标签:extension text asc body rect append 静态资源 one nbsp
本文基于.net core 的控制台程序作为服务端
main函数:
1 class Program 2 { 3 static void Main(string[] args) 4 { 5 Console.WriteLine("The server is starting......"); 6 7 new Server().StartServer(); 8 9 Console.ReadLine(); 10 } 11 }
其中核心代码在Server这个类上面:
1 public class Server 2 { 3 private Socket socketWatch = null; 4 private Thread threadWatch = null; 5 private string ipAddress = "127.0.0.1"; 6 private string port = "11111"; 7 8 public Server() 9 { 10 socketWatch = new Socket(AddressFamily.InterNetwork, SocketType.Stream, ProtocolType.Tcp); 11 socketWatch.Bind(new IPEndPoint(IPAddress.Parse(ipAddress), int.Parse(port))); 12 socketWatch.Listen(100); 13 // 创建Thread->后台执行 14 threadWatch = new Thread(ListenClientConnect); 15 threadWatch.IsBackground = true; 16 } 17 18 public void StartServer() 19 { 20 threadWatch.Start(socketWatch); 21 } 22 23 private void ListenClientConnect(object objSocket) 24 { 25 Socket socketListen = objSocket as Socket; 26 27 while (true) 28 { 29 Socket proxSocket = socketListen.Accept(); 30 byte[] data = new byte[1024 * 1024 * 2]; 31 int length = proxSocket.Receive(data, 0, data.Length, SocketFlags.None); 32 // Step1:接收HTTP请求 33 string requestText = Encoding.Default.GetString(data, 0, length); 34 HttpContext context = new HttpContext(requestText); 35 // Step2:处理HTTP请求 36 HttpApplication application = new HttpApplication(); 37 application.ProcessRequest(context); 38 // Step3:响应HTTP请求 39 Console.WriteLine(string.Format("{0} {1} from {2}", context.Request.HttpMethod, context.Request.Url, proxSocket.RemoteEndPoint.ToString())); 40 proxSocket.Send(context.Response.GetResponseHeader()); 41 proxSocket.Send(context.Response.Body); 42 // Step4:即时关闭Socket连接 43 proxSocket.Shutdown(SocketShutdown.Both); 44 proxSocket.Close(); 45 } 46 } 47 }
上面代码中,主要是基于Socket和线程。在构造函数中初始化了服务器端Socket,还初始化了Thread,并且设置为后台线程。ListenClientConnect函数主要做的事情是接受浏览器请求,并且转化为HttpContext和HttpApplication,最后输出响应并且关闭socket。
这里面有几个比较重要的类,主要如下:
1 public class HttpContext 2 { 3 public HttpRequest Request { get; set; } 4 public HttpResponse Response { get; set; } 5 6 public HttpContext(string requestText) 7 { 8 Request = new HttpRequest(requestText); 9 Response = new HttpResponse(); 10 } 11 }
HttpContext模拟asp的HttpContext,里面有两个看起来很熟悉的类,HttpRequest和HttpResponse
1 public class HttpRequest 2 { 3 public HttpRequest(string requestText) 4 { 5 string[] lines = requestText.Replace("\r\n", "\r").Split(‘\r‘); 6 string[] requestLines = lines[0].Split(‘ ‘); 7 // 获取HTTP请求方式、请求的URL地址、HTTP协议版本 8 if(requestLines.Length >= 2) 9 { 10 HttpMethod = requestLines[0]; 11 Url = requestLines[1]; 12 HttpVersion = requestLines[2]; 13 } 14 } 15 // 请求方式:GET or POST? 16 public string HttpMethod { get; set; } 17 // 请求URL 18 public string Url { get; set; } 19 // Http协议版本 20 public string HttpVersion { get; set; } 21 // 请求头 22 public Dictionary<string, string> HeaderDictionary { get; set; } 23 // 请求体 24 public Dictionary<string, string> BodyDictionary { get; set; } 25 }
1 public class HttpResponse 2 { 3 // 响应状态码 4 public string StateCode { get; set; } 5 // 响应状态描述 6 public string StateDescription { get; set; } 7 // 响应内容类型 8 public string ContentType { get; set; } 9 //响应报文的正文内容 10 public byte[] Body { get; set; } 11 12 // 生成响应头信息 13 public byte[] GetResponseHeader() 14 { 15 string strRequestHeader = string.Format(@"HTTP/1.1 {0} {1} 16 Content-Type: {2} 17 Accept-Ranges: bytes 18 Server: Microsoft-IIS/7.5 19 X-Powered-By: ASP.NET 20 Date: {3} 21 Content-Length: {4} 22 23 ", StateCode, StateDescription, ContentType, string.Format("{0:R}", DateTime.Now), Body.Length); 24 25 return Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes(strRequestHeader); 26 } 27 }
