标签:address open lock success slave deb start receive mutex
1. Linux内核支持I2C通用设备驱动(用户态驱动:由应用层实现对硬件的控制可以称之为用户态驱动),实现文件位于drivers/i2c/i2c-dev.c,设备文件为/dev/i2c-0
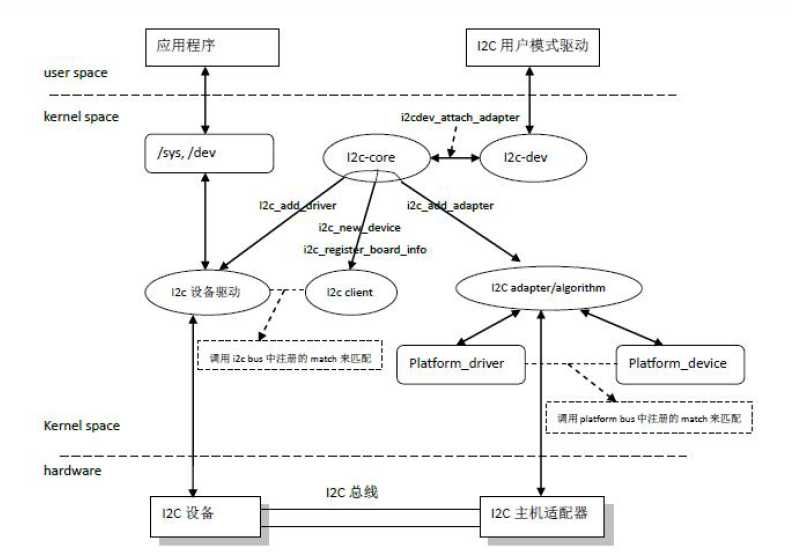
2. I2C通用设备驱动以字符设备注册进内核的
static const struct file_operations i2cdev_fops = { .owner = THIS_MODULE, .llseek = no_llseek, .read = i2cdev_read, .write = i2cdev_write, .unlocked_ioctl = i2cdev_ioctl, .open = i2cdev_open, .release = i2cdev_release, }; res = register_chrdev(I2C_MAJOR, "i2c", &i2cdev_fops);
3. 对设备文件进行读写时,可以调用read、write或者ioctl等方法,他们都是通过调用函数i2c_transfer来实现的
int i2c_transfer(struct i2c_adapter * adap, struct i2c_msg *msgs, int num) { int ret; /* REVISIT the fault reporting model here is weak: * * - When we get an error after receiving N bytes from a slave, * there is no way to report "N". * * - When we get a NAK after transmitting N bytes to a slave, * there is no way to report "N" ... or to let the master * continue executing the rest of this combined message, if * that‘s the appropriate response. * * - When for example "num" is two and we successfully complete * the first message but get an error part way through the * second, it‘s unclear whether that should be reported as * one (discarding status on the second message) or errno * (discarding status on the first one). */ if (adap->algo->master_xfer) { #ifdef DEBUG for (ret = 0; ret < num; ret++) { dev_dbg(&adap->dev, "master_xfer[%d] %c, addr=0x%02x, " "len=%d%s\n", ret, (msgs[ret].flags & I2C_M_RD) ? ‘R‘ : ‘W‘, msgs[ret].addr, msgs[ret].len, (msgs[ret].flags & I2C_M_RECV_LEN) ? "+" : ""); } #endif if (in_atomic() || irqs_disabled()) { ret = mutex_trylock(&adap->bus_lock); if (!ret) /* I2C activity is ongoing. */ return -EAGAIN; } else { mutex_lock_nested(&adap->bus_lock, adap->level); } ret = adap->algo->master_xfer(adap,msgs,num); mutex_unlock(&adap->bus_lock); return ret; } else { dev_dbg(&adap->dev, "I2C level transfers not supported\n"); return -EOPNOTSUPP; } }
4. i2c_transfer通过代码可以看出,i2c_transfer 通过调用相应的 adapter 的 master_xfer 方法实现的,而 master_xfer 主要是根据 struct i2c_msg 类型的msgs来进行处理的。
struct i2c_msg { __u16 addr; /* slave address */ __u16 flags; #define I2C_M_TEN 0x0010 /* this is a ten bit chip address */ #define I2C_M_RD 0x0001 /* read data, from slave to master */ #define I2C_M_NOSTART 0x4000 /* if I2C_FUNC_PROTOCOL_MANGLING */ #define I2C_M_REV_DIR_ADDR 0x2000 /* if I2C_FUNC_PROTOCOL_MANGLING */ #define I2C_M_IGNORE_NAK 0x1000 /* if I2C_FUNC_PROTOCOL_MANGLING */ #define I2C_M_NO_RD_ACK 0x0800 /* if I2C_FUNC_PROTOCOL_MANGLING */ #define I2C_M_RECV_LEN 0x0400 /* length will be first received byte */ __u16 len; /* msg length */ __u8 *buf; /* pointer to msg data */ };
5. I2C用户态驱动简单示例
标签:address open lock success slave deb start receive mutex
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/wulei0630/p/9607606.html