标签:cab author 环境 was factor 不能 possible pos span
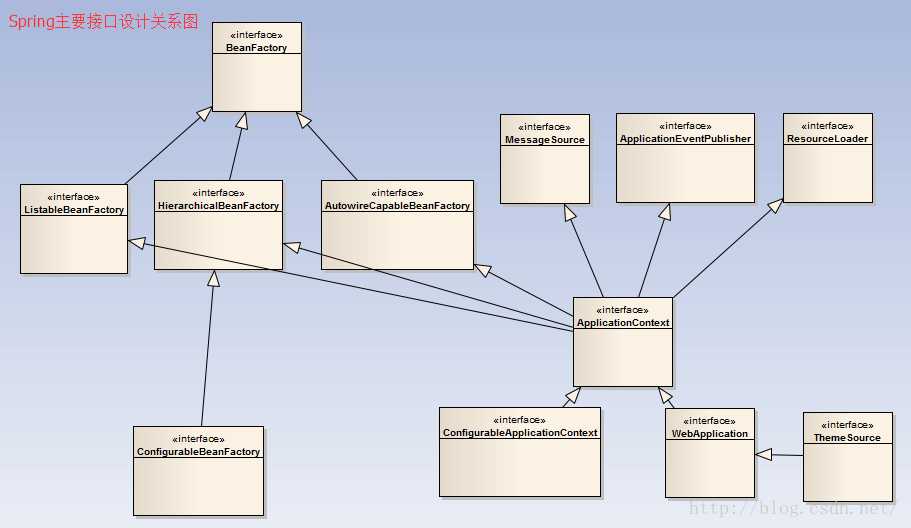
1.从接口BeanFactory到HierarchicalBeanFactory,再到ConfigurableBeanFactory,这是一条主要的
BeanFactory设计路径。
在这条接口设计路径中,BeanFactory,是一条主要的BeanFactory设计路径,其定义了基本的Ioc容器
的规范。在这个接口定义中,包括了getBean()这样的Ioc容器的基本方法(通过这个方法可以从容器中
取得Bean)。
而HierarchicalBeanFactory接口在继承了BeanFactory的基本接口后,增加了
getParentBeanFactory()的接口功能,使BeanFactory具备了双亲Ioc容器的管理功能。
在接下来的ConfigurableBeanFactory接口中,主要定义了一些对BeanFactory的配置功能,
比如通过setParentBeanFactory()设置双亲Ioc容器,
通过addBeanPostProcessor()配置Bean后置处理器,等等。
通过这些接口设计的叠加,定义了BeanFactory就是最简单的Ioc容器的基本功能。
2.第二条接口设计主线是,以ApplicationContext作为核心的接口设计,这里涉及的主要接口设计
有,从BeanFactory到ListableBeanFactory,再到ApplicationContext,再到我们常用的
WebApplicationContext或者ConfigurableApplicationContext接口。
我们常用的应用基本都是org.framework.context 包里的WebApplicationContext或者
ConfigurableApplicationContext实现。
在这个接口体现中,ListableBeanFactory和HierarchicalBeanFactory两个接口,连接BeanFactory
接口定义和ApplicationContext应用的接口定义。
在ListableBeanFactory接口中,细化了许多BeanFactory的接口功能,比如定义了
getBeanDefinitionNames()接口方法;
对于ApplicationContext接口,它通过继承MessageSource、ResourceLoader、
ApplicationEventPublisher接口,在BeanFactory简单Ioc容器的基础上添加了许多对高级容器的特性
支持功能。
3.这个接口系统是以BeanFactory和ApplicationContext为核心设计的,而BeanFactory是Ioc容器
中最基本的接口。
在ApplicationContext的设计中,一方面,可以看到它继承了BeanFactory接口体系中的
ListableBeanFactory、AutowireCapableBeanFactory、HierarchicalBeanFactory等
BeanFactory的接口,具备了BeanFactory Ioc容器的基本功能;
另一方面,通过继承MessageSource、ResourceLoadr、ApplicationEventPublisher这些接口,
BeanFactory为ApplicationContext赋予了更高级的Ioc容器特性。对于ApplicationContext而言,
为了在Web环境中使用它,还设计了WebApplicationContext接口,
而这个接口通过继承ThemeSource接口来扩充
/*
* Copyright 2002-2006 the original author or authors.
