标签:org www. stat agg load 多实例 sel ycm his
MongoDB是一个著名的NoSQL数据库,即非关系型数据库(没有外键,我们之前介绍的redis也属于非关系型数据库)
MongoDB 将数据存储为一个文档,数据结构由键值(key=>value)对组成。MongoDB 文档类似于 JSON 对象
MongoDB是文件型数据库,不存在关系
MongoDB中基本上存储了大量的冗余数据
MongoDB中没有字段的概念
MongoDB是非常灵活的数据库
特点:可以处理超大量的数据
MongoDB是由C++编写的,易用性强
MongoDB设计旨在保持它的高性能
支持bootstrap
MongoDB数据结构类型:
[ { ids:1, names:子龙, ages:84, courses:python, scores:99 }, { id:2, name:xiaoqinglong, age:73, course:javascript, score1:99 } ]
这里每一个字典的数据可以看做是我们关系型数据库中的每一行数据
地址链接,获取它的msi安装包,直接下一步下一步即可
安装完后需要配置环境变量,获取我们安装下的bin文件路径,它当中包含着可执行文件(exe结尾)
开启服务端:
配置完后直接在终端下输入mongod,开启数据库服务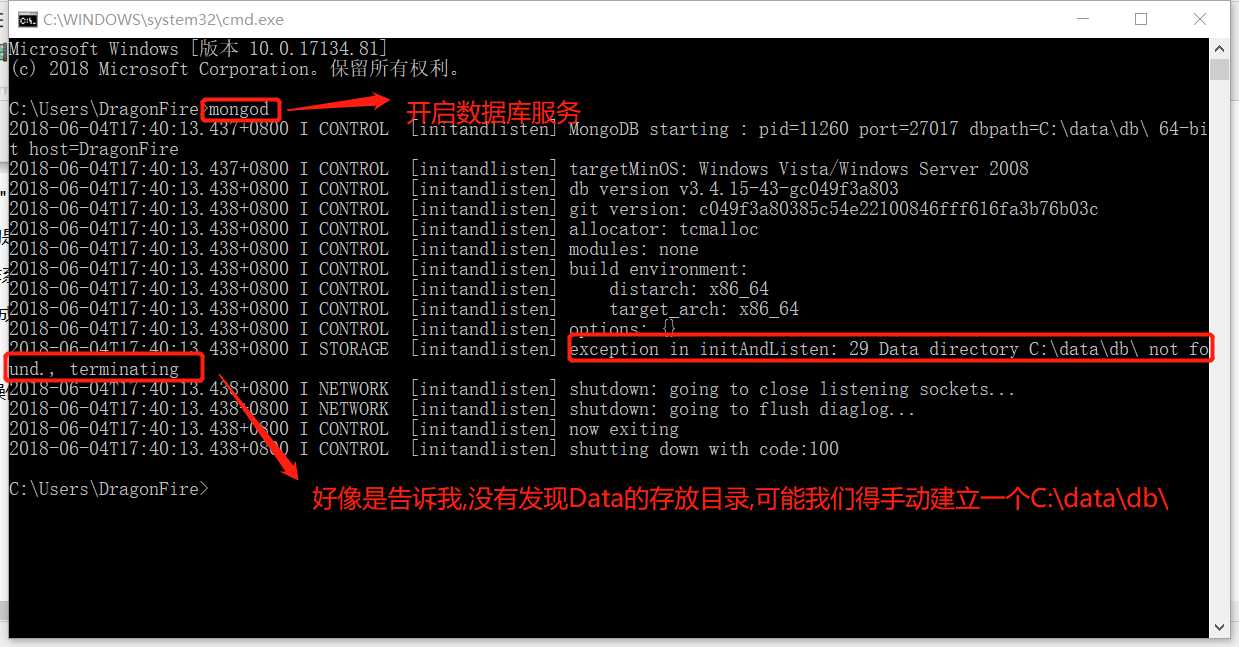
终端提示需要一个data文件,当中必须有一个db文件,来存放我们的数据,直接通过mkdir c:\data\db命令创建即可
再次运行ok,最终显示等待连接,会一直hang住,此时服务端开启成功
开启客户端:
在开启一个终端,输入mongo命令,既可以开启我们的服务端(这里它会默认连接27017端口)
补充说明:如果没有装在C盘,比如在D盘。每次启动时需要切换到D盘来启动我们的数据库,我就是这样,我把db文件也创建在了D盘,只有这样每次才能连接上我们的db文件
详细安装教程参考:猛戳此处
1、显示数据库列表:show dbs
2、切换/创建数据库: use dabaseA (dabaseA为数据库名,如果该数据库不存在,则会创建)
3、删除当前数据库:db.dropDatabase() --当执行use dabaseA命令后,当前数据库就是dabaseA,所以再执行db.dropDatabase(),删除的当前数据库就是dabaseA。
4、显示当前数据库中的操作命令:db.help()
5、显示当前数据库中的集合:show collections (这里的集合类似关系数据库中的表)
6、显示数据库中某集合的操作命令: db.table.help() (这里的table是当前数据库中一个集合)
7、往某一集合中插入数据:db.person.insert({‘name‘:‘小王‘, ‘age‘ : 20, ‘sex‘:‘男‘}) 或者 db.person.save({‘name‘:‘小王‘, ‘age‘ : 20, ‘sex‘:‘男‘})
8、mongodb的save和insert函数都可以向collection里插入数据,但两者是有两个区别:
•使用save函数里,如果原来的对象不存在,那他们都可以向collection里插入数据,如果已经存在,save会调用update更新里面的记录,
而insert则会忽略操作•insert可以一次性插入一个列表,而不用遍历,效率高, save则需要遍历列表,一个个插入,效率稍低
例如:已存在数据: {_id : ‘abc123‘, " name " : " 小王 " },再次进行插入操作时,
insert({_id : ‘abc123‘, " name " : " 小李 " }) 会报主键重复的错误提示
save({ _id : ‘abc123‘, " name " : " 小李 " }) 会把 小王 修改为 小李 。
如果集合中不存在 _id : ‘abc123‘,
insert({_id : ‘abc123‘, " name " : " 小李 " }) 增加一条数据
save({ _id : ‘abc123‘, " name " : " 小李 " }) 增加一条数据
9、查看当前使用的数据库:db 或 db.getName() 两者效果一样
10、显示当前数据库的状态:db.stats()
11、显示当前数据库的版本 :db.version()
12、显示当前数据库链接的地址:db.getMongo()
13、在指定的机器上,从数据库A,负责数据到B:db.copyDatabase("mydb", "temp", "127.0.0.1") 将本机的mydb的数据复制到temp数据库中
14、显示当前数据库中所有集合: db.getCollectionNames()
15、显示数据库的状态:db.table.stats()
16、删除当前数据库中某个集合:db.table.drop() 删除集合 table
17、删除当前数据库某个集合中的所有数据:db.table.remove({}) 删除集合 table中所有数据
18、删除当前数据库某个集合中 name=‘test‘的记录:db.table.remove({name:‘test‘})
19、删除当前数据库某个集合中所有数据:db.Information.remove({})
查看集合基本命令
1、查看当前数据库中某集合中的帮助:db.table.help()
