标签:several lvm das 3.0 教程 发行版 mod move lse
本文转自:https://www.cnblogs.com/alex3714/articles/5465198.html
目前Python主要应用领域:
Python在一些公司的应用:
编译器是把源程序的每一条语句都编译成机器语言,并保存成二进制文件,这样运行时计算机可以直接以机器语言来运行此程序,速度很快;
而解释器则是只在执行程序时,才一条一条的解释成机器语言给计算机来执行,所以运行速度是不如编译后的程序运行的快的.
这是因为计算机不能直接认识并执行我们写的语句,它只能认识机器语言(是二进制的形式)
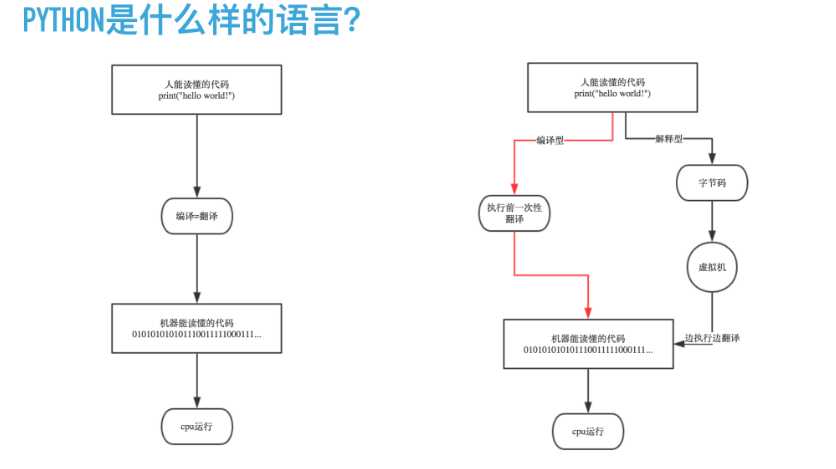
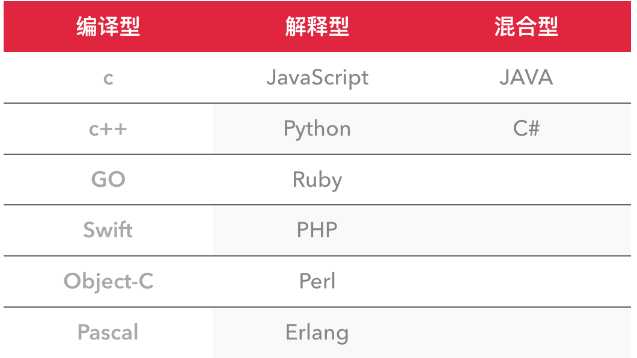
编译型
优点:编译器一般会有预编译的过程对代码进行优化。因为编译只做一次,运行时不需要编译,所以编译型语言的程序执行效率高。可以脱离语言环境独立运行。
缺点:编译之后如果需要修改就需要整个模块重新编译。编译的时候根据对应的运行环境生成机器码,不同的操作系统之间移植就会有问题,需要根据运行的操作系统环境编译不同的可执行文件。
解释型
优点:有良好的平台兼容性,在任何环境中都可以运行,前提是安装了解释器(虚拟机)。灵活,修改代码的时候直接修改就可以,可以快速部署,不用停机维护。
缺点:每次运行的时候都要解释一遍,性能上不如编译型语言。
先看优点
再看缺点:
当我们编写Python代码时,我们得到的是一个包含Python代码的以.py为扩展名的文本文件。要运行代码,就需要Python解释器去执行.py文件。
由于整个Python语言从规范到解释器都是开源的,所以理论上,只要水平够高,任何人都可以编写Python解释器来执行Python代码(当然难度很大)。事实上,确实存在多种Python解释器。
当我们从Python官方网站下载并安装好Python 2.7后,我们就直接获得了一个官方版本的解释器:CPython。这个解释器是用C语言开发的,所以叫CPython。在命令行下运行python就是启动CPython解释器。
CPython是使用最广的Python解释器。教程的所有代码也都在CPython下执行。
IPython是基于CPython之上的一个交互式解释器,也就是说,IPython只是在交互方式上有所增强,但是执行Python代码的功能和CPython是完全一样的。好比很多国产浏览器虽然外观不同,但内核其实都是调用了IE。
CPython用>>>作为提示符,而IPython用In [序号]:作为提示符。
PyPy是另一个Python解释器,它的目标是执行速度。PyPy采用JIT技术,对Python代码进行动态编译(注意不是解释),所以可以显著提高Python代码的执行速度。
绝大部分Python代码都可以在PyPy下运行,但是PyPy和CPython有一些是不同的,这就导致相同的Python代码在两种解释器下执行可能会有不同的结果。如果你的代码要放到PyPy下执行,就需要了解PyPy和CPython的不同点。
Jython是运行在Java平台上的Python解释器,可以直接把Python代码编译成Java字节码执行。
IronPython和Jython类似,只不过IronPython是运行在微软.Net平台上的Python解释器,可以直接把Python代码编译成.Net的字节码。
In summary : Python 2.x is legacy(遗产), Python 3.x is the present and future of the language
Python 3.0 was released in 2008. The final 2.x version 2.7 release came out in mid-2010, with a statement of
extended support for this end-of-life release. The 2.x branch will see no new major releases after that. 3.x is
under active development and has already seen over five years of stable releases, including version 3.3 in 2012,
3.4 in 2014, and 3.5 in 2015. This means that all recent standard library improvements, for example, are only
available by default in Python 3.x.
