标签:filter 回调 手写 tor pre string sel data none
k-近邻(kNN, k-NearestNeighbor)算法是一种基本分类与回归方法,
通俗点来说,就是给定一个训练数据集,对新的输入实例,在训练数据集中找到与该实例最邻近的 k 个实例,这 k 个实例的多数属于某个类,就把该输入实例分为这个类。
python 第三方库scikit-learn(sklearn)提供了knn的分类器。
MNIST手写数字数据库(Mixed National Institute of Standards and Technology database)包含
70000张手写数字图片。这些数字是通过美国国家统计局的员工和美国高校的学生收集的。每张图片
都是28x28的灰度图。
用mnist数据集训练出一个knn分类器,对新输入的手写数字进行识别。
1.安装必要的第三方库:
pip install scikit-learn
pip install numpy
pip install wxPython
安装PIL,在以下地址下载PIL库进行安装:
http://effbot.org/media/downloads/PIL-1.1.7.win32-py2.7.exe
(或在http://effbot.org/downloads/ 中找到与你操作系统及python版本相对应
版本的PIL)
2.下载mnist数据集:
可以从以下地址下载mnist数据集。
http://yann.lecun.com/exdb/mnist/
如下:
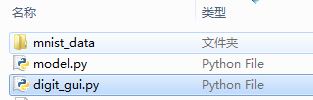
整体的项目结构十分简单,一共两个脚本文件,一个是GUI界面脚本(digit_gui.py),
一个是分类器脚本(model.py)。
如下:
1. 在model.py中导入相关的库:
import numpy as np import os from PIL import Image import random from sklearn.neighbors import KNeighborsClassifier as knn from sklearn.externals import joblib
2. 编写model.py中的相关函数,
将图片转为向量:
def img2vec(fname):
‘‘‘将jpg等格式的图片转为向量‘‘‘
im = Image.open(fname).convert(‘L‘)
im = im.resize((28,28))
tmp = np.array(im)
vec = tmp.ravel()
return vec
随机抽取1000张图片作为训练集:
def split_data(paths):
‘‘‘随机抽取1000张图片作为训练集‘‘‘
fn_list = os.llistdir(paths)
X = []
y = []
d0 = random.sample(fn_list,1000)
for i,name in enumerate(d0):
y.append(name[0])
X.append(img2vec(name))
dataset = np.array([X,y])
return X,y
构建分类器:
def knn_clf(X_train,label):
‘‘‘构建分类器‘‘‘
clf = knn()
clf.fit(X_train,label)
return clf
保存模型:
def save_model(model,output_name):
‘‘‘保存模型‘‘‘
joblib.dump(model,ouotput_name)
3. 训练模型:
X_train,y_label = split_data(file_path) clf = knn_clf(X_train,y_label) save_model(clf,‘mnist_knn1000.m‘)
4. 在digit_gui.py中编写用户界面:
导入相关的库:
import wx from collections import namedtuple from PIL import Image import os import model
编写界面:
class MainWindow(wx.Frame):
def __init__(self,parent,title):
wx.Frame.__init__(self,parent,title=title,size=(600,-1))
static_font = wx.Font(12, wx.SWISS, wx.NORMAL, wx.NORMAL)
Size = namedtuple("Size",[‘x‘,‘y‘])
s = Size(100,50)
sm = Size(100,25)
self.fileName = None
self.model = model
b_labels = [u‘open‘,u‘run‘]
TipString = [u‘选择图片‘, u‘识别数字‘]
funcs = [self.choose_file,self.run]
‘‘‘create input area‘‘‘
self.in1 = wx.TextCtrl(self,-1,size = (2*s.x,3*s.y))
self.out1 = wx.TextCtrl(self,-1,size = (s.x,3*s.y))
‘‘‘create button‘‘‘
self.sizer0 = wx.FlexGridSizer(rows=1, hgap=4, vgap=2)
self.sizer0.Add(self.in1)
buttons = []
for i,label in enumerate(b_labels):
b = wx.Button(self, id = i,label = label,size = (1.5*s.x,s.y))
buttons.append(b)
self.sizer0.Add(b)
self.sizer0.Add(self.out1)
‘‘‘set the color and size of labels and buttons‘‘‘
for i,button in enumerate(buttons):
button.SetForegroundColour(‘red‘)
button.SetFont(static_font)
button.SetToolTipString(TipString[i])
button.Bind(wx.EVT_BUTTON,funcs[i])
‘‘‘layout‘‘‘
self.SetSizer(self.sizer0)
self.SetAutoLayout(1)
self.sizer0.Fit(self)
self.CreateStatusBar()
self.Show(True)
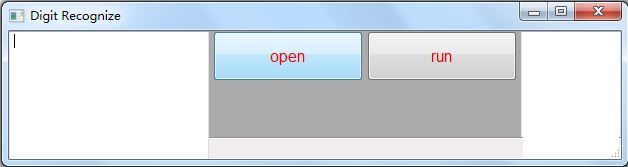
界面如下:
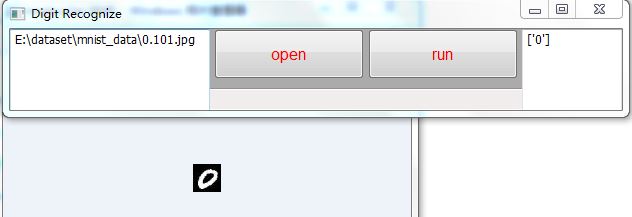
编写控件的回调函数:
def run(self,evt):
if self.fileName is None:
self.raise_msg(u‘请选择一幅图片‘)
return None
else:
model_path = os.path.join(origin_path,‘mnist_knn1000.m‘)
clf = model.load_model(model_path)
ans = model.tester(self.fileName,clf)
self.out1.Clear()
self.out1.write(str(ans))
def choose_file(self,evt):
‘‘‘choose img‘‘‘
dlg = wx.FileDialog(
self, message="Choose a file",
defaultDir=os.getcwd(),
defaultFile="",
wildcard=wildcard,
style=wx.OPEN | wx.MULTIPLE | wx.CHANGE_DIR
)
if dlg.ShowModal() == wx.ID_OK:
paths = dlg.GetPaths()
dlg.Destroy()
self.in1.Clear()
self.in1.write(paths[0])
self.fileName = paths[0]
im = Image.open(self.fileName)
im.show()
else:
return None
标签:filter 回调 手写 tor pre string sel data none
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/demodashi/p/9452947.html