标签:style blog http color io os 使用 ar java
一、Set概述。
Set集合的特点是元素不允许重复,而且是无序的(添加和取出的顺序不一致)。
Set接口中的方法和Collection接口中的方法几乎相同,略。
Set接口下常用的两个类:HashSet、TreeSet。
二、HashSet类。
1、概述。
HashSet内部的数据结构是哈希表,而且是不同步的。
如果添加了重复元素,则重复的元素不会被添加,只保留第一次的对象。
HashSet的底层实现是怎么样的?
2.底层实现。
HashSet底层的数据结构是哈希表,什么是哈希表?哈希表根据对象的不同特点将对象放在内存中的不同地方,根据的是一个算法,类似这样的结构:
1 function (element) 2 { 3 //一个算法,对元素进行计算,并获取其位置。 4 return index; 5 }
因此,如果想要查找这个对象,只需要通过此算法再算一次,即可找到该对象,这就使得通过哈希表查找元素的速度非常快,而不需要从头遍历。
注意,每个对象都有哈希值,不同的对象拥有不同的哈希值。
3.哈希表是怎么判断相同元素的?
(1)哈希表确定元素是否相同第一步判断的是两个元素的哈希值是否相同。如果相同再判断两个对象的内容是否相同。
(2)判断哈希值是否相同其实判断的就是hashCode方法。判断内容是否相同,使用equals方法(自定义对象的时候两个方法均要重写)。
注意:如果哈希值不同,则不需要判断equals方法。
4.当哈希值相同,而内容不同的时候,该怎么将对象存储?
通过顺延、挂上新链等方式。
5.示例代码:
使用HashSet存储自定义对象。
初始代码:

1 package p01.BaseCollectionDemo; 2 3 import java.util.HashSet; 4 5 class Person 6 { 7 private String name; 8 private int age; 9 public String getName() { 10 return name; 11 } 12 public Person(String name, int age) { 13 super(); 14 this.name = name; 15 this.age = age; 16 } 17 public Person() { 18 super(); 19 } 20 public void setName(String name) { 21 this.name = name; 22 } 23 public int getAge() { 24 return age; 25 } 26 public void setAge(int age) { 27 this.age = age; 28 } 29 @Override 30 public String toString() { 31 return "Person [name=" + name + ", age=" + age + "]\n"; 32 } 33 } 34 35 public class HashSetDemo { 36 37 public static void main(String[] args) { 38 Demo1(); 39 40 } 41 42 private static void Demo1() { 43 HashSet hs=new HashSet(); 44 hs.add(new Person("张三",13)); 45 hs.add(new Person("李四",14)); 46 hs.add(new Person("王五",15)); 47 hs.add(new Person("赵六",16)); 48 hs.add(new Person("陈七",17)); 49 50 hs.add(new Person("张三",13)); 51 hs.add(new Person("李四",14)); 52 System.out.println(hs); 53 } 54 55 }
运行结果:

可以看出,张三、李四添加了两次,这和Set集合不允许添加重复元素相违背。
分析:每次调用add方法都需要和已有的对象做比较,先比较哈希值是否同,如果相同再比较内容是否相同,两个比较是通过hashCode方法、equals方法实现的,但是我们没有重写这两个方法,所以调用了默认的方法,即在Object类中继承而来的方法,hashCode方法是将内存地址转换成整数得到的哈希吗,而equals比较的是对象第至是否相同。因为创建的对象在内存中地址不可能相同,所以HashSet认为是不同的对象。
解决方法:重写hashCode方法和equals方法(这里由于使用了代码补全的功能,所以包括健壮性的判断等做的都很好,可以自定义做出自己的风格)。

1 package p01.BaseCollectionDemo; 2 3 import java.util.HashSet; 4 5 class Person 6 { 7 private String name; 8 private int age; 9 @Override 10 public int hashCode() { 11 final int prime = 31; 12 int result = 1; 13 result = prime * result + age; 14 result = prime * result + ((name == null) ? 0 : name.hashCode()); 15 return result; 16 } 17 @Override 18 public boolean equals(Object obj) { 19 if (this == obj) 20 return true; 21 if (obj == null) 22 return false; 23 if (getClass() != obj.getClass()) 24 return false; 25 Person other = (Person) obj; 26 if (age != other.age) 27 return false; 28 if (name == null) { 29 if (other.name != null) 30 return false; 31 } else if (!name.equals(other.name)) 32 return false; 33 return true; 34 } 35 public String getName() { 36 return name; 37 } 38 public Person(String name, int age) { 39 super(); 40 this.name = name; 41 this.age = age; 42 } 43 public Person() { 44 super(); 45 } 46 public void setName(String name) { 47 this.name = name; 48 } 49 public int getAge() { 50 return age; 51 } 52 public void setAge(int age) { 53 this.age = age; 54 } 55 @Override 56 public String toString() { 57 return "Person [name=" + name + ", age=" + age + "]\n"; 58 } 59 } 60 61 public class HashSetDemo { 62 63 public static void main(String[] args) { 64 Demo1(); 65 66 } 67 68 private static void Demo1() { 69 HashSet hs=new HashSet(); 70 hs.add(new Person("张三",13)); 71 hs.add(new Person("李四",14)); 72 hs.add(new Person("王五",15)); 73 hs.add(new Person("赵六",16)); 74 hs.add(new Person("陈七",17)); 75 76 hs.add(new Person("张三",13)); 77 hs.add(new Person("李四",14)); 78 System.out.println(hs); 79 } 80 81 }