2、查看某集合的数据条数:db.table.count()
3、查看某集合数据空间大小: db.table.dataSize() 单位是字节
4、查看某集合的总空间大小:db.table.storageSize()
详细介绍参考此处,细节介绍很详细
创建数据库:
use test_db # 有则使用,无则创建
insert(不推荐)
inertOne
insertMany
db.test_one.insertOne({"name":"sss","age":22})
样式
{ "acknowledged" : true, "insertedId" : ObjectId("5b990a644dce8e90571e7ddf") }
find
> db.test_one.find() { "_id" : ObjectId("5b99080912f2dacc6d2d710f"), "name" : "learning", "age" : 23 } { "_id" : ObjectId("5b9909cf8c013a2e4cfbadac"), "name" : "bib", "age" : 22 } { "_id" : ObjectId("5b990a0c8c013a2e4cfbadad"), "name" : "orc", "age" : 22 } { "_id" : ObjectId("5b990a644dce8e90571e7ddf"), "name" : "sss", "age" : 22 } >
MongoDB自动给我们添加到系统唯一标识"_id" 是一个ObjectId 类型
按条件查找
> db.test_one.find({"name":"orc"})
{ "_id" : ObjectId("5b990a0c8c013a2e4cfbadad"), "name" : "orc", "age" : 22 }
>
findOne() # 默认查找当前Collection的第一条数据
> db.test_one.findOne() { "_id" : ObjectId("5b99080912f2dacc6d2d710f"), "name" : "learning", "age" : 23 } >
update(不推荐使用)
updateOne
updateMany
# 把learning的修改成24
> db.test_one.updateOne({"name":"learning"},{$set:{"age":24}})
{ "acknowledged" : true, "matchedCount" : 1, "modifiedCount" : 1 }
>
remove -->可以根据条件删除
remove({}) -->删除所有数据
# 删除用户learning的数据
> db.test_one.remove({"name":"learning"})
WriteResult({ "nRemoved" : 1 })
>
详细介绍参考博客:猛戳此处
Object ID :Documents 自生成的 _id
String: 字符串,必须是utf-8
Boolean:布尔值,true 或者false (这里有坑哦~在我们大Python中 True False 首字母大写)
Integer:整数 (Int32 Int64 你们就知道有个Int就行了,一般我们用Int32)
Double:浮点数 (没有float类型,所有小数都是Double)
Arrays:数组或者列表,多个值存储到一个键 (list哦,大Python中的List哦)
Object:如果你学过Python的话,那么这个概念特别好理解,就是Python中的字典,这个数据类型就是字典
Null:空数据类型 , 一个特殊的概念,None Null
Timestamp:时间戳
Date:存储当前日期或时间unix时间格式 (我们一般不用这个Date类型,时间戳可以秒杀一切时间类型)
Arrays
{ "_id" : ObjectId("5b151f8536409809ab2e6b26"), "name" : "Apple", "place" : ["China","America","New Zealand"] }
Object
{ "_id" : ObjectId("5b151f8536409809ab2e6b26"), "name" : "LuffyCity", "course" : {"name" : "Python","price" : 19800 } }
1、查询索引记录:相当于select * from table
db.table.find()
2、查询age = 22的记录
db.table.find({age:22})
3、查询age >22的记录
db.table.find({age:{$gt:22}})
db.table.find("this.age>22")
4、查询age>=22的记录
db.table.find({age:{$gte:22}})
db.table.find("this.age>=22")
5、查询age <30的记录
db.table.find({age:{$lt:30}})
db.table.find("this.age<30")
6、查询age <=30的记录
db.table.find({age:{$lte:30}})
db.table.find("this.age<=30")
7、查询age >20 并且age<30的记录
