标签:ini ali absolute 指定 one bottom cal 网页 div
一、position属性
1、relative(相对定位)
看下面的例子:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge"> <title>相对定位</title> <style type="text/css"> .box1,.box2,.box3{ width: 100px; height: 100px; } .box1{ background-color: red; } .box2{ background-color:blue; } .box3{ background-color: yellow; } </style> </head> <body> <div class="box"></div> <div class="box1"></div> <div class="box2"></div> <div class="box3"></div> </body> </html>
效果:
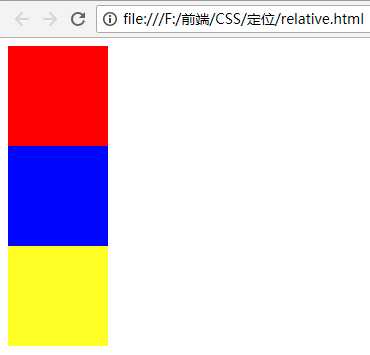
然后分别给第一个和第二个盒子添加定位:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge"> <title>相对定位</title> <style type="text/css"> .box1,.box2,.box3{ width: 100px; height: 100px; } .box1{ background-color: red; position: relative; left: 100px; } .box2{ background-color:blue; position: relative; left: 100px; top: 50px; } .box3{ background-color: yellow; } </style> </head> <body> <div class="box"></div> <div class="box1"></div> <div class="box2"></div> <div class="box3"></div> </body> </html>
效果:
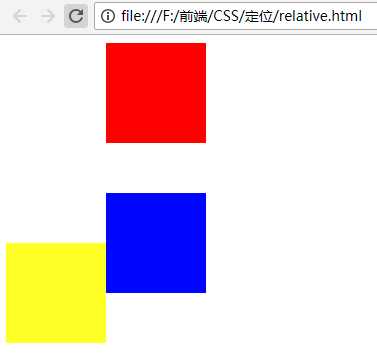
观察上面的截图会发现:第一个和第二个盒子分别相对于原来的位置进行了偏移,但是对父级盒子和相邻的盒子都没有影响。
2、absolute(绝对定位)
看下面的例子:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge"> <title>绝对定位</title> <style type="text/css"> .box1,.box2,.box3{ width: 100px; height: 100px; } .box1{ background-color: red; position: relative; left: 100px; } .box2{ background-color:blue; position: absolute; left: 100px; top: 50px; } .box3{ background-color: yellow; width: 120px; } </style> </head> <body> <div class="box"></div> <div class="box1"></div> <div class="box2"></div> <div class="box3"></div> </body> </html>
效果:
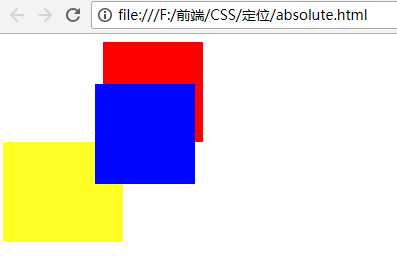
观察上面的截图可以发现:absolute定位是脱离文档流的,是相对于父元素进行偏移。
3、fixed(相对浏览器固定定位,IE6不支持)