6.思考题:去除重复元素(自定义对象)。
代码一:

1 package p01.BaseCollectionDemo; 2 import java.util.ArrayList; 3 import java.util.HashSet; 4 import java.util.Iterator; 5 class Person 6 { 7 private String name; 8 private int age; 9 public String getName() { 10 return name; 11 } 12 public Person(String name, int age) { 13 super(); 14 this.name = name; 15 this.age = age; 16 } 17 public Person() { 18 super(); 19 } 20 public void setName(String name) { 21 this.name = name; 22 } 23 public int getAge() { 24 return age; 25 } 26 public void setAge(int age) { 27 this.age = age; 28 } 29 @Override 30 public String toString() { 31 return "Person [name=" + name + ", age=" + age + "]\n"; 32 } 33 } 34 35 public class HashSetDemo { 36 37 public static void main(String[] args) { 38 Demo1(); 39 } 40 41 private static void Demo1() { 42 ArrayList hs=new ArrayList(); 43 hs.add(new Person("张三",13)); 44 hs.add(new Person("李四",14)); 45 hs.add(new Person("王五",15)); 46 hs.add(new Person("赵六",16)); 47 hs.add(new Person("陈七",17)); 48 49 hs.add(new Person("张三",13)); 50 hs.add(new Person("李四",14)); 51 System.out.println(hs); 52 ArrayList la=removeCF(hs); 53 System.out.println(la); 54 } 55 56 private static ArrayList removeCF(ArrayList hs) { 57 ArrayList la=new ArrayList(); 58 for(Iterator it=hs.iterator();it.hasNext();) 59 { 60 Person p=(Person)it.next(); 61 if(!la.contains(p)) 62 { 63 la.add(p); 64 } 65 } 66 return la; 67 } 68 69 70 }
运行结果:
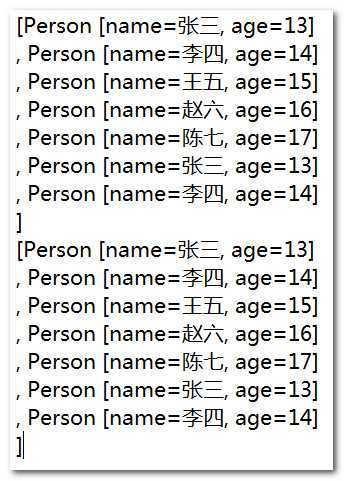
经过比较,发现去除重复元素失败。
原因分析:问题代码肯定出现在
1 if(!la.contains(p))
这里,也就是说contains方法的实现有问题。
查找API,API的描述如下:
如果此列表中包含指定的元素,则返回 true。更确切地讲,当且仅当此列表包含至少一个满足 (o==null ? e==null : o.equals(e)) 的元素 e 时,则返回 true。
所以我们知道了ArrayList 中的contain是方法底层使用的是equals方法,但是我们并没有重写equals方法,这就使得调用了继承自Object类的equals方法,比较的是对象的地址。所以肯定不相同。
解决方法:重写equals方法。