db.table.find({age:{gt:20,gt:20,lt :30}})
db.table.find("this.age>20 && this.age<30")
8、查询集合中name 包含mongo的数据,相当于like ‘%mongo%‘ 模糊查询
db.table.find({name:/mongo/})
9、查询集合中 name中以mongo开头的数据,相当于like ‘mongo%‘ 模糊查询
db.table.find({name:/^mongo/})
10、查询集合中,只查询,name和age两列
db.table.find({},{name:1,age:1})
11、查询结合中age>10 ,并且只查询 name 和 age两列
db.table.find({age:{$gt:10}},{name:1,age:1})
12、按年龄排序
db.table.find().sort({age:1,name:1}) 按照年龄和姓名升序
db.table.find().sort({age:-1,name:1}) 按照年龄降序,姓名升序
python:db.table.find().sort(‘age‘,pymongo.ASCENDING) 或 db.table.find().sort(‘age‘,1)升序;
db.table.find().sort(‘age‘,pymongo.DESCENDING) 或db.table.find().sort(‘age‘,-1)降序
db.table.find().sort([(‘age‘,pymongo.DESCENDING),(‘name‘,pymongo.ASCENDING)]) 年龄降序,姓名升序
或db.table.find().sort([(‘age‘,-1),(‘name‘:1)])年龄降序,姓名升序
注意mongo和python里面命令的区别是冒号,python是逗号
13、查询前10条数据,相当于select top 10 from table
db.table.find().limit(10)
14、查询10条以后的数据,相当于 select * from table where id not in (select top * from table )
db.table.find().skip(10)
15、查询5-10条之间的数据
db.table.find().skip(5).limit(10)
16、查询 age =10 or age =20的记录
db.table.find({$or:[{age:20},{age:30}]})
17、查询age >20的记录条数
db.table.find({age:{$gt:20}}).count()
18、查询age>30 or age <20 的记录
db.table.find({or:[{age:{or:[{age:{gt:30}},{age:{$lt:20}}]})
db.table.find("this.age>30 || this.age<20")
19、查询age >40 or name =‘mike‘的记录
db.table.find({or:[{age:{or:[{age:{gt:40}},{name:‘mike‘}]})
20、查询age >40 or name =‘mike‘的记录,只查询name 和age两列,并且按照name升序,age降序
db.table.find({or:[{age:{or:[{age:{gt:40}},{name:‘mike‘}]},{name:1,age:-1})
查询age >40 并且 name =‘mike‘的记录,只查询name 和age两列,并且按照name升序,age降序
db.table.find({and:[{age:{and:[{age:{gt:40}},{name:‘mike‘}]},{name:1,age:-1})
python 代码:db.table.find({‘and‘:[{age:{‘$gt‘:40}},{‘name‘:‘mike‘}]},{‘name‘:1,‘age‘:-1}) 像and‘:[{age:{‘$gt‘:40}},{‘name‘:‘mike‘}]},{‘name‘:1,‘age‘:-1}) 像and和字段名必须在引号内,否则报错
21、查询age 在[30,40] 内的记录
db.table.find({age:{$in:[30,40]}})
22、查询age不在[30,40]范围内的记录
db.table.find({age:{$nin:[30,40]}})
23、查询age能被3整除的记录
db.table.find({age:{$mod:[3,0]}})
23、查询age能被3整除余2的记录
db.table.find({age:{$mod:[3,2]}})
//假如有以下文档 { ‘name‘ : { ‘first‘ : ‘Joe‘, ‘last‘ : ‘Schmoe‘ } ‘age‘ : 45 }
24、查询姓名为询姓名是Joe Schmoe的记录
db.table.find({‘name.first‘:‘Joe‘,‘name.last‘:‘Schmoe‘})
db.table.find({name:{first:‘Joe‘,last:‘Schmoe‘}})
25、如果需要多个元素来匹配数组,就需要使用$all了
//假设在我们表中3个下面的文档:
