclDesc(exclDesc);
tradeDateExcl.setExclDate(exclDate);
tradeDateExcl.setDayOfWeek(dayOfWeek);
boolean executeFlag = tradeDateService.insertTradeDateExcl(tradeDateExcl);
if (executeFlag) {
return TradeDateMonitorMBean.OK_RESP;
} else {
return TradeDateMonitorMBean.FAIL_RESP;
}
}
@ManagedOperation(description = "delete_trade_date_excl")
@ManagedOperationParameters(value = {
@ManagedOperationParameter(name = "financeMic", description = "financeMic"),
@ManagedOperationParameter(name = "exclDate", description = "exclDate")
})
public String deleteTradeDateExcl(String financeMic, int exclDate) {
TradeDateExclKey exclKey = new TradeDateExclKey();
exclKey.setExclDate(exclDate);
exclKey.setFinanceMic(financeMic);
boolean executeFlag = tradeDateService.deleteTradeDateExcl(exclKey);
if (executeFlag) {
return TradeDateMonitorMBean.OK_RESP;
} else {
return TradeDateMonitorMBean.FAIL_RESP;
}
}
}
jmx serviceUrl暴露
package com.jing.quote.server.config;
import org.apache.commons.logging.Log;
import org.apache.commons.logging.LogFactory;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.DependsOn;
import org.springframework.jmx.support.ConnectorServerFactoryBean;
import org.springframework.remoting.rmi.RmiRegistryFactoryBean;
@Configuration
public class JmxAutoConfiguration {
private static final Log LOGGER = LogFactory.getLog(JmxAutoConfiguration.class);
@Value("${jmx.rmi.host:localhost}")
private String rmiHost;
@Value("${jmx.rmi.port:9888}")
private Integer rmiPort;
@Bean
public RmiRegistryFactoryBean rmiRegistry() {
// 指定端口可以开放创建名字服务
final RmiRegistryFactoryBean rmiRegistryFactoryBean = new RmiRegistryFactoryBean();
rmiRegistryFactoryBean.setPort(rmiPort);
rmiRegistryFactoryBean.setAlwaysCreate(true);
LOGGER.info("RmiRegistryFactoryBean create success !!");
return rmiRegistryFactoryBean;
}
@Bean
@DependsOn("rmiRegistry")
public ConnectorServerFactoryBean connectorServerFactoryBean() throws Exception {
final ConnectorServerFactoryBean connectorServerFactoryBean = new ConnectorServerFactoryBean();
connectorServerFactoryBean.setObjectName("connector:name=rmi");
connectorServerFactoryBean.setServiceUrl(
String.format("service:jmx:rmi://%s:%s/jndi/rmi://%s:%s/jmxrmi", rmiHost, rmiPort, rmiHost, rmiPort));
LOGGER.info("ConnectorServerFactoryBean create success !!");
return connectorServerFactoryBean;
}
}jconsole访问,直接远程连接至service:jmx:rmi://localhost:9888/jndi/rmi://localhost:9888/jmxrmi即可(默认)
读者在阅读本博文的时候,建议首先按照笔者上述给出的文献链接查阅jmx相关知识点,再结合此文便会对springboot整合jmx框架有一定的了解
标签:and nap hash 4.0 free spring trade any ppc
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/question-sky/p/9437050.html