标签:获取 window win 语句 数字 put 字符 use .com
1.python文件的后缀为.py
2.python执行方式:(1)python解释器 python路径(2)进入python解释器:实时输入并获取执行结果
3.python解释器路径:#!/usr/bin/env python 在windows上执行有没有没有任何影响;在Linux下必须有这句以显示解释器路径
4.python编码:# -*- coding:utf8 -*- python3版本无需关注;python2版本每个文件中只要出现中文,头部必须加上此编码
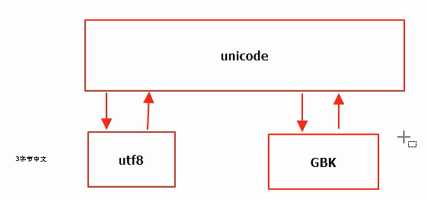
utf8表示汉字用3个字节,GBK则用2个字节
5.input的用法:永远等待,直到用户输入了值,就会将输入的值赋值给一个东西。input输出的数据类型是字符串
6.变量名的构成:字母、数字、下划线。数字不能开头 ;不能是关键字;最好不好和python内置的东西重复
7.if条件语句:缩进用4个空格(Tab键即可)
n1 = input(‘>>>‘) if "alex" == "alex": n2 = input(‘>>>‘) if n2 == "确认": print(‘alex yes‘) else: print(‘alex no‘) else: print(‘error‘)
其中,n1 = "alex" 表示赋值;n1 == ‘alex‘ 表示比较,即是否等于
if 条件1: pass elif 条件2: pass elif 条件3: pass else: pass print(‘end‘)
其中,pass 代指空代码,无意义,仅仅用于表示代码块
and和or:
if n1 == "alex" or n2 == "alex!23": print(‘OK‘) else: print(‘error‘)
8.基本数据类型及运算
字符串:n1 = "alex" n2 = ‘root‘ n3 = """eric""" n4=‘‘‘tony‘‘‘
数字: age=21 weight = 64 fight = 5
字符串可进行加法与乘法运算:
加法:n1 = "alex"
n2 = "b"
n4 = "d"
n3 = n1 + n2 + n4
# "alexbd"
乘法:n1 = "alex"
n3 = n1 * 10
数字:
n1 = 9
n2 = 2
n3 = n1 + n2
n3 = n1 - n2
n3 = n1 * n2
n3 = n1 / n2
n3 = n1 % n2(取余)n3 = n1 // n2(取商)
n3 = n1 ** n2(幂运算)
9.while循环语句:
while 1==1: print(‘ok‘)
这是一个死循环,无限输出ok
a.while else的用法也存在,类似于if else,区别在于while下面的内容要进行循环
b.continue和break
continue:不执行continue以下的命令,终止当前循环直接跳入下一个循环
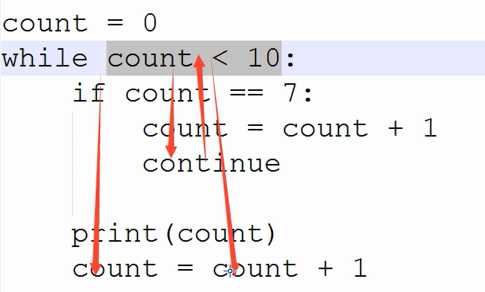
break:不执行break以下的命令,并终止所有循环
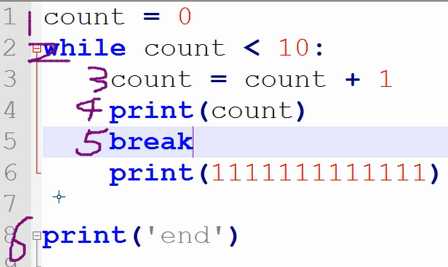
10.练习
a.使用while循环输入 1 2 3 4 5 6 8 9 10
n=1 while n<11: if n==7: pass else: print(n) n=n+1 print(‘---end---‘)
b.求1-100的所有数的和
n=1 s=0 while n<101: s=s+n n=n+1 print(s)
c.输出 1-100 内的所有奇数
n=1 while n<101: temp=n%2
if temp==1: print(n) else: pass n=n+1 print(‘---end---‘)
d.输出 1-100 内的所有偶数
n=1 while n<101: temp=n%2 if temp==0: print(n) else: pass n=n+1 print(‘---end---‘)
e.求1-2+3-4+5 ... 99的所有数的和
s=0 n=1 while n<100: temp n%2 if temp==0: s=s-n else: s=s+n n=n+1 print(s)
f.用户登录,有三次机会重试
count=0 while count<3: user=input(‘>>>‘) pwd=input(‘>>>‘) if user=‘alex‘ and pwd=‘123‘ print(‘欢迎登录‘) print(‘.......‘) break else: print(‘用户名或密码错误,请重新登录‘) count=count+1
标签:获取 window win 语句 数字 put 字符 use .com
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/quyao/p/9451789.html