db.food.insert({‘_id‘ : 1,‘fruit‘ : [‘apple‘, ‘banana‘, ‘peach‘]})
db.food.insert({‘_id‘ : 2,‘fruit‘ : [‘apple‘, ‘kumquat‘, ‘orange‘]})
db.food.insert({‘_id‘ : 3,‘fruit‘ : [‘cherry‘, ‘banana‘, ‘apple‘]})
要找到既有apple又有banana的文档:
db.food.find({fruit:{$all:[‘apple‘, ‘banana‘]}})
26、查询age不是30并且性别不是‘男’的记录,就用到 $nor
db.person.find({$nor:[{age:30},{sex:‘男‘}]})
db.jdftdata.find({$nor:[{content:"-1"}]})
27、查询age不大于30的记录 ,用到not,not,not执行逻辑NOT运算,选择出不能匹配表达式的文档 ,包括没有指定键的文档。
db.person.find({age:{not:{not:{gt:30}}})
28、如果$exists的值为true,选择存在该字段的文档;若值为false则选择不包含该字段的文档。
选择age存在,且不在[30,40]只能的记录
db.person.find({age:{exists:true,exists:true,nin:[30,40]}})
29、查询name中包括字母t的记录,类似 name like ‘%t%‘
db.person.find({name:/t/})
db.person.find({name:{$regex:/t/}})
db.person.find({name:/t/i}) i在这里是不区分大小写
db.person.find({name:{regex:/t/,regex:/t/,options:‘i‘}}) i在这里是不区分大小写
30、查询name中以t字母结尾的记录,类似 name like ‘%t‘, 要用到符号$
db.person.find({name:/t$/})
31、如果在查询的时候需要多个元素来匹配数组,就需要用到$all了,这样就匹配一组元素。
例如:假如创建了包含3个元素的如下集合:
{ "_id" : 1, "fruit" : [ "apple", "banana", "peach" ] }
{ "_id" : 2, "fruit" : [ "apple", "pear", "orange" ] }
{ "_id" : 3, "fruit" : [ "cherry", "banana", "apple" ] }
要找到既有apple, 又有banana的文档,就要用到$all
db.food.find({fruit:{$all:[‘apple‘,‘banana‘]}})
查询结果如下:
> db.food.find({fruit:{$all:[‘apple‘,‘banana‘]}})
{ "_id" : 1, "fruit" : [ "apple", "banana", "peach" ] }
{ "_id" : 3, "fruit" : [ "cherry", "banana", "apple" ] }
注意两条结果记录的apple和banana的顺序是不一样的,也就是说,顺序无关紧要。
要是想查询指定数组位置的元素,则需要用key.index语法指定下标
db.food.find({‘fruit.2‘:‘peach‘}),结果为:
{ "_id" : 1, "fruit" : [ "apple", "banana", "peach" ] }
32、null
null比较奇怪,它确实能匹配本身,假如有下面的数据:
{ "_id" : 1, "fruit" : [ "apple", "banana", "peach" ] }
{ "_id" : 2, "fruit" : [ "apple", "pear", "orange" ] }
{ "_id" : 3, "fruit" : [ "cherry", "banana", "apple" ] }
{ "_id" : 4, "fruit" : null }
db.food.find({fruit:null}) 查询结果:{ "_id" : 4, "fruit" : null }
但是null不仅能匹配本身,而且能匹配“不存在的” ,例如:
db.food.find({x: null}) ,food集合中本来不包含x键的,结果如下:
> db.food.find({x:null})
{ "_id" : 1, "fruit" : [ "apple", "banana", "peach" ] }
{ "_id" : 2, "fruit" : [ "apple", "pear", "orange" ] }
{ "_id" : 3, "fruit" : [ "cherry", "banana", "apple" ] }
{ "_id" : 4, "fruit" : null }
33、$size 对于查询来说也是意义非凡,顾名思义就是可用它来查询指定长度的数组。
比如有以下数据:
{ "_id" : 1, "fruit" : [ "apple", "banana", "peach" ] }
{ "_id" : 2, "fruit" : [ "apple", "pear", "orange" ] }