1 package p01.BaseCollectionDemo; 2 import java.util.ArrayList; 3 import java.util.HashSet; 4 import java.util.Iterator; 5 class Person 6 { 7 private String name; 8 private int age; 9 public String getName() { 10 return name; 11 } 12 @Override 13 public boolean equals(Object obj) { 14 if (this == obj) 15 return true; 16 if (obj == null) 17 return false; 18 if (getClass() != obj.getClass()) 19 return false; 20 Person other = (Person) obj; 21 if (age != other.age) 22 return false; 23 if (name == null) { 24 if (other.name != null) 25 return false; 26 } else if (!name.equals(other.name)) 27 return false; 28 return true; 29 } 30 public Person(String name, int age) { 31 super(); 32 this.name = name; 33 this.age = age; 34 } 35 public Person() { 36 super(); 37 } 38 public void setName(String name) { 39 this.name = name; 40 } 41 public int getAge() { 42 return age; 43 } 44 public void setAge(int age) { 45 this.age = age; 46 } 47 @Override 48 public String toString() { 49 return "Person [name=" + name + ", age=" + age + "]\n"; 50 } 51 } 52 53 public class HashSetDemo { 54 55 public static void main(String[] args) { 56 Demo1(); 57 } 58 59 private static void Demo1() { 60 ArrayList hs=new ArrayList(); 61 hs.add(new Person("张三",13)); 62 hs.add(new Person("李四",14)); 63 hs.add(new Person("王五",15)); 64 hs.add(new Person("赵六",16)); 65 hs.add(new Person("陈七",17)); 66 67 hs.add(new Person("张三",13)); 68 hs.add(new Person("李四",14)); 69 System.out.println(hs); 70 ArrayList la=removeCF(hs); 71 System.out.println(la); 72 } 73 74 private static ArrayList removeCF(ArrayList hs) { 75 ArrayList la=new ArrayList(); 76 for(Iterator it=hs.iterator();it.hasNext();) 77 { 78 Person p=(Person)it.next(); 79 if(!la.contains(p)) 80 { 81 la.add(p); 82 } 83 } 84 return la; 85 } 86 87 88 }
运行结果。

假设我们将ArrayList换成HashSet,将以上的过程走一遍,结果又如何?结果是两次都失败!原因还在contains方法上。
contains方法的底层实现是
1 final Entry<K,V> getEntry(Object key) { 2 int hash = (key == null) ? 0 : hash(key); 3 for (Entry<K,V> e = table[indexFor(hash, table.length)]; 4 e != null; 5 e = e.next) { 6 Object k; 7 if (e.hash == hash && 8 ((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k)))) 9 return e; 10 } 11 return null; 12 }
通过这段代码我们可以发现其中一句非常关键:
1 if (e.hash == hash && 2 8 ((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k)))) 3 9 return e;
它将不仅使用equals比较对象内容,而且还比较两个对象的哈希值是否相同。即e.hash==hash这一句。所以,还必须重写hashCode方法才行。

1 package p01.BaseCollectionDemo; 2 import java.util.HashSet; 3 import java.util.Iterator; 4 class Person 5 { 6 private String name; 7 private int age; 8 public String getName() { 9 return name; 10 } 11 12 @Override 13 public int hashCode() { 14 final int prime = 31; 15 int result = 1; 16 result = prime * result + age; 17 result = prime * result + ((name == null) ? 0 : name.hashCode()); 18 return result; 19 } 20 21 @Override 22 public boolean equals(Object obj) { 23 if (this == obj) 24 return true; 25 if (obj == null) 26 return false; 27 if (getClass() != obj.getClass()) 28 return false; 29 Person other = (Person) obj; 30 if (age != other.age) 31 return false; 32 if (name == null) { 33 if (other.name != null) 34 return false; 35 } else if (!name.equals(other.name)) 36 return false; 37 return true; 38 } 39 40 public Person(String name, int age) { 41 super(); 42 this.name = name; 43 this.age = age; 44 } 45 public Person() { 46 super(); 47 } 48 public void setName(String name) { 49 this.name = name; 50 } 51 public int getAge() { 52 return age; 53 } 54 public void setAge(int age) { 55 this.age = age; 56 } 57 @Override 58 public String toString() { 59 return "Person [name=" + name + ", age=" + age + "]\n"; 60 } 61 } 62 63 public class HashSetDemo { 64 65 public static void main(String[] args) { 66 Demo1(); 67 } 68 69 private static void Demo1() { 70 HashSet hs=new HashSet(); 71 hs.add(new Person("张三",13)); 72 hs.add(new Person("李四",14)); 73 hs.add(new Person("王五",15)); 74 hs.add(new Person("赵六",16)); 75 hs.add(new Person("陈七",17)); 76 77 hs.add(new Person("张三",13)); 78 hs.add(new Person("李四",14)); 79 System.out.println(hs); 80 HashSet la=removeCF(hs); 81 System.out.println(la); 82 } 83 84 private static HashSet removeCF(HashSet hs) { 85 HashSet la=new HashSet(); 86 for(Iterator it=hs.iterator();it.hasNext();) 87 { 88 Person p=(Person)it.next(); 89 if(!la.contains(p)) 90 { 91 la.add(p); 92 } 93 } 94 return la; 95 } 96 97 98 }
但是,重写hashCode方法之后,第一次的添加就已经将重复元素去掉了,这体现了JAVA的高度的安全性。
标签:style blog http color io os 使用 ar java
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/kuangdaoyizhimei/p/4009845.html