标签:constant inf form ati 1.4 public util 环境 测试
1:还是先上一个类的继承关系比较图吧!
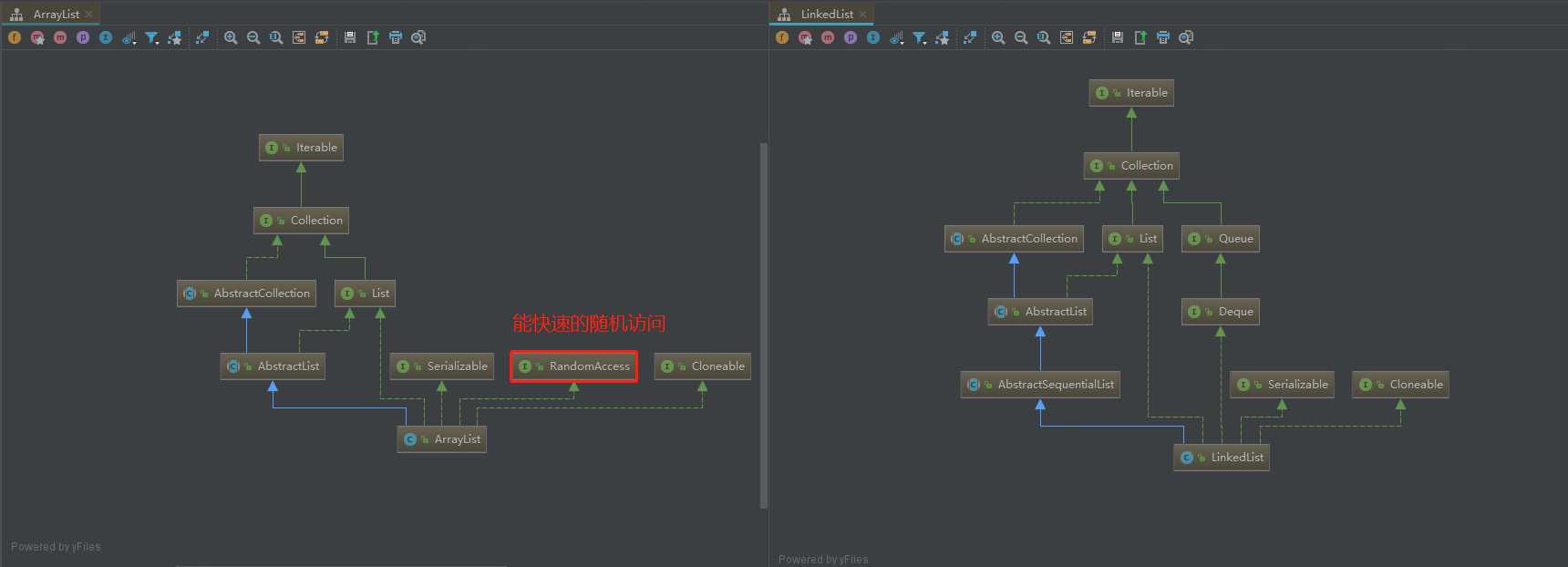
2:看一下 RandomAccess.java 的源码,空空如也,什么都没有,那她有什么用处呢?
/** * Marker interface used by <tt>List</tt> implementations to indicate that * they support fast (generally constant time) random access. The primary * purpose of this interface is to allow generic algorithms to alter their * behavior to provide good performance when applied to either random or * sequential access lists. * * <p>The best algorithms for manipulating random access lists (such as * <tt>ArrayList</tt>) can produce quadratic behavior when applied to * sequential access lists (such as <tt>LinkedList</tt>). Generic list * algorithms are encouraged to check whether the given list is an * <tt>instanceof</tt> this interface before applying an algorithm that would * provide poor performance if it were applied to a sequential access list, * and to alter their behavior if necessary to guarantee acceptable * performance. * * <p>It is recognized that the distinction between random and sequential * access is often fuzzy. For example, some <tt>List</tt> implementations * provide asymptotically linear access times if they get huge, but constant * access times in practice. Such a <tt>List</tt> implementation * should generally implement this interface. As a rule of thumb, a * <tt>List</tt> implementation should implement this interface if, * for typical instances of the class, this loop: * <pre> * for (int i=0, n=list.size(); i < n; i++) * list.get(i); * </pre> * runs faster than this loop: * <pre> * for (Iterator i=list.iterator(); i.hasNext(); ) * i.next(); * </pre> * * <p>This interface is a member of the * <a href="{@docRoot}/../technotes/guides/collections/index.html"> * Java Collections Framework</a>. * * @since 1.4 */ public interface RandomAccess { }
有点磕磕巴巴,阅读了源码中的注释,大概讲解了一下 RandomAccess.java 接口的作用,它是一个标记接口,表示实现它的类支持快速随机访问,通过上图的对比我们看到实现List接口的类,有些是支持快速随机访问的,有些不支持,怎么标记哪?就是用 RandomAccess.java 接口来标记,这样有什么好处呢?可以在通用的实现List集合遍历的时候算法中,针对实现 RandomAccess.java 接口的集合,可以有选择性的使用性能更好的遍历方式,我也实验了一把,继续往下看吧!