*
* Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
* you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
* You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*/
package org.springframework.beans.factory;
import org.springframework.beans.BeansException;
/**
* The root interface for accessing a Spring bean container.
* This is the basic client view of a bean container; further interfaces
* such as <code>ListableBeanFactory</code> and <code>ConfigurableBeanFactory</code>
* are available for specific purposes.
*
* <p>This interface is implemented by objects that hold a number of bean definitions,
* each uniquely identified by a String name. Depending on the bean definition,
* the factory will return either an independent instance of a contained object
* (the Prototype design pattern), or a single shared instance (a superior
* alternative to the Singleton design pattern, in which the instance is a
* singleton in the scope of the factory). Which type of instance will be returned
* depends on the bean factory configuration: the API is the same. The Singleton
* approach is more useful and more common in practice.
*
* <p>The point of this approach is that the BeanFactory is a central registry
* of application components, and centralizes configuration of application
* components (no more do individual objects need to read properties files,
* for example). See chapters 4 and 11 of "Expert One-on-One J2EE Design and
* Development" for a discussion of the benefits of this approach.
*
* <p>Note that it is generally better to rely on Dependency Injection
* ("push" configuration) to configure application objects through setters
* or constructors, rather than use any form of "pull" configuration like a
* BeanFactory lookup. Spring‘s Dependency Injection functionality is
* implemented using BeanFactory and its subinterfaces.
*
* <p>Normally a BeanFactory will load bean definitions stored in a configuration
* source (such as an XML document), and use the org.springframework.beans package
* to configure the beans. However, an implementation could simply return Java
* objects it creates as necessary directly in Java code. There are no constraints
* on how the definitions could be stored: LDAP, RDBMS, XML, properties file etc.
* Implementations are encouraged to support references amongst beans, to either
* Singletons or Prototypes.
*
* <p>In contrast to the methods in ListableBeanFactory, all of the methods in this
* interface will also check parent factories if this is a HierarchicalBeanFactory.
* If a bean is not found in this factory instance, the immediate parent is asked.
* Beans in this factory instance are supposed to override beans of the same name
* in any parent factory.
*
* <p>Bean factory implementations should support the standard bean lifecycle interfaces
* as far as possible. The full set of initialization methods and their standard order is:<br>
* 1. BeanNameAware‘s <code>setBeanName</code><br>
* 2. BeanClassLoaderAware‘s <code>setBeanClassLoader</code><br>
* 3. BeanFactoryAware‘s <code>setBeanFactory</code><br>
* 4. ResourceLoaderAware‘s <code>setResourceLoader</code>
* (only applicable when running in an application context)<br>
* 5. ApplicationEventPublisherAware‘s <code>setApplicationEventPublisher</code>
* (only applicable when running in an application context)<br>
* 6. MessageSourceAware‘s <code>setMessageSource</code>
* (only applicable when running in an application context)<br>
* 7. ApplicationContextAware‘s <code>setApplicationContext</code>
* (only applicable when running in an application context)<br>
* 8. ServletContextAware‘s <code>setServletContext</code>
* (only applicable when running in a web application context)<br>
* 9. <code>postProcessBeforeInitialization</code> methods of BeanPostProcessors<br>
* 10. InitializingBean‘s <code>afterPropertiesSet</code><br>
* 11. a custom init-method definition<br>
* 12. <code>postProcessAfterInitialization</code> methods of BeanPostProcessors
*
* <p>On shutdown of a bean factory, the following lifecycle methods apply:<br>
* 1. DisposableBean‘s <code>destroy</code><br>
* 2. a custom destroy-method definition
*
* @author Rod Johnson
* @author Juergen Hoeller
* @since 13 April 2001
* @see ListableBeanFactory
* @see org.springframework.beans.factory.config.ConfigurableBeanFactory
* @see BeanNameAware#setBeanName
* @see BeanClassLoaderAware#setBeanClassLoader
* @see BeanFactoryAware#setBeanFactory
* @see org.springframework.context.ResourceLoaderAware#setResourceLoader
* @see org.springframework.context.ApplicationEventPublisherAware#setApplicationEventPublisher
* @see org.springframework.context.MessageSourceAware#setMessageSource
* @see org.springframework.context.ApplicationContextAware#setApplicationContext
* @see org.springframework.web.context.ServletContextAware#setServletContext
* @see org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanPostProcessor#postProcessBeforeInitialization
* @see InitializingBean#afterPropertiesSet
* @see org.springframework.beans.factory.support.RootBeanDefinition#getInitMethodName
* @see org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanPostProcessor#postProcessAfterInitialization
* @see DisposableBean#destroy
* @see org.springframework.beans.factory.support.RootBeanDefinition#getDestroyMethodName
*/
public interface BeanFactory {
/**
* Used to dereference a FactoryBean and distinguish it from beans
* <i>created</i> by the FactoryBean. For example, if the bean named
* <code>myEjb</code> is a FactoryBean, getting <code>&myEjb</code> will
* return the factory, not the instance returned by the factory.
