标签:语言 bubuko 链表 融合 img one nts lib sort
思路:
已知两个指针head1,head2;
首先定义返回的指针head;
比较head1,和head2中data的值,将值较小的指针赋值给head。
定义一个当前指针current;
此时current = head;
定义p1 ,p2 指针分别遍历两个序列。
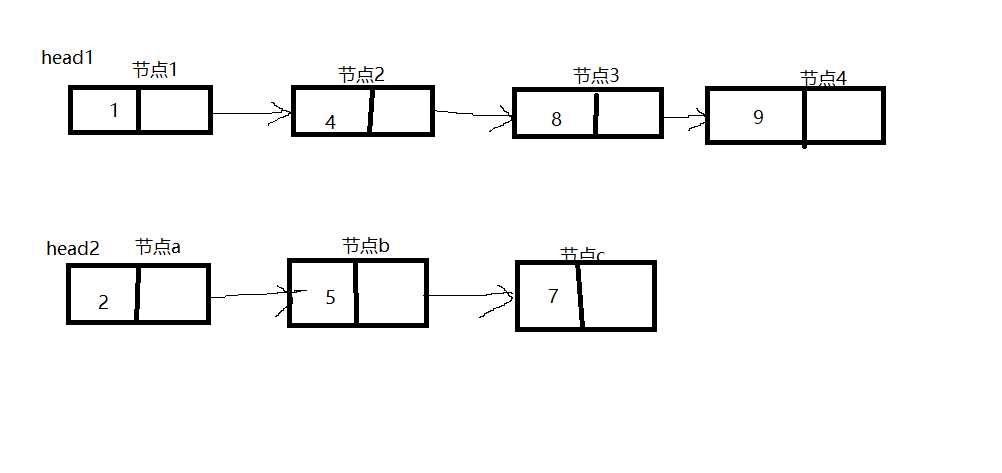
若两个链表初始化为上图,由于节点1的值小于节点a的值,则head = 节点1,current = 节点1, p1 = 节点2, p2 = 节点a。
循环比较p1 和 p2 节点的值,将值较小的节点连在上一个节点。 如节点a的值小于节点2的值, 则 current->next = 节点a, current = 节点a, p2 = p2->next 即p2 = 节点b。p1不变。当p1 且 p2 都为空时结束循环。返回head指针即可。
代码如下:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
//定义结构体,data是值
struct studentStruct{
int data;
struct studentStruct * next;
};
typedef struct studentStruct student;
//关键方法,传入两个链表的头指针,返回融合的链表指针
student * sortMethod(student * head1,student * head2){
student * p1=NULL ;
student * p2=NULL ;
student * head=NULL;
if(head1->data>head2->data){
head = head2;
p2 = head2->next;
p1 = head1;
}else{
head = head1;
p1 = head1->next;
p2 = head2;
}
student * current = head;
while(!(p1== NULL && p2==NULL)){
if(p1==NULL){
current->next = p2;
break;
}
if(p2==NULL){
current->next = p1;
break;
}
if(p1->data>p2->data){
current->next = p2;
current = p2;
p2 = p2->next;
}else{
current->next = p1;
current = p1;
p1 = p1->next;
}
}
return head;
}
student * createOneHead(int n){
student * head = NULL;
student * p2 = NULL;
student * p1 = NULL;
while(n>0){
p2 = (student *)malloc(sizeof(student));
printf("请输入data:\n");
scanf("%d",&(p2->data));
p2->next = NULL;
if(head==NULL){
head = p2;
p1 = head;
}else{
p1->next = p2;
p1 = p2;
}
n--;
}
return head;
}
void print(student * head){
student * p = head;
while(p!=NULL){
printf("%d\n",p->data);
p = p->next;
}
}
int main()
{
printf("初始化第一个序列\n");
student *h1 = createOneHead(4);
printf("初始化第2个序列\n");
student *h2 = createOneHead(3);
student *head = sortMethod(h1,h2);
print(head);
return 0;
}
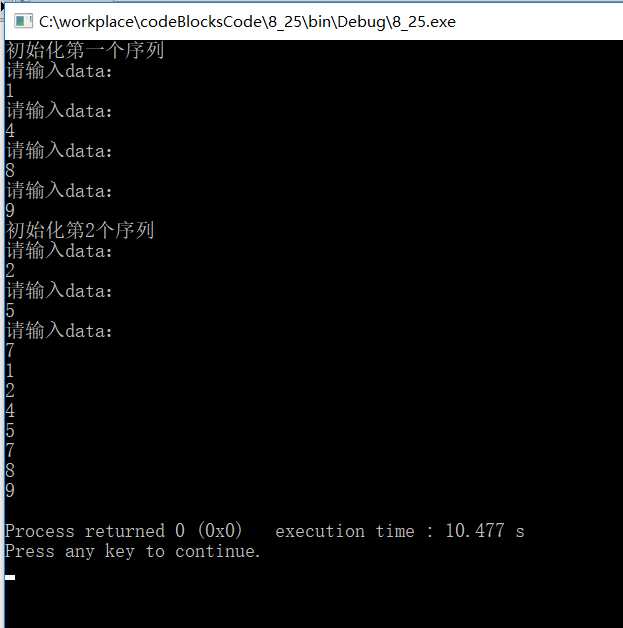
运行结果:
标签:语言 bubuko 链表 融合 img one nts lib sort
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/cavinchen/p/9535018.html