标签:style blog http color io os 使用 ar for
2014-09-28
待测程序
测试程序
创建测试用例以及测试结果存储
执行T-SQL脚本
使用BCP工具导入测试用例数据
创建T-SQL 测试套件
当待测存储过程返回行集的时候,如何判断测试结果是否通过
当待测存储过程返回out参数时,如何判断测试结果是否通过
当待测存储过程没有返回值时,如何判断测试结果是否通过
许多基于Windows的系统都使用了SQL Server作为后台组件。待测程序经常通过存储过程来访问数据库。对于这些应用场景,可以把SQL存储过程当成应用程序的辅助函数。有两种方法可以用来编写对SQL存储过程的自动化测试:
下面代码创建数据库‘dbEmployees’;创建表‘talEmployee’,插入相应数据;创建存储过程‘usp_HireAfter’,创建登陆用户‘employeesLogin’并赋予访问数据库和存储过程的权限:
makeDbEmployees.sql:

1 -- Database setup: makeDbEmployees.sql 2 3 use master 4 go 5 6 if exists (select * from sysdatabases where name=‘dbEmployees‘) 7 drop database dbEmployees 8 go 9 10 if exists (select * from syslogins where name = ‘employeesLogin‘) 11 exec sp_droplogin ‘employeesLogin‘ 12 go 13 14 create database dbEmployees 15 go 16 17 use dbEmployees 18 go 19 20 create table tblEmployees 21 ( 22 empID char(3) primary key, 23 empLast varchar(35) not null, 24 empDOH datetime not null, 25 ) 26 go 27 28 -- this is dev data, not test case data 29 insert into tblEmployees values(‘e11‘,‘Adams‘, ‘06/15/1998‘) 30 insert into tblEmployees values(‘e22‘,‘Baker‘, ‘06/15/2001‘) 31 go 32 33 exec sp_addlogin ‘employeesLogin‘, ‘September,2014‘ 34 go 35 exec sp_grantdbaccess ‘employeesLogin‘ 36 go 37 38 create procedure usp_HiredAfter 39 @dt datetime 40 as 41 select * from tblEmployees where empDOH > @dt 42 go 43 44 grant execute on usp_HiredAfter to employeesLogin 45 go 46 47 -- end script
注意:当测试SQL存储过程时,有两个理由使你最好不要使用用于开发的数据库进行测试:
SQL数据库支持两种不同的安全模式:使用Windows认证可通过Windows账号ID和密码连接数据库,使用混合模式认证可以通过SQL登陆ID和SQL密码来连接数据库。若想通过SQL认证来连接测数据库,应该使用系统存储过程sp_addlogin()创建SQL登陆账号和密码。
SQL登陆账号和SQL用户区别:
当为一个SQL登陆账号分配权限的时候,会自动创建一个名为SQL用户。所以最终会有一个SQL登陆账号和一个SQL用户,两个名字相同且相互关联。当然也可以让不同名字的登陆账号和用户相互关联。
以下T-SQL脚本,创建一个数据库然后创建一些表用来保存测试用例的输入数据和测试结果;创建一个专用SQL登陆账号,赋予一定权限:
makeDbTestCasesAndResults.sql:

1 -- Test case data and results setup: makeDbTestCasesAndResults.sql 2 3 use master 4 go 5 6 if exists (select * from sysdatabases where name=‘dbTestCasesAndResults‘) 7 drop database dbTestCasesAndResults 8 go 9 10 if exists (select * from syslogins where name = ‘testLogin‘) 11 exec sp_droplogin ‘testLogin‘ 12 go 13 14 create database dbTestCasesAndResults 15 go 16 17 use dbTestCasesAndResults 18 go 19 20 create table tblTestCases 21 ( 22 caseID char(4) primary key, 23 input datetime not null, 24 expectedChecksum int not null 25 ) 26 go 27 28 -- this is the test case data for usp_HiredAfter using a checksum expected 29 -- value approach 30 -- can also read from a text file using BCP, DTS, or a C# program 31 insert into tblTestCases values(‘0001‘,‘01/01/1998‘, 1042032) 32 insert into tblTestCases values(‘0002‘,‘01/01/1998‘, 9999999) -- deliberate error 33 insert into tblTestCases values(‘0003‘,‘01/01/2000‘, 25527856) 34 insert into tblTestCases values(‘0004‘,‘01/01/2006‘, 0) 35 go 36 37 create table tblResults 38 ( 39 caseID char(4) not null, 40 result char(4) null, 41 whenRun datetime not null 42 ) 43 go 44 45 exec sp_addlogin ‘testLogin‘, ‘September,2014‘ 46 go 47 exec sp_grantdbaccess ‘testLogin‘ 48 go 49 50 grant select, insert, delete, update on tblTestCases to testLogin 51 go 52 53 grant select, insert, delete, update on tblResults to testLogin 54 go 55 56 -- end script
运行T-SQL脚本,有好几种方法:
下面使用osql.exe程序使用以下命令执行这个脚本:
osql.exe -S(local) -U loginID -P loginPassword -i makeDbTestCasesAndResults.sql -n > RESULT.txt
或
osql.exe -S(local) -E -i makeDbTestCasesAndResults.sql -n > RESULT.txt
-E表示使用Windows认证模式。
注意:osql.exe的参数是大小写敏感的。
创建一个BCP格式的文件,用于把你想要导入的文本文件信息映射到目标SQL表中。然后把上述格式的文件作为参数传给命令行工具bcp.exe
Step 1: 先看一下如何从表‘tblTestCases’中导出数据
create table ‘tblTestCases‘的脚本:

1 create table tblTestCases 2 ( 3 caseID char(4) primary key, 4 input datetime not null, 5 expectedChecksum int not null 6 )
用BCP导出表‘tblTestCases’到dat文件中:
bcp dbTestCasesAndResults.dbo.tblTestCases out C:\Code\AutomationTest\newData.dat -c -T
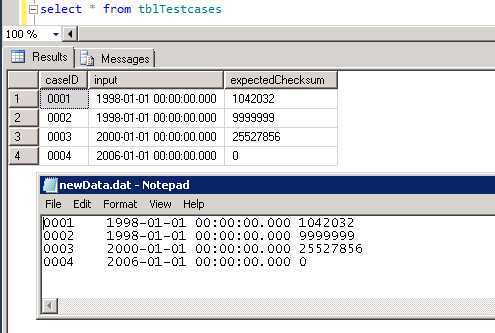
图1导出的数据
Step 2: 用BCP导出格式文件
EXEC master..xp_cmdshell ‘bcp dbTestCasesAndResults.dbo.tblTestCases format nul -f C:\Code\AutomationTest\newData.fmt -c -T‘
newData.fmt内容:

1 11.0 2 3 3 1 SQLCHAR 0 4 "\t" 1 caseID SQL_Latin1_General_CP1_CI_AS 4 2 SQLCHAR 0 24 "\t" 2 input "" 5 3 SQLCHAR 0 12 "\r\n" 3 expectedChecksum ""
上述内容中,
Step3: 修改newData.dat,导入
修改后newData.dat内容:
000 2007-01-01 00:00:00.000 7
用BCP命令导入:

1 bcp.exe dbTestCasesAndResults.dbo.tblTestCases in newData.dat -f newData.fmt -S. -T
使用SQL游标(cursor)遍历这个测试用例数据表。针对每个测试用例,调用待测存储过程并且取得它的返回值。把它的实际值于期望值进行比较,判定结果,保存测试结果。
SQL游标设计用来处理单个的数据行并不向其他SQL操作那个处理行集(rowset)。
首先声明一个指向保存测试数据的SQL表的游标

1 declare tCursor cursor fast_forward 2 for select caseID, input, expectedChecksum 3 from dbTestCasesAndResults.dbo.tblTestCases 4 order by caseID
注意:游标于其它SQL变量不同,游标变量的名字前面并没有@字符。可供声明游标的有好几种。FAST_FORWARD最适合用来读取测试用例数据,它实际上就是FORWAR_ONLY和READ_ONLY的别名。
在使用游标前,必须先打开游标。然后,如果想要遍历整个数据库表,则必须通过fetch next语句于都数据库表的第一行:

1 open tCursor 2 fetch next 3 from tCursor 4 into @caseID, @input, @expectedChecksum
对第一行进行预读是为了对下面的循环进行控制,我们使用变量@@fetch_status来控制用于读取的这个循环,这个变量表示最近一次fetch操作的状态。如果操作成功,@@fetch_status值为0;若失败,@@fetch_status值为-1,-2。因此,可向下面这样遍历整个数据库表:

1 while @@fetch_status = 0 2 begin 3 4 --运行测试用例 5 6 fetch next 7 from tCursor 8 into @caseID, @input, @expectedChecksum 9 end
在主循环内部,我们需要调用待测存储过程,并且把测试用力输入数据传给它。去会的值打印出来:
(注意:下面脚本调用存储过程‘dbEmployees.dbo.usp_HiredAfter时,这里假设它只返回单个值)

1 exec @actual = dbEmployees.dbo.usp_HiredAfter @input 2 3 if(@actual=@expected) 4 begin 5 set @resultLine=@caseID + ‘: Pass‘ 6 print @resultLine 7 end 8 else 9 begin 10 set @resultLine=@caseID + ‘: Fail‘ 11 print @resultLine 12 end
使用完一个SQL游标之后,必须关闭这个游标并且调用deallocate命令把它作为一个资源释放:

