标签:lam 命名空间 one 数据 play 接下来 style 命名 序列
三、判断/循环语句,函数,命名空间,作用域
1、Python3 条件控制
Python中if语句的一般形式如下所示:
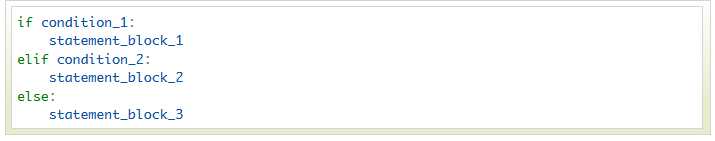
Python 中用 elif 代替了 else if,所以if语句的关键字为:if – elif – else。
注意:
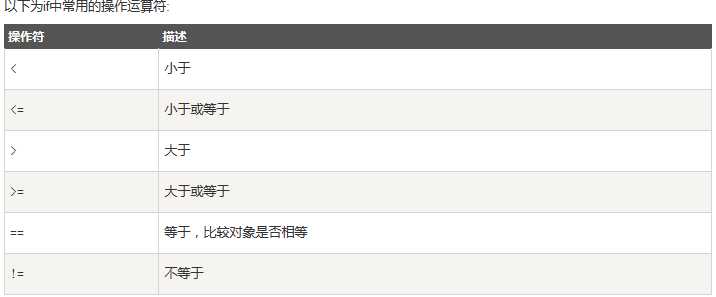
2、Python3 循环语句
Python中的循环语句有 for 和 while。
2.1、while 循环
Python中while语句的一般形式:同样需要注意冒号和缩进。另外,在Python中没有do..while循环。


1 #!/usr/bin/env python3 2 3 n = 100 4 5 sum = 0 6 counter = 1 7 while counter <= n: 8 sum = sum + counter 9 counter += 1 10 11 print("1 到 %d 之和为: %d" % (n,sum))
while 循环使用 else 语句:在 while … else 在条件语句为 false 时执行 else 的语句块:

1 #!/usr/bin/python3 2 3 count = 0 4 while count < 5: 5 print (count, " 小于 5") 6 count = count + 1 7 else: 8 print (count, " 大于或等于 5")
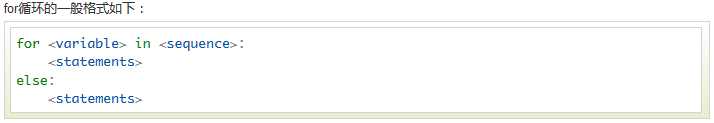
2.2、for 语句
Python for循环可以遍历任何序列的项目,如一个列表或者一个字符串。

1 #!/usr/bin/python3 2 3 sites = ["Baidu", "Google","Runoob","Taobao"] 4 for site in sites: 5 if site == "Runoob": 6 print("菜鸟教程!") 7 break 8 print("循环数据 " + site) 9 else: 10 print("没有循环数据!") 11 print("完成循环!")
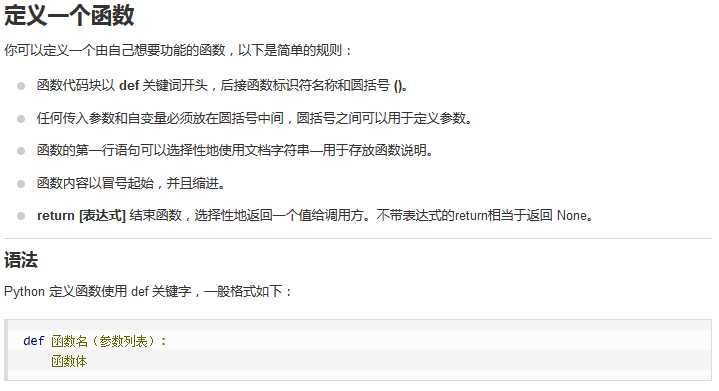
3、函数
函数是组织好的,可重复使用的,用来实现单一,或相关联功能的代码段。函数能提高应用的模块性,和代码的重复利用率。
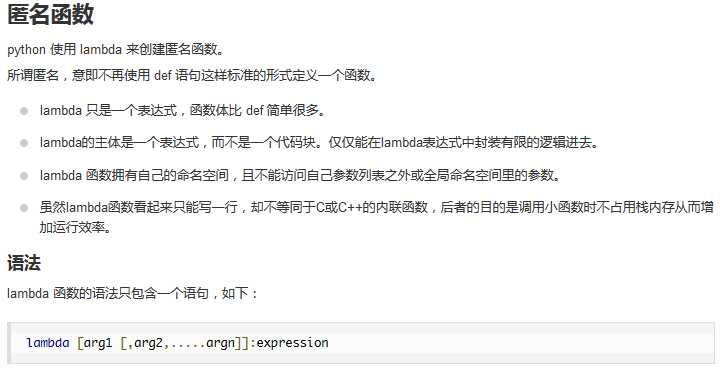

1 #!/usr/bin/python3 2 3 # 可写函数说明 4 sum = lambda arg1, arg2: arg1 + arg2 5 6 # 调用sum函数 7 print ("相加后的值为 : ", sum( 10, 20 )) 8 print ("相加后的值为 : ", sum( 20, 20 ))
4、变量作用域
Python 中,程序的变量并不是在哪个位置都可以访问的,访问权限决定于这个变量是在哪里赋值的。
变量的作用域决定了在哪一部分程序可以访问哪个特定的变量名称。Python的作用域一共有4种,分别是:

Python 中只有模块(module),类(class)以及函数(def、lambda)才会引入新的作用域,其它的代码块(如 if/elif/else/、try/except、for/while等)是不会引入新的作用域的,也就是说这些语句内定义的变量,外部也可以访问,如下代码:

定义在函数内部的变量拥有一个局部作用域,定义在函数外的拥有全局作用域。
4.1、global 和 nonlocal关键字
当内部作用域想修改外部作用域的变量时,就要用到global和nonlocal关键字了。
1 #!/usr/bin/python3 2 3 num = 1 4 def fun1(): 5 global num # 需要使用 global 关键字声明 6 print(num) 7 num = 123 8 print(num) 9 fun1() 10 print(num)
如果要修改嵌套作用域(enclosing 作用域,外层非全局作用域)中的变量则需要 nonlocal 关键字了,如下实例:
1 #!/usr/bin/python3 2 3 def outer(): 4 num = 10 5 def inner(): 6 nonlocal num # nonlocal关键字声明 7 num = 100 8 print(num) 9 inner() 10 print(num) 11 outer()
标签:lam 命名空间 one 数据 play 接下来 style 命名 序列
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/jays2018/p/9510993.html