标签:数字 表达 理论 分享图片 buffered lis 字符串 格式化 ima
理论知识学习部分
第一章:简单了解java语言的程序设计平台及java的优劣。
第二章:安装java开发工具包,使用命令行工具,使用集成开发环境,进行简单的java程序设计。
第三章:3.1-3.7 了解注释类型,数据类型,变量,运算符,字符串,输入输出(读取输入,格式化输出,文件输入与输出)。
3.8 五种语句:控制语句:if,switch(分支),for while,do while(循环)
方法调用语句:system.out.pritln(“...”)
表达式语句:x=23;i++;
复合语句:{z=x+3;ststem.out...}用{}括起来
package语句和import语句
3.9 当基本的整数和浮点数精度不能满足需求是,可以使用java.math包中的两种类:BigInteger和BigDecimal。
3.10 数组名字=new 数组元素类型【个数】
如:boy=new float[5]
int[] age=new int[10]
for each 循环语句的循环变量会历遍数组中每个元素,而不需要使用下标值。
实验部分
实验2:
公民身份证号码按照GB11643—1999《公民身份证号码》国家标准编制,由18位数字组成:前6位为行政区划分代码,第7位至14位为出生日期码,第15位至17位为顺序码,第18位为校验码。从键盘输入1个身份证号,将身份证号的年月日抽取出来,按年-月-日格式输出。注意:输入使用Scanner类的nextLine()方法,以免出错。
输入样例:
34080019810819327X
输出样例:
1981-08-19
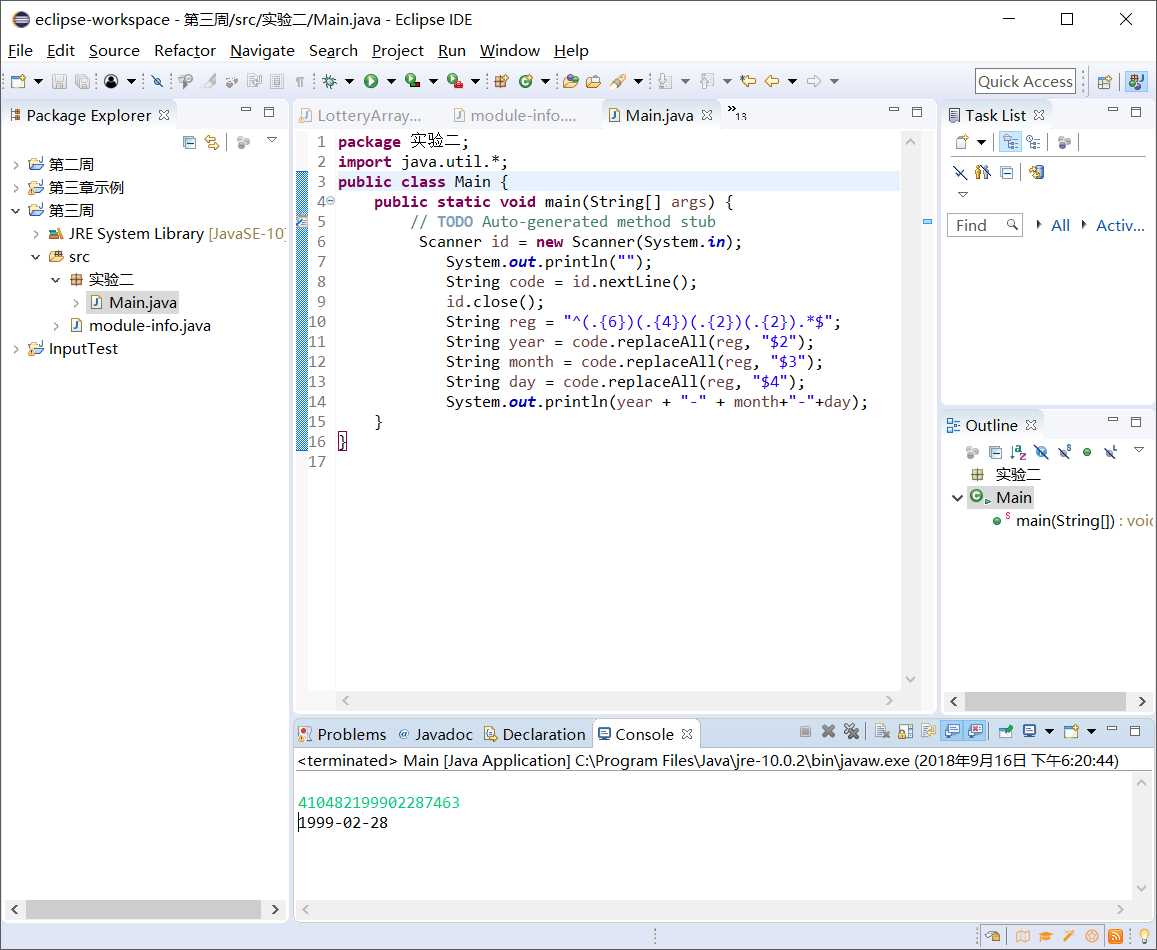
ps:本实验做字符串截取
实验3:
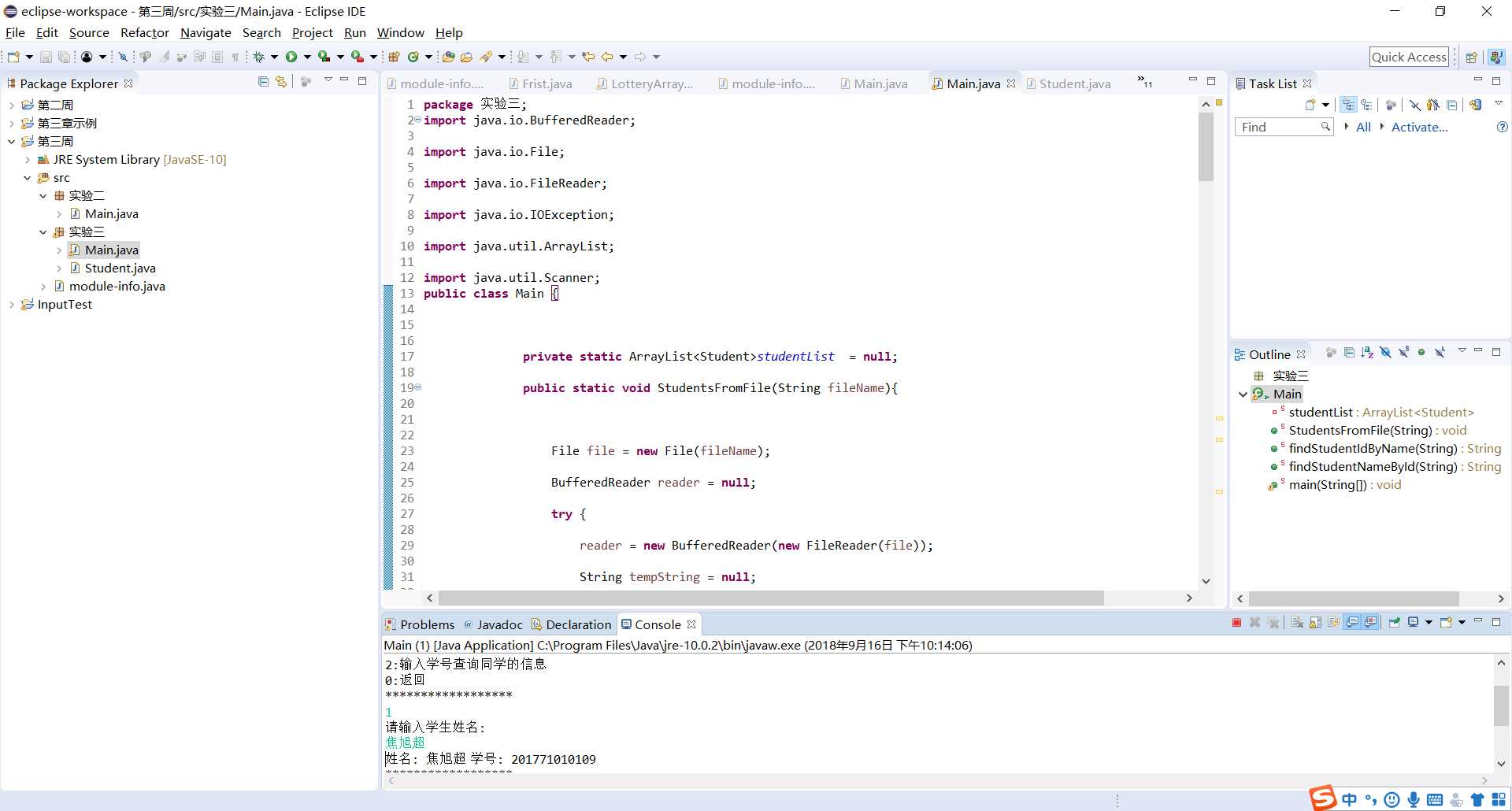
studentfile.txt文件内容是本班同学的学号与姓名,利用此文件编制一个程序,将studentfile.txt文件的信息读入到内存,并提供两类查询功能:
(1)输入姓名查询学号;(2)输入学号查询姓名。
要求程序具有友好人机交互界面。
(1)从文件中读入学生信息,可以编写如下函数:
public static void StudentsFromFile(String fileName))
(2)输入姓名查找学生学号,可以编写如下函数:
public static String findStudent(String name)
(3)输入学号查找学生姓名,可以编写如下函数:
public static String findStudent(String ID)
代码如下:
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