看下面的例子:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge"> <title>fixed</title> <style type="text/css"> .box1,.box2,.box3{ width: 100px; height: 100px; } .box1{ background-color: red; position: relative; left: 100px; } .box2{ background-color:blue; position: absolute; left: 100px; top: 50px; } .box3{ background-color: yellow; width: 120px; position: fixed; left: 100px; top: 200px; } </style> </head> <body> <div class="box"></div> <div class="box1"></div> <div class="box2"></div> <div class="box3"></div> <br /><br /><br /><br /><br /><br /><br /><br /><br /><br /><br /><br /><br /><br /><br /> <br /><br /><br /><br /><br /><br /><br /><br /><br /><br /><br /><br /><br /> <br /><br /><br /><br /><br /><br /><br /><br /><br /><br /><br /><br /><br /> <br /><br /><br /><br /><br /><br /><br /> </body> </html>
效果:
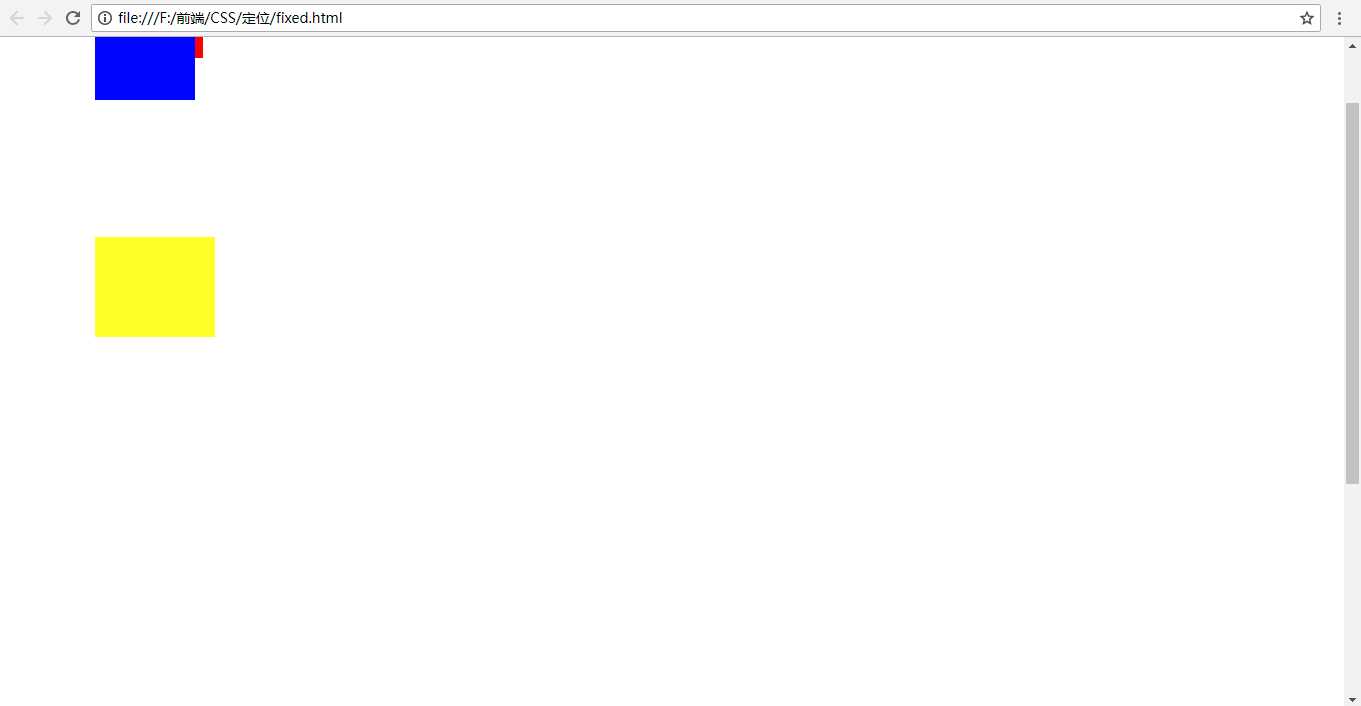
上下移动滚动条的时候你会发现,第三个盒子的位置不会随着滚动条的滚动而上下移动,相对于浏览器是固定的。
4、static(默认)
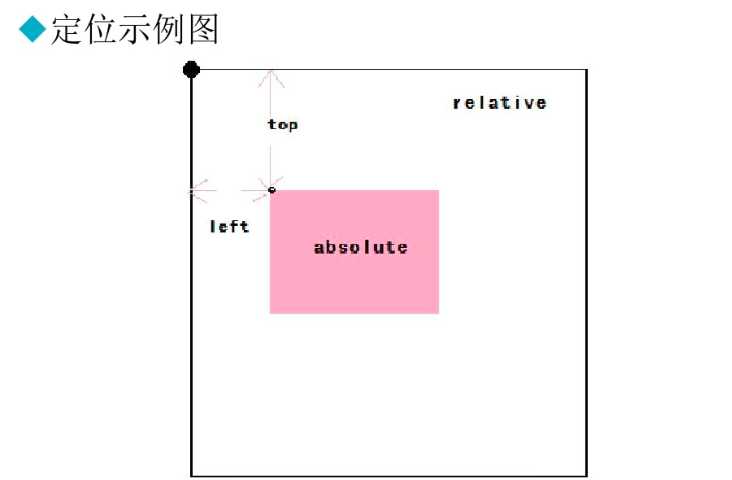
5、定位图解
6、Z-Index
Z-Index用来设置定位盒子的层级
例如:Z-Index:2;
注意:
看下面的例子:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge"> <title>绝对定位</title> <style type="text/css"> .box1,.box2,.box3{ width: 100px; height: 100px; } .box1{ background-color: red; position: relative; left: 100px; } .box2{ background-color:blue; position: absolute; left: 100px; top: 50px; } .box3{ background-color: yellow; width: 120px; } </style> </head> <body> <div class="box"></div> <div class="box1"></div> <div class="box2"></div> <div class="box3"></div> </body> </html>
效果:
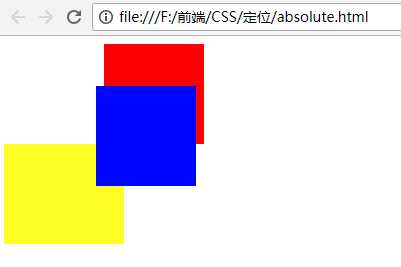
现在给box1添加层级:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge"> <title>绝对定位</title> <style type="text/css"> .box1,.box2,.box3{ width: 100px; height: 100px; } .box1{ background-color: red; position: relative; left: 100px; z-index: 1; } .box2{ background-color:blue; position: absolute; left: 100px; top: 50px; } .box3{ background-color: yellow; width: 120px; } </style> </head> <body> <div class="box"></div> <div class="box1"></div> <div class="box2"></div> <div class="box3"></div> </body> </html>
