标签:std 匹配 bin ase nat 等于 alt else ace
一、概念

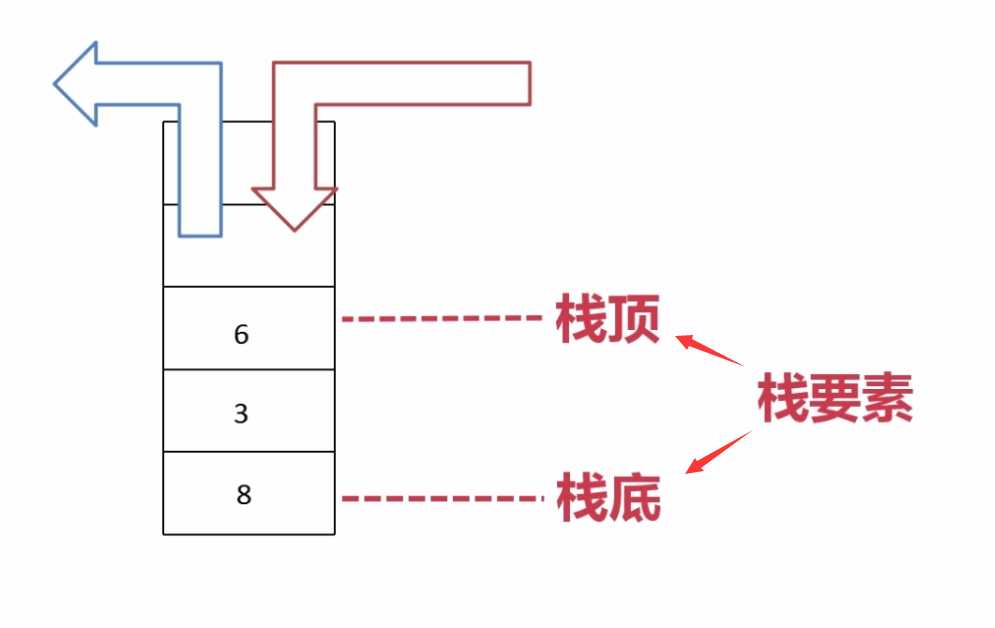
二、应用实例
1.进制转换
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include "MyStack.h"
#include "Coordinate.h"
using namespace std;
#define BINARY 2
#define OCTONARY 8
#define HEXADECIMAL 16
void main ( )
{
//MyStack<int> s(30);
MyStack<char> s(30);
char num[]="0123456789ABCDEF";
int N=1348;
int mod=0;
while (N!=0)
{
mod=N%16;
s.push(num[mod]);
N=N/16;
}
s.stackTraverse(false);
/*
int elem=0;
for (int i=s.stackLength()-1;i>=0;i--)
{
s.pop(elem);
cout<<num[elem];
}*/
/*while(!s.stackEmpty())
{
s.pop(elem);
cout<<num[elem];
}*/
system("pause");
}
2.括号匹配
MyStack<char> s(30); //存放未匹配的括号
MyStack<char> s1(30); //存放栈顶括号的另一半
char str[] = "([])["; //存放待匹配文本目标,要求无空格 e.g. [()()] ([]([]))
char current=0; //当前括号需要匹配的另一半
for (int i=0;i<strlen(str);i++)
{
if (current!=str[i])
{
s.push(str[i]);
switch(str[i])
{
case ‘[‘: //case 后面数据类型是int,单个字符会转换成其ASC码
if (current!=0)
{
s1.push(current);
}
current=‘]‘;
break;
case ‘(‘:
if (current!=0)
{
s1.push(current);
}
current=‘)‘;
break;
default:
cout<<"括号不匹配."<<endl; //default后面语句可以注释掉,因为current不等于str[i]时str[i]就会入栈,第一个栈不为零匹配就会失败
}
}
else
{
char elem;
s.pop(elem);
if(!s1.pop(current))
{
current=0;
}
}
}
if (s.stackEmpty())
{
cout<<"括号匹配"<<endl;
}
else
{
cout<<"括号不匹配"<<endl;
}
system("pause");
标签:std 匹配 bin ase nat 等于 alt else ace
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/Tang-tangt/p/9557559.html