1 close tCursor 2 deallocate tCursor
SQLspTest.sql测试脚本:

1 -- =========================================================== 2 -- TestAuto.sql 3 4 truncate table dbEmployees.dbo.tblEmployees 5 6 insert into dbEmployees.dbo.tblEmployees 7 values(‘e11‘,‘Adams‘, ‘06/15/1998‘) 8 insert into dbEmployees.dbo.tblEmployees 9 values(‘e22‘,‘Baker‘, ‘06/15/2001‘) 10 insert into dbEmployees.dbo.tblEmployees 11 values(‘e33‘,‘Young‘, ‘06/15/1998‘) 12 insert into dbEmployees.dbo.tblEmployees 13 values(‘e44‘,‘Zetta‘, ‘06/15/2001‘) 14 -- other data would be inserted too 15 16 17 declare tCursor cursor fast_forward 18 for select caseID, input, expectedChecksum 19 from dbTestCasesAndResults.dbo.tblTestCases 20 order by caseID 21 22 declare @caseID char(4), @input datetime, @expectedChecksum int 23 declare @whenRun datetime 24 declare @actualChecksum int 25 declare @resultLine varchar(50) 26 27 set @whenRun = getdate() 28 29 open tCursor 30 fetch next 31 from tCursor 32 into @caseID, @input, @expectedChecksum 33 34 while @@fetch_status = 0 35 begin 36 37 exec @actualChecksum=dbEmployees.dbo.usp_HiredAfter @input 38 39 if (@actualChecksum = @expectedChecksum) 40 begin 41 set @resultLine = @caseID + ‘ Pass‘ 42 print @resultLine 43 insert into dbTestCasesAndResults.dbo.tblResults values(@caseID, ‘Pass‘, @whenRun) 44 end 45 else 46 begin 47 set @resultLine = @caseID + ‘ Fail‘ 48 print @resultLine 49 insert into dbTestCasesAndResults.dbo.tblResults values(@caseID, ‘Fail‘, @whenRun) 50 end 51 52 fetch next 53 from tCursor 54 into @caseID, @input, @expectedChecksum 55 56 end 57 58 close tCursor 59 deallocate tCursor 60 -- end script
待测存储过程脚本如下:

1 create procedure usp_HiredAfter 2 @dt datetime 3 as 4 select * from tblEmployees where empDOH > @dt
首先,应该创建一个临时表,用于保存存储过程返回的QL行集:

1 create table #resultRowset 2 ( 3 empID char(3) primary key, 4 empLast varchar(35) not null, 5 empDOH datetime not null, 6 )
然后,我们可以调用待测存储过程并把返回的行集存入临时表:

1 insert #resultRowset (empID, empLast, empDOH) -- call sp under test 2 exec dbEmployees.dbo.usp_HiredAfter @input
接下来,我们计算临时表的聚合校验,并把实际值和期望值进行比较:

if (@@rowcount = 0) set @actualChecksum =0 else select @actualChecksum = checksum_agg(binary_checksum(*)) from #resultRowset if (@actualChecksum = @expectedChecksum) print ‘Pass‘ else print ‘Fail‘
上面脚本中,内建的binary_checksum()函数返回表里的一行的校验和。checksum_agg()函数返回一组值的聚合校验和。这是待测存储过程返回行集的时候,判断测试是否通过的一种方法。
示例‘SQLspTest.sql’脚本:

1 -- =========================================================== 2 -- Test automation harness: SQLspTest.sql 3 -- test dbEmployees..usp_HiredAfter 4 -- reads test case data and writes results 5 -- to dbTestCasesAndResults 6 7 set nocount on 8 9 if not exists 10 (select * from master.dbo.sysdatabases where name=‘dbTestCasesAndResults‘) 11 raiserror(‘Fatal error: dbTestCasesAndResults not found‘, 16, 1) 12 go 13 14 if exists (select * from sysobjects where name=‘tap_Reset‘) 15 drop procedure tap_Reset 16 go 17 18 create procedure tap_Reset 19 as 20 truncate table dbEmployees.dbo.tblEmployees 21 22 insert into dbEmployees.dbo.tblEmployees 23 values(‘e11‘,‘Adams‘, ‘06/15/1998‘) 24 insert into dbEmployees.dbo.tblEmployees 25 values(‘e22‘,‘Baker‘, ‘06/15/2001‘) 26 insert into dbEmployees.dbo.tblEmployees 27 values(‘e33‘,‘Young‘, ‘06/15/1998‘) 28 insert into dbEmployees.dbo.tblEmployees 29 values(‘e44‘,‘Zetta‘, ‘06/15/2001‘) 30 -- other data would be inserted too 31 go 32 33 -- prepare dbEmployees with rich data 34 exec tap_Reset 35 go 36 37 declare tCursor cursor fast_forward 38 for select caseID, input, expectedChecksum 39 from dbTestCasesAndResults.dbo.tblTestCases 40 order by caseID 41 42 declare @caseID char(4), @input datetime, @expectedChecksum int 43 declare @whenRun datetime 44 declare @resultMsg varchar(80) 45 declare @actualChecksum int 46 47 create table #resultRowset -- for checksum technique 48 ( 49 empID char(3) primary key, 50 empLast varchar(35) not null, 51 empDOH datetime not null, 52 ) 53 54 set @whenRun = getdate() 55 56 print ‘Stored procedure under test = usp_HiredAfter‘ 57 print ‘ ‘ 58 print ‘CaseID Input Expected Actual Result‘ 59 print ‘===============================================‘ 60 61 open tCursor 62 fetch next 63 from tCursor 64 into @caseID, @input, @expectedChecksum 65 66 while @@fetch_status = 0 67 begin 68 69 exec tap_Reset -- reset test bed data 70 71 truncate table #resultRowset -- empty out the result rowset 72 73 insert #resultRowset (empID, empLast, empDOH) -- call sp under test 74 exec dbEmployees.dbo.usp_HiredAfter @input 75 76 if (@@rowcount = 0) 77 set @actualChecksum = 0 78 else 79 select @actualChecksum = checksum_agg(binary_checksum(*)) from #resultRowset 80 81 if (@actualChecksum = @expectedChecksum) 82 begin 83 set @resultMsg = @caseID + ‘ ‘ + cast(@input as varchar(11)) + 84 ‘ ‘ + cast(@expectedChecksum as varchar(20)) + ‘ ‘ + 85 cast(@actualChecksum as varchar(20)) + ‘ Pass‘ 86 print @resultMsg 87 insert into dbTestCasesAndResults.dbo.tblResults values(@caseID, ‘Pass‘, 88 @whenRun) 89 end 90 else 91 begin 92 set @resultMsg = @caseID + ‘ ‘ + cast(@input as varchar(11)) + 93 ‘ ‘ + cast(@expectedChecksum as varchar(20)) + ‘ ‘ + 94 cast(@actualChecksum as varchar(20)) + ‘ FAIL‘ 95 print @resultMsg 96 insert into dbTestCasesAndResults.dbo.tblResults values(@caseID, ‘FAIL‘, 97 @whenRun) 98 end 99 100 fetch next 101 from tCursor 102 into @caseID, @input, @expectedChecksum 103 104 end 105 106 close tCursor 107 deallocate tCursor 108 109 drop table #resultRowset 110 111 -- end script
待测存储过程脚本如下:

1 create procedure usp_GetLast 2 @empID char(3) 3 @empLast varchar(35) out 4 as 5 select @empLast =empLast from tblEmployees where empID = @empID 6 return @@rowcount
测试这个存储过程的脚本如下:

1 declare @input char(3) 2 declare @empLat varchar(35) 3 declare @retval int 4 5 declare @expectedLast varchar(35) 6 declare @expectedRet int 7 8 set @input = ‘e22‘ 9 set @expectedLast = ‘Baker‘ 10 set @expectedRet=1 11 12 exec @retval =dbEmployees.dbo.usp_GetLast @input, @empLat out 13 if(@retval=@expectedRet and @empLat = @expectedLast) 14 print ‘Pass‘ 15 else 16 print ‘Fail‘
注解:
SQL存储过程有一个常用的设计模式,即存储过程可以通过参数返回一个或多个值。当存储过程返回的值不是int类型时,这个模式是必须的,因为return关键字只接受int类型的变量。
待测存储过程脚本如下:

1 create procedure usp_DeleteEmployee 2 @empID char(3) 3 as 4 delete from dbEmployees.dbo.tblEmployees where empID=@empID
测试这个存储过程的脚本如下:

1 declare @input char(3) 2 3 declare @expected int 4 declare @actual int 5 6 set @input = ‘e22‘ 7 set @expected = 150847775 8 9 exec dbEmployees.dbo.usp_DeleteEmployee @input 10 select @actual=checksum_agg(checksum(*)) from dbEmployees.dbo.tblEmployees 11 if(@actual=@expected) 12 print ‘Pass‘ 13 else 14 print ‘Fail‘
参考
[1] bcp命令详解
标签:style blog http color io os 使用 ar for
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/Ming8006/p/4000157.html