{ "_id" : 3, "fruit" : [ "cherry", "banana", "apple" ] }
{ "_id" : 4, "fruit" : null }
{ "_id" : 5, "fruit" : [ "apple", "orange" ] }
db.food.find({fruit:{$size:3}}) 查询结果如下:fruit对应的数组的长度为3
{ "_id" : 1, "fruit" : [ "apple", "banana", "peach" ] }
{ "_id" : 2, "fruit" : [ "apple", "pear", "orange" ] }
{ "_id" : 3, "fruit" : [ "cherry", "banana", "apple" ] }
db.food.find({fruit:{$size:1}}) 查询结果如下:fruit对应的数组的长度为1
{ "_id" : 5, "fruit" : [ "apple", "orange" ] }
34、slice 可以按偏移量返回记录,针对数组。如{"slice 可以按偏移量返回记录,针对数组。如{"slice":10}返回前10条,{"$slice":{[23,10]}}从24条取10条
例如在集合food中有数据如下:
{ "_id" : 1, "fruit" : [ "apple", "pear", "orange", "strawberry", "banana" ], "name" : "fruitName1" }
{ "_id" : 2, "fruit" : [ "apple", "orange", "pear", "banana" ], "name" : "fruitName2" }
{ "_id" : 3, "fruit" : [ "cherry", "banana", "apple" ], "name" : "fruitName3" }
{ "_id" : 4, "fruit" : null }
针对fruit 如何只获取该键对应数据前个数据,{"$slice":2}
查询语句:db.food.find({},{fruit:{$slice:2}}) 查询结果为:
{ "_id" : 1, "fruit" : [ "apple", "pear" ], "name" : "fruitName1" } 注意fruit对应的数据,只获取了,前两个数据,后面的去掉了
{ "_id" : 2, "fruit" : [ "apple", "orange" ], "name" : "fruitName2" }
{ "_id" : 3, "fruit" : [ "cherry", "banana" ], "name" : "fruitName3" }
{ "_id" : 4, "fruit" : null }
针对fruit 如何只获取该键对应数据从第二个数据开始取,取两个,{"$slice":[1,2]}
查询语句:db.food.find({},{fruit:{$slice:[1,2]}}) 查询结果为:
{ "_id" : 1, "fruit" : [ "pear", "orange" ], "name" : "fruitName1" }
{ "_id" : 2, "fruit" : [ "orange", "pear" ], "name" : "fruitName2" }
{ "_id" : 3, "fruit" : [ "banana", "apple" ], "name" : "fruitName3" }
{ "_id" : 4, "fruit" : null }
35、 $elemMatch
如果对象有一个元素是数组,那么$elemMatch可以匹配内数组内的元素。
例如数据集school中有如下数据:
{ "_id" : 1, "zipcode" : "63109", "students" : [ { "name" : "john", "school" : 102, "age" : 10 }, { "name" : "jess", "school" : 102, "age" : 11 },
{ "name" : "jeff", "school" : 108, "age" : 15 } ] }
{ "_id" : 2, "zipcode" : "63110", "students" : [ { "name" : "ajax", "school" : 100, "age" : 7 }, { "name" : "achilles", "school" : 100, "age" : 8 } ] }
{ "_id" : 3, "zipcode" : "63108", "students" : [ { "name" : "ajax", "school" : 100, "age" : 7 }, { "name" : "achilles", "school" : 100, "age" : 8 } ] }
{ "_id" : 4, "zipcode" : "63109", "students" : [ { "name" : "barney", "school" : 102, "age" : 7 }, { "name" : "ruth", "school" : 102, "age" : 16 } ] }