*/
String FACTORY_BEAN_PREFIX = "&";
/**
* Return an instance, which may be shared or independent, of the given bean name.
* This method allows a Spring BeanFactory to be used as a replacement for the
* Singleton or Prototype design pattern.
* <p>Callers may retain references to returned objects in the case of Singleton beans.
* <p>Translates aliases back to the corresponding canonical bean name.
* Will ask the parent factory if the bean cannot be found in this factory instance.
* @param name the name of the bean to return
* @return the instance of the bean
* @throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException if there is no bean definition
* with the specified name
* @throws BeansException if the bean could not be obtained
*/
Object getBean(String name) throws BeansException;
/**
* Return an instance (possibly shared or independent) of the given bean name.
* <p>Behaves the same as getBean(String), but provides a measure of type safety by
* throwing a Spring BeansException if the bean is not of the required type.
* This means that ClassCastException can‘t be thrown on casting the result correctly,
* as can happen with <code>getBean(String)</code>.
* @param name the name of the bean to return
* @param requiredType type the bean must match. Can be an interface or superclass
* of the actual class, or <code>null</code> for any match. For example, if the value
* is <code>Object.class</code>, this method will succeed whatever the class of the
* returned instance.
* @return an instance of the bean (never <code>null</code>)
* @throws BeanNotOfRequiredTypeException if the bean is not of the required type
* @throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException if there‘s no such bean definition
* @throws BeansException if the bean could not be created
*/
Object getBean(String name, Class requiredType) throws BeansException;
/**
* Does this bean factory contain a bean definition with the given name?
* <p>Will ask the parent factory if the bean cannot be found in this factory instance.
* @param name the name of the bean to query
* @return whether a bean with the given name is defined
*/
boolean containsBean(String name);
/**
* Is this bean a singleton? That is, will <code>getBean</code> always return the same object?
* <p>Will ask the parent factory if the bean cannot be found in this factory instance.
* @param name the name of the bean to query
* @return is this bean a singleton
* @throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException if there is no bean with the given name
* @see #getBean
*/
boolean isSingleton(String name) throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException;
/**
* Determine the type of the bean with the given name.
* More specifically, checks the type of object that <code>getBean</code> would return.
* For a FactoryBean, returns the type of object that the FactoryBean creates.
* @param name the name of the bean to query
* @return the type of the bean, or <code>null</code> if not determinable
* @throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException if there is no bean with the given name
* @since 1.1.2
* @see #getBean
* @see FactoryBean#getObjectType()
*/
Class getType(String name) throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException;
/**
* Return the aliases for the given bean name, if defined.
* <p>If the given name is an alias, the corresponding original bean name
* and other aliases (if any) will be returned, with the original bean name
* being the first element in the array.
* <p>Will ask the parent factory if the bean cannot be found in this factory instance.
* @param name the bean name to check for aliases
* @return the aliases, or an empty array if none
*/
String[] getAliases(String name);
}
ApplicationContext源码:
/*
* Copyright 2002-2006 the original author or authors.
*
* Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
* you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
* You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*/
package org.springframework.context;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.HierarchicalBeanFactory;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.ListableBeanFactory;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.AutowireCapableBeanFactory;
import org.springframework.core.io.support.ResourcePatternResolver;
/**
* Central interface to provide configuration for an application.