效果:
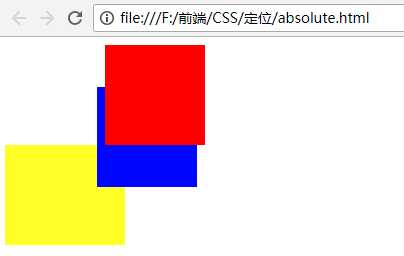
这时box1就会在box2上面。
也可以给box2添加层级:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge"> <title>绝对定位</title> <style type="text/css"> .box1,.box2,.box3{ width: 100px; height: 100px; } .box1{ background-color: red; position: relative; left: 100px; /* z-index: 1; 添加层级 */ } .box2{ background-color:blue; position: absolute; left: 100px; top: 50px; z-index: -2;/*添加负数的层级*/ } .box3{ background-color: yellow; width: 120px; } </style> </head> <body> <div class="box"></div> <div class="box1"></div> <div class="box2"></div> <div class="box3"></div> </body> </html>
效果:

实例:
实现网页横幅的效果:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge"> <title>定位基本应用</title> <style type="text/css"> #adverImg{ width: 426px; height: 130px;/*和图片的宽度和高度一致*/ position: relative;/*父元素添加相对定位*/ border: 1px solid red; } #number{ position: absolute; right: 5px; bottom: -10px; } /*li标签设置样式,使用后代选择器*/ #number li{ list-style: none;/*设置li标签样式:不显示前面的圆点*/ float: left; /*设置浮动:使li标签在一行显示*/ width: 20px; height: 20px; border: 1px solid #666666;/*设置边框*/ margin-left: 5px;/*设置向左的外边距,使每个li标签之间有空格*/ text-align: center;/*设置文字水平方向居中*/ line-height: 20px;/*设置文字垂直方向居中*/ /* color: white; */ cursor: pointer;/*设置鼠标移动到li标签时显示小手的形状*/ background-color: white; } </style> </head> <body> <div id="adverImg"> <img src="images/adver-01.jpg" alt="商品促销" /> <ul id="number"> <li>1</li> <li>2</li> <li>3</li> <li>4</li> <li>5</li> </ul> </div> </body> </html>
效果:
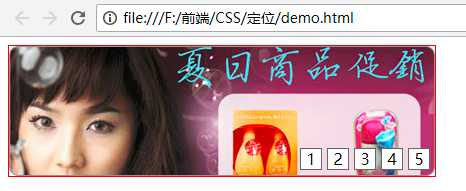
标签:ini ali absolute 指定 one bottom cal 网页 div
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/dotnet261010/p/9563324.html