{ "_id" : 5, "zipcode" : "63109", "students" : [ { "name" : "barney", "school" : 102, "age" : 12 }, { "name" : "ruth", "school" : 102, "age" : 16 } ] }
要查询 zipcode="63109" ,school= ‘102’ 并且 age>10的记录
db.school.find( { zipcode: "63109" },{ students: { elemMatch: { school: 102 ,age:{elemMatch: { school: 102 ,age:{gt: 10}} } } )
查询结果:
{ "_id" : 1, "students" : [ { "name" : "jess", "school" : 102, "age" : 11 } ] }
{ "_id" : 4, "students" : [ { "name" : "ruth", "school" : 102, "age" : 16 } ] }
{ "_id" : 5, "students" : [ { "name" : "barney", "school" : 102, "age" : 12 } ] }
36、$exists
判断某个字段是否存在,查询school集合中存在zipcode字段的记录
db.school.find({zipcode:{$exists:1}})
37、假如有集合school ,数据如下:
{ "_id" : 1, "zipcode" : "63109", "students" : [ { "name" : "john", "school" : 102, "age" : 10 }, { "name" : "jess", "school" : 102, "age" : 11 }, { "name" : "jeff", "school" : 108, "age" : 15 } ] }
{ "_id" : 2, "zipcode" : "63110", "students" : [ { "name" : "ajax", "school" : 100, "age" : 7 }, { "name" : "achilles", "school" : 100, "age" : 8 } ] }
{ "_id" : 3, "zipcode" : "63109", "students" : [ { "name" : "ajax", "school" : 100, "age" : 7 }, { "name" : "achilles", "school" : 100, "age" : 8 } ] }
{ "_id" : 4, "zipcode" : "63109", "students" : [ { "name" : "barney", "school" : 102, "age" : 7 }, { "name" : "ruth", "school" : 102, "age" : 16 } ] }
{ "_id" : 5, "zipcode" : "63109", "students" : [ { "name" : "barney", "school" : 102, "age" : 12 }, { "name" : "ruth", "school" : 102, "age" : 16 } ] }
如果只查询students字段里面的内容,并且只查询school =102 的姓名和年龄信息:
查询语句为:db.school.find({‘students.school‘ : 102},{‘students.name‘:1,‘students.age‘:1})
结果如下:
{ "_id" : 1, "students" : [ { "name" : "john", "age" : 10 }, { "name" : "jess", "age" : 11 }, { "name" : "jeff", "age" : 15 } ] }
{ "_id" : 4, "students" : [ { "name" : "barney", "age" : 7 }, { "name" : "ruth", "age" : 16 } ] }
{ "_id" : 5, "students" : [ { "name" : "barney", "age" : 12 }, { "name" : "ruth", "age" : 16 } ] }
假设school 集合中包含一些记录:students字段对应一个数据字典
{ "_id" : 7, "zipcode" : "63109", "students" : { "name" : "jike", "school" : "102", "age" : 45 } }
{ "_id" : 8, "zipcode" : "63109", "students" : { "name" : "Marry", "school" : "100", "age" : 75 } }
如果只查询字段students对应name和age信息,则查询语句如下:
db.school.find({_id : {$gt:5}},{‘students.name‘:1,‘students.age‘:1})
结果为:这里_id是必须要显示的
{ "_id" : 7, "students" : { "name" : "jike", "age" : 45 } }
{ "_id" : 8, "students" : { "name" : "Marry", "age" : 75 } }