* This is read-only while the application is running, but may be
* reloaded if the implementation supports this.
*
* <p>An ApplicationContext provides:
* <ul>
* <li>Bean factory methods, inherited from ListableBeanFactory.
* This avoids the need for applications to use singletons.
* <li>The ability to resolve messages, supporting internationalization.
* Inherited from the MessageSource interface.
* <li>The ability to load file resources in a generic fashion.
* Inherited from the ResourceLoader interface.
* <li>The ability to publish events. Implementations must provide a means
* of registering event listeners.
* <li>Inheritance from a parent context. Definitions in a descendant context
* will always take priority. This means, for example, that a single parent
* context can be used by an entire web application, while each servlet has
* its own child context that is independent of that of any other servlet.
* </ul>
*
* <p>In addition to standard bean factory lifecycle capabilities,
* ApplicationContext implementations need to detect ApplicationContextAware
* beans and invoke the setApplicationContext method accordingly.
*
* @author Rod Johnson
* @author Juergen Hoeller
* @see ApplicationContextAware#setApplicationContext
* @see ConfigurableApplicationContext
*/
public interface ApplicationContext extends ListableBeanFactory, HierarchicalBeanFactory,
MessageSource, ApplicationEventPublisher, ResourcePatternResolver {
/**
* Return the parent context, or <code>null</code> if there is no parent,
* and this is the root of the context hierarchy.
* @return the parent context, or <code>null</code> if there is no parent
*/
ApplicationContext getParent();
/**
* Expose AutowireCapableBeanFactory functionality for this context.
* <p>This is not typically used by application code, except for the purpose
* of initializing bean instances that live outside the application context,
* applying the Spring bean lifecycle (fully or partly) to them.
* <p>Alternatively, the internal BeanFactory exposed by the
* ConfigurableApplicationContext interface offers access to the
* AutowireCapableBeanFactory interface too. The present method mainly
* serves as convenient, specific facility on the ApplicationContext
* interface itself.
* @throws IllegalStateException if the context does not support
* the AutowireCapableBeanFactory interface or does not hold an autowire-capable
* bean factory yet (usually if <code>refresh()</code> has never been called)
* @see ConfigurableApplicationContext#refresh()
* @see ConfigurableApplicationContext#getBeanFactory()
*/
AutowireCapableBeanFactory getAutowireCapableBeanFactory() throws IllegalStateException;
/**
* Return a friendly name for this context.
* @return a display name for this context
*/
String getDisplayName();
/**
* Return the timestamp when this context was first loaded.
* @return the timestamp (ms) when this context was first loaded
*/
long getStartupDate();
}
BeanFacotry是spring中比较原始的Factory。它无法支持spring的许多插件,如AOP功能、Web应用等。
ApplicationContext接口,它由BeanFactory接口派生而来,因而提供BeanFactory所有的功能。
ApplicationContext以一种更向面向框架的方式工作以及对上下文进行分层和实现继承,
ApplicationContext包还提供了以下的功能: • MessageSource, 提供国际化的消息访问 • 资源访问,如URL和文件 • 事件传播 • 载入多个(有继承关系)上下文 ,使得每一个上下文都专注于一个特定的层次,
比如应用的web层BeanFactroy采用的是延迟加载形式来注入Bean的,
即只有在使用到某个Bean时(调用getBean()),
才对该Bean进行加载实例化,这样,我们就不能发现一些存在的Spring的配置问题。
而ApplicationContext则相反,它是在容器启动时,一次性创建了所有的Bean。这样,在容器启动时,
我们就可以发现Spring中存在的配置错误。
【学习心得】 1.在学习框架的时候,从源码着手,会是个比较清晰的方向,毕竟是第一手资料。
再结合一些视频、书籍和文章的资料,看源码的困难也减少了。
2.再看源码的时候,注释是非常重要的。代码很简单,可能觉得没什么问题,
而当你看完注释后,你会对源码产生更加深刻的理解。
一头扎进Spring之---------Spring核心容器
标签:cab author 环境 was factor 不能 possible pos span
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/hanxue112253/p/9532494.html