Guido van Rossum (the original creator of the Python language) decided to clean up Python 2.x properly, with less regard for backwards compatibility than is the case for new releases in the 2.x range. The most drastic improvement is the better Unicode support (py3支持各种字符编码)(with all text strings being Unicode by default) as well as saner bytes/Unicode separation.
Besides, several aspects of the core language (such as print and exec being statements, integers using floor division) have been adjusted to be easier for newcomers to learn and to be more consistent with the rest of the language, and old cruft has been removed (for example, all classes are now new-style, "range()" returns a memory efficient iterable, not a list as in 2.x).
PRINT IS A FUNCTION
The statement has been replaced with a print() function, with keyword arguments to replace most of the special syntax of the old statement (PEP 3105). Examples:
Old: print "The answer is", 2*2 New: print("The answer is", 2*2) Old: print x, # Trailing comma suppresses newline New: print(x, end=" ") # Appends a space instead of a newline Old: print # Prints a newline New: print() # You must call the function! Old: print >>sys.stderr, "fatal error" New: print("fatal error", file=sys.stderr) Old: print (x, y) # prints repr((x, y)) New: print((x, y)) # Not the same as print(x, y)!
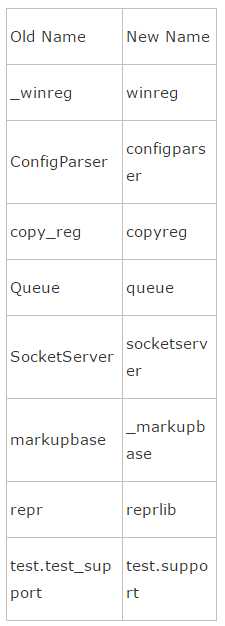
某些库改名了
1、下载安装包 https://www.python.org/downloads/ 2、安装 默认安装路径:C:\python27 3、配置环境变量 【右键计算机】--》【属性】--》【高级系统设置】--》【高级】--》【环境变量】--》【在第二个内容框中找到 变量名为Path 的一行,双击】 --> 【Python安装目录追加到变值值中,用 ; 分割】 如:原来的值;C:\python27,切记前面有分号
linux、Mac
无需安装,原装Python环境
ps:如果自带2.6,请更新至2.7
在linux 下创建一个文件叫hello.py,并输入
print("Hello World!")
然后执行命令:python hello.py ,输出
localhost:~ jieli$ vim hello.py localhost:~ jieli$ python hello.py Hello World!
指定解释器
上一步中执行 python hello.py 时,明确的指出 hello.py 脚本由 python 解释器来执行。
如果想要类似于执行shell脚本一样执行python脚本,例: ./hello.py ,那么就需要在 hello.py 文件的头部指定解释器,如下:
#!/usr/bin/env python #声明为可执行程序 还有种写法是 #!/usr/bin/python 这个和前面的有什么区别?注意,这个是原装python下解释器 ,env python是到环境变量下去寻找python解释器,因为你自己安装的python很可能不在bin下 print "hello,world"
如此一来,执行: ./hello.py 即可。
ps:执行前需给予 hello.py 执行权限,chmod 755 hello.py
在交互器中执行
除了把程序写在文件里,还可以直接调用python自带的交互器运行代码
1 localhost:~ jieli$ python 2 Python 2.7.10 (default, Oct 23 2015, 18:05:06) 3 [GCC 4.2.1 Compatible Apple LLVM 7.0.0 (clang-700.0.59.5)] on darwin 4 Type "help", "copyright", "credits" or "license" for more information. 5 >>> print("Hello World!") 6 Hello World!