1、$set 用法:{ $set : { field : value } } 就是相当于sql的set field = value,全部数据类型都支持$set。例: db.col.update({‘title‘:‘MongoDB 教程‘},{$set:{‘title‘:‘MongoDB‘}}) db.col.update({‘title‘:‘MongoDB 教程‘},{$set:{‘title‘:‘MongoDB‘,‘flag‘:1}}) 一次更新两个字段 更多实例: 只更新第一条记录: db.col.update( { "count" : { $gt : 2 } } , { $set : { "test" : "Yes"} } ); 全部更新: db.col.update( { "count" : { $gt : 6 } } , { $set : { "test" : "Yes"} },false,true ); 只添加第一条: db.col.update( { "count" : { $gt : 2 } } , { $set : { "test" : "Yes"} },true,false ); 全部更新: db.col.update( { "count" : { $gt : 30 } } , { $inc : { "count" : 1} },false,true ); 只更新第一条记录: db.col.update( { "count" : { $gt : 50 } } , { $inc : { "count" : 1} },false,false ); 2、$inc 用法:{ $inc : { field : value } } 意思对一个数字字段field增加value,例:在集合food中有一条数据: { "_id" : 5, "count" : 6 } ,如果count的值增加2,则更新语句为: db.food.update({_id : 5},{$inc : {count : 2}}) 执行结果为: { "_id" : 5, "count" : 8 } 3、$unset 用法:{ $unset : { field : 1} } 顾名思义,就是删除字段了. 有数据如下: { "_id" : 1, "fruit" : [ "apple", "pear", "orange", "strawberry", "banana" ], "name" : "fruitName1" } { "_id" : 2, "fruit" : [ "apple", "orange", "pear", "banana" ], "name" : "fruitName2" } { "_id" : 3, "fruit" : [ "cherry", "banana", "apple" ], "name" : "fruitName3" } { "_id" : 4, "fruit" : null } { "_id" : 5, "count" : 17 } 如果要把第一条数据中name字段删除,更新语句为: db.food.update({_id : 1},{$unset : {name : 1}}) 4、$push 用法:{ $push : { field : value } } 把value追加到field里面去,field一定要是数组类型才行,如果field不存在,会新增一个数组类型加进去。 现在集合food中有数据如下: { "_id" : 1, "fruit" : [ "apple", "pear", "orange", "strawberry", "banana" ] } 给fruit对应的数组中增加一个数据:"peach",则更新语句为: db.food.update({_id : 1}, {$push : {fruit : ‘peach‘}}) 执行结果为 { "_id" : 1, "fruit" : [ "apple", "pear", "orange", "strawberry", "banana", "peach" ] } 如果再给这条数据中更新,一个不存在的字段addCol的数据‘newColumn‘,则增加进去,如下: db.food.update({_id : 1}, {$push : {addCol:‘newColumn‘}}) 则执行结果如下: { "_id" : 1, "fruit" : [ "apple", "pear", "orange", "strawberry", "banana", "peach" ], "addCol" : [ "newColumn" ] } 5、 $pushAll 用法:{ $pushAll : { field : value_array } } 同$push,只是一次可以追加多个值到一个数组字段内。 