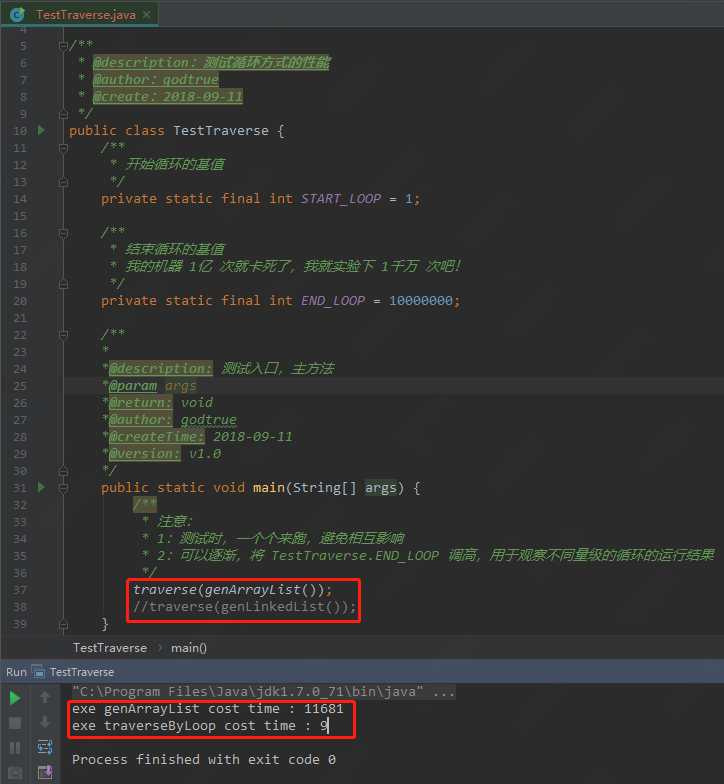
3:简单的集合遍历性能对比小栗子,代码比较简单,可以调整参数自行玩一玩
/** * @description:测试循环方式的性能 * @author:godtrue * @create:2018-09-11 */ public class TestTraverse { /** * 开始循环的基值 */ private static final int START_LOOP = 1; /** * 结束循环的基值 * 我的机器 1亿 次就卡死了,我就实验下 1千万 次吧! */ private static final int END_LOOP = 10000000; /** * *@description: 测试入口,主方法 *@param args *@return: void *@author: godtrue *@createTime: 2018-09-11 *@version: v1.0 */ public static void main(String[] args) { /** * 注意: * 1:测试时,一个个来跑,避免相互影响 * 2:可以逐渐,将 TestTraverse.END_LOOP 调高,用于观察不同量级的循环的运行结果 */ traverse(genArrayList()); //traverse(genLinkedList()); } /** * *@description: 遍历 list 集合,这里能体现到 RandomAccess 接口的作用,可以选择不同的遍历集合的方式 *@param list *@return: void *@author: godtrue *@createTime: 2018-09-11 *@version: v1.0 */ private static void traverse(List list){ if(list instanceof RandomAccess){ traverseByLoop(list); }else { traverseByIterator(list); } } /** * *@description: 循环遍历 list 集合 *@param list *@return: void *@author: godtrue *@createTime: 2018-09-11 *@version: v1.0 */ private static void traverseByLoop(List list){ long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); for(int i=0,sum=list.size();i<sum;i++){ list.get(i); } System.out.println("exe traverseByLoop cost time : "+(System.currentTimeMillis()-startTime)); } /** * *@description: 迭代遍历 list 集合 *@param list *@return: void *@author: godtrue *@createTime: 2018-09-11 *@version: v1.0 */ private static void traverseByIterator(List list){ long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); for (Iterator i=list.iterator(); i.hasNext(); ){ i.next(); } System.out.println("exe traverseByIterator cost time : "+(System.currentTimeMillis()-startTime)); } /** * *@description: 生成 ArrayList 数据信息 *@param *@return: java.util.List<java.lang.String> *@author: godtrue *@createTime: 2018-09-11 *@version: v1.0 */ private static List<String> genArrayList(){ long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); List<String> list = new ArrayList<String>(); for(int i=TestTraverse.START_LOOP;i<TestTraverse.END_LOOP;i++){ list.add(String.valueOf(i)); } System.out.println("exe genArrayList cost time : "+(System.currentTimeMillis()-startTime)); return list; } /** * *@description: 生成 LinkedList 数据信息 *@param *@return: java.util.List<java.lang.String> *@author: godtrue *@createTime: 2018-09-11 *@version: v1.0 */ private static List<String> genLinkedList(){ long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); List<String> list = new LinkedList<String>(); for(int i=TestTraverse.START_LOOP;i<TestTraverse.END_LOOP;i++){ list.add(String.valueOf(i)); } System.out.println("exe genLinkedList cost time : "+(System.currentTimeMillis()-startTime)); return list; } }
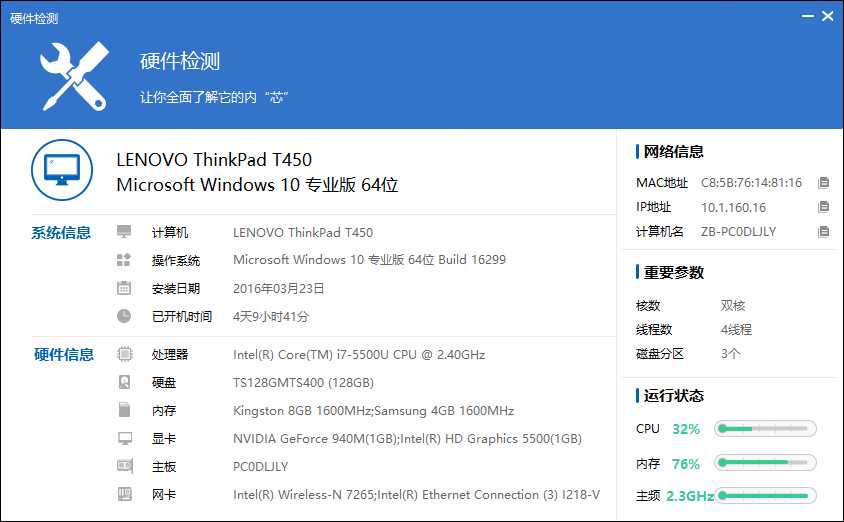
4:下面是实验环境的信息和结果
4-1)实验的硬件信息
4-2)运行时的性能指标参数
4-3)迭代遍历的运行情况
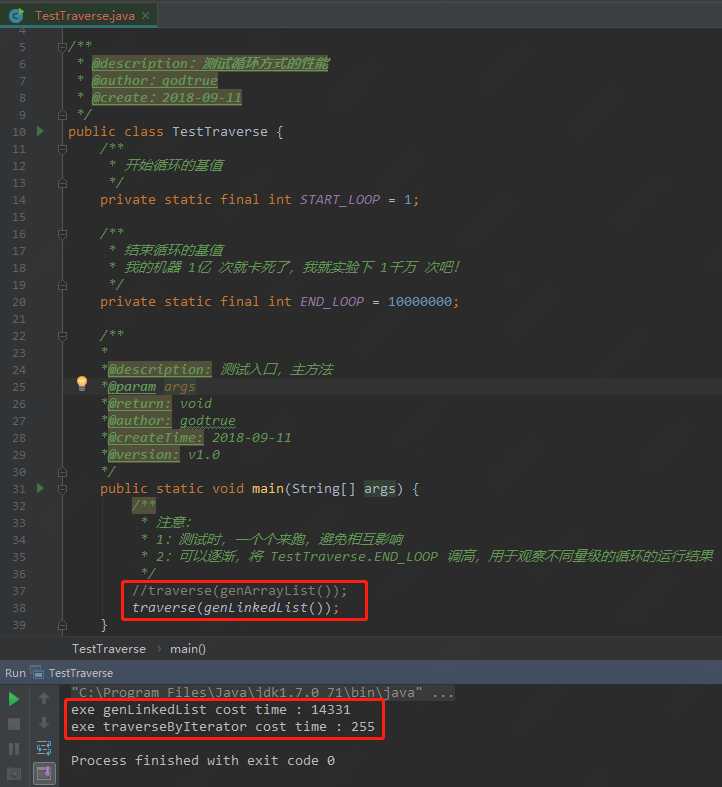
4-4)随机遍历的运行情况,对比一下,可以看出性能相差的还是蛮多的
标签:constant inf form ati 1.4 public util 环境 测试
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/godtrue/p/9630498.html