这两个核心类是关于请求和响应的。
IHttpHandler是另外一个很熟悉的接口,一般处理程序中都会实例化它
1 public interface IHttpHandler 2 { 3 void ProcessRequest(HttpContext context); 4 }
我们处理请求的时候就是依靠实例化这个接口了,在我们的实例上面就是HttpApplication
1 public class HttpApplication : IHttpHandler 2 { 3 // 对请求上下文进行处理 4 public void ProcessRequest(HttpContext context) 5 { 6 // 1.获取网站根路径 7 if(string.IsNullOrEmpty(context.Request.Url)) 8 { 9 return; 10 } 11 string bastPath = AppDomain.CurrentDomain.BaseDirectory; 12 string fileName = Path.Combine(bastPath, "LZZWebSite", context.Request.Url.TrimStart(‘/‘)); 13 string fileExtension = Path.GetExtension(context.Request.Url); 14 // 2.处理动态文件请求 15 if (fileExtension.Equals(".aspx") || fileExtension.Equals(".ashx")) 16 { 17 string className = Path.GetFileNameWithoutExtension(context.Request.Url); 18 IHttpHandler handler = Assembly.GetExecutingAssembly().CreateInstance($"lzzWebServerDemo.Page.{className}", true) as IHttpHandler; 19 handler.ProcessRequest(context); 20 return; 21 } 22 // 3.处理静态文件请求 23 if (!File.Exists(fileName)) 24 { 25 context.Response.StateCode = "404"; 26 context.Response.StateDescription = "Not Found"; 27 context.Response.ContentType = "text/html"; 28 string notExistHtml = Path.Combine(bastPath, @"LZZWebSite\notfound.html"); 29 context.Response.Body = File.ReadAllBytes(notExistHtml); 30 } 31 else 32 { 33 context.Response.StateCode = "200"; 34 context.Response.StateDescription = "OK"; 35 context.Response.ContentType = GetContenType(Path.GetExtension(context.Request.Url)); 36 context.Response.Body = File.ReadAllBytes(fileName); 37 } 38 } 39 40 // 根据文件扩展名获取内容类型 41 public string GetContenType(string fileExtension) 42 { 43 string type = "text/html; charset=UTF-8"; 44 switch (fileExtension) 45 { 46 case ".aspx": 47 case ".html": 48 case ".htm": 49 type = "text/html; charset=UTF-8"; 50 break; 51 case ".png": 52 type = "image/png"; 53 break; 54 case ".gif": 55 type = "image/gif"; 56 break; 57 case ".jpg": 58 case ".jpeg": 59 type = "image/jpeg"; 60 break; 61 case ".css": 62 type = "text/css"; 63 break; 64 case ".js": 65 type = "application/x-javascript"; 66 break; 67 default: 68 type = "text/plain; charset=gbk"; 69 break; 70 } 71 return type; 72 }
上面的业务比较清晰,如果是静态资源,就直接响应返回。如果是动态资源,例如aspx、ashx的话就通过反射实例化对应的处理类。我们例子上是这样模拟的:
1 public class LzzPage: IHttpHandler 2 { 3 public void ProcessRequest(HttpContext context) 4 { 5 StringBuilder sbText = new StringBuilder(); 6 sbText.Append("<html>"); 7 sbText.Append("<head></head>"); 8 sbText.Append("<body>"); 9 sbText.Append("<h1>demo</h1>"); 10 sbText.Append("lzzdemolzzdemo"); 11 sbText.Append(string.Format("<h3>time:{0}</h3>", DateTime.Now.ToString())); 12 sbText.Append("</body>"); 13 sbText.Append("</html>"); 14 context.Response.Body = Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes(sbText.ToString()); 15 context.Response.StateCode = "200"; 16 context.Response.ContentType = "text/html"; 17 context.Response.StateDescription = "OK"; 18 } 19 }
最后来一张整个体统的结构图
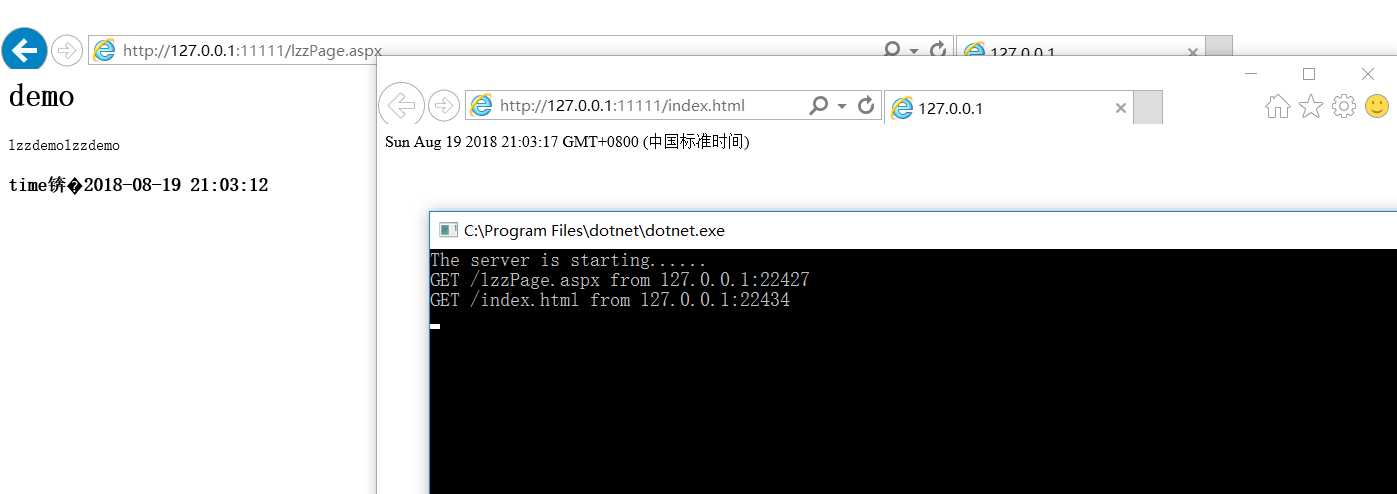
运行图:
标签:extension text asc body rect append 静态资源 one nbsp
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/lizhizhang/p/9502639.html