例如在集合food 中有一条数据如下: { "_id" : 3, "fruit" : [ "cherry", "banana", "apple" ], "name" : "fruitName3" } 如果要把 "orange", "strawberry" 数据更新到fruit对应的数组中,则更新语句为: db.food.update({_id : 3} , {$pushAll : {fruit :["orange", "strawberry"]}})执行结果如下: { "_id" : 3, "fruit" : [ "apple", "orange", "strawberry", "orange", "strawberry" ], "name" : "fruitName3" } 6、 $addToSet 用法:{ $addToSet : { field : value } } 增加一个值到数组内,而且只有当这个值不在数组内才增加 例如集合food中有一下数据: { "_id" : 1, "fruit" : [ "apple", "pear", "orange", "strawberry", "banana", "peach" ], "addCol" : [ "newColumn" ] } { "_id" : 2, "fruit" : [ "apple", "orange", "pear", "banana" ], "name" : "fruitName2" } { "_id" : 3, "fruit" : [ "apple", "orange", "strawberry", "orange", "strawberry" ], "name" : "fruitName3" } 如果给集合中所有fruit对应的数组中增加一个数据"peach",更新语句为: db.food.update({_id :{$gt: 0}},{$addToSet : {fruit : ‘peach‘},false,true}) 执行结果为: { "_id" : 1, "fruit" : [ "apple", "pear", "orange", "strawberry", "banana", "peach" ], "addCol" : [ "newColumn" ] } { "_id" : 2, "fruit" : [ "apple", "orange", "pear", "banana", "peach" ], "name" : "fruitName2" } { "_id" : 3, "fruit" : [ "apple", "orange", "strawberry", "orange", "strawberry", "peach" ], "name" : "fruitName3" } 7、 $pop 删除数组内的一个值 用法:删除最后一个值:{ pop : { field : 1 } }删除第一个值:{pop : { field : 1 } }删除第一个值:{pop : { field : -1 } } 注意,只能删除一个值 对于数据:{ "_id" : 1, "fruit" : [ "apple", "pear", "orange", "strawberry" ], "addCol" : [ "newColumn" ] } 执行 db.food.update({_id : 1},{$pop : {fruit : 1}}) 把 "strawberry"删除掉结果如下: { "_id" : 1, "fruit" : [ "apple", "pear", "orange" ], "addCol" : [ "newColumn" ] } 再执行 db.food.update({_id : 1},{$pop : {fruit : -1}}) 把 "apple"删除掉结果如下: { "_id" : 1, "fruit" : ["pear", "orange" ], "addCol" : [ "newColumn" ] } 8、$pull 用法:$pull : { field : value } } 从数组field内删除一个等于value值。 对应集合food的数据{ "_id" : 1, "fruit" : [ "apple", "pear", "orange", "strawberry", "banana", "peach" ], "addCol" : [ "newColumn" ] } 删除 "orange" 更新语句为:db.food.update({_id : 1},{$pull : {fruit :‘orange‘}}) 结果为:{ "_id" : 1, "fruit" : [ "apple", "pear", "strawberry", "banana", "peach" ], "addCol" : [ "newColumn" ] } 9、$pullAll 用法:{ $pullAll : { field : value_array } } 同$pull,可以一次删除数组内的多个值。 对于集合food中的数据{ "_id" : 1, "fruit" : [ "orange", "strawberry", "banana", "apple", "peach" ], "addCol" : [ "newColumn" ] } 如果删除 ‘apple‘和‘orange‘ 那么更新语句为:db.food.update({_id : 1}, {$pullAll: {fruit : [‘apple‘, ‘orange‘]}}) 执行结果为:{ "_id" : 1, "fruit" : [ "strawberry", "banana", "peach" ], "addCol" : [ "newColumn" ] }
来源参考:猛戳此处
标签:org www. stat agg load 多实例 sel ycm his
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/LearningOnline/p/9637739.html