对比下其它语言的hello world

1 1 #include <iostream> 2 2 int main(void) 3 3 { 4 4 std::cout<<"Hello world"; 5 5 }

1 #include <stdio.h> 2 int main(void) 3 { 4 printf("\nhello world!"); 5 return 0; 6 } 7 8 C

1 public class HelloWorld{ 2 // 程序的入口 3 public static void main(String args[]){ 4 // 向控制台输出信息 5 System.out.println("Hello World!"); 6 } 7 }

1 <?php 2 echo "hello world!"; 3 ?>
Variables are used to store information to be referenced and manipulated in a computer program. They also provide a way of labeling data with a descriptive name, so our programs can be understood more clearly by the reader and ourselves. It is helpful to think of variables as containers that hold information. Their sole purpose is to label and store data in memory. This data can then be used throughout your program.
声明变量
1 #_*_coding:utf-8_*_ 2 3 name = "Alex Li"
上述代码声明了一个变量,变量名为: name,变量name的值为:"Alex Li"
变量定义的规则:
变量的赋值
name = "Alex Li" name2 = name print(name,name2) name = "Jack" print("What is the value of name2 now?")
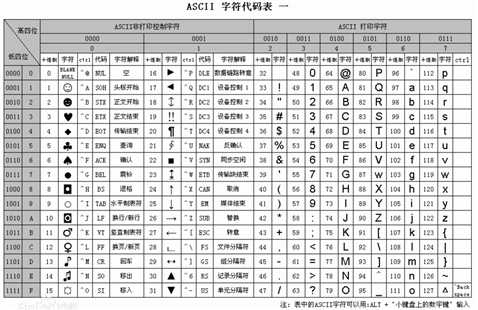
python解释器在加载 .py 文件中的代码时,会对内容进行编码(默认ascill)
ASCII(American Standard Code for Information Interchange,美国标准信息交换代码)是基于拉丁字母的一套电脑编码系统,主要用于显示现代英语和其他西欧语言,其最多只能用 8 位来表示(一个字节),即:2**8 = 256-1,所以,ASCII码最多只能表示 255 个符号。
关于中文
为了处理汉字,程序员设计了用于简体中文的GB2312和用于繁体中文的big5。
GB2312(1980年)一共收录了7445个字符,包括6763个汉字和682个其它符号。汉字区的内码范围高字节从B0-F7,低字节从A1-FE,占用的码位是72*94=6768。其中有5个空位是D7FA-D7FE。
GB2312 支持的汉字太少。1995年的汉字扩展规范GBK1.0收录了21886个符号,它分为汉字区和图形符号区。汉字区包括21003个字符。2000年的 GB18030是取代GBK1.0的正式国家标准。该标准收录了27484个汉字,同时还收录了藏文、蒙文、维吾尔文等主要的少数民族文字。现在的PC平台必须支持GB18030,对嵌入式产品暂不作要求。所以手机、MP3一般只支持GB2312。
从ASCII、GB2312、GBK 到GB18030,这些编码方法是向下兼容的,即同一个字符在这些方案中总是有相同的编码,后面的标准支持更多的字符。在这些编码中,英文和中文可以统一地处理。区分中文编码的方法是高字节的最高位不为0。按照程序员的称呼,GB2312、GBK到GB18030都属于双字节字符集 (DBCS)。
有的中文Windows的缺省内码还是GBK,可以通过GB18030升级包升级到GB18030。不过GB18030相对GBK增加的字符,普通人是很难用到的,通常我们还是用GBK指代中文Windows内码。
显然ASCII码无法将世界上的各种文字和符号全部表示,所以,就需要新出一种可以代表所有字符和符号的编码,即:Unicode
Unicode(统一码、万国码、单一码)是一种在计算机上使用的字符编码。Unicode 是为了解决传统的字符编码方案的局限而产生的,它为每种语言中的每个字符设定了统一并且唯一的二进制编码,规定虽有的字符和符号最少由 16 位来表示(2个字节),即:2 **16 = 65536,
注:此处说的的是最少2个字节,可能更多
UTF-8,是对Unicode编码的压缩和优化,他不再使用最少使用2个字节,而是将所有的字符和符号进行分类:ascii码中的内容用1个字节保存、欧洲的字符用2个字节保存,东亚的字符用3个字节保存...
所以,python解释器在加载 .py 文件中的代码时,会对内容进行编码(默认ascill),如果是如下代码的话:
报错:ascii码无法表示中文
1 #!/usr/bin/env python 2 3 print "你好,世界"
改正:应该显示的告诉python解释器,用什么编码来执行源代码,即:
1 #!/usr/bin/env python 2 # -*- coding: utf-8 -*- 3 4 print "你好,世界"
当行注视:# 被注释内容(ctrl+#)
多行注释:""" 被注释内容 """
标签:several lvm das 3.0 教程 发行版 mod move lse
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/Jungle1219/p/9523529.html