private static ArrayList<Student>studentList = null;
public static void StudentsFromFile(String fileName){
File file = new File(fileName);
BufferedReader reader = null;
try {
reader = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(file));
String tempString = null;
while ((tempString = reader.readLine()) != null) {
String str[] = tempString.split(" ");
if(studentList!= null && str.length > 1) {
//Object studentId;
Student student = new Student();
student.setStudentId(str[0]);
student.setName(str[1]);
studentList.add(student);
}
}
reader.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if (reader != null) {
try {
reader.close();
} catch (IOException e1) {
}
}
}
}
public static String findStudentIdByName(String name) {
String studentId = null;
for(Student student : studentList) {
if(student.getName().equals(name)) {
studentId = student.getStudentId();
break;
}
}
return studentId;
}
public static String findStudentNameById(String ID) {
String studentName = null;
for(Student student : studentList) {
if(student.getStudentId().equals(ID)) {
studentName = student.getName();
break;
}
}
return studentName;
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
String path = "C:\\studentfile.txt";
studentList = new ArrayList<Student>();
StudentsFromFile(path);
int statu = 1;
System.out.println();
while(statu != 0) {
System.out.println("******************");
System.out.println("1:输入姓名查询同学的信息");
System.out.println("2:输入学号查询同学的信息");
System.out.println("0:返回");
System.out.println("******************");
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
statu = in.nextInt();
switch(statu) {
case 1:{ System.out.println("请输入学生姓名:");
Scanner scanner1 = new Scanner(System.in);
String name = scanner1.nextLine();
String Id = findStudentIdByName(name);
if(Id != null) {
System.out.println("姓名: "+name+" 学号: "+Id);
}else {
System.out.println("无此学生,请确认");
}
}break;
case 2:{
System.out.println("请输入学生学号:");
Scanner scanner2 = new Scanner(System.in);
String Id = scanner2.nextLine();
String name = findStudentNameById(Id);
if(name != null) {
System.out.println("姓名: "+name+" 学号: "+Id);
}else {
System.out.println("无此学生,请确认");
}
}break;
case 0:
statu = 0; break;
default:
System.out.println("输入错误");
}
}
System.out.println("结束!");
}
}
实验总结
这一周学习的理论知识不多,但都比较重要,流程控制语句如:条件语句,循环语句等相关语句的知识,和大数值的和数组的知识。实验三用到了前面学习的文件读写等内容,难度比较大,所以请教了其他同学。通过本次实验我知道前面学习的知识都没有掌握。接下来还要继续努力。
焦旭超201771010109《面向对象程序设计(java)》第三周学习总结
标签:数字 表达 理论 分享图片 buffered lis 字符串 格式化 ima
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/lcjcc/p/9657818.html