标签:else 一起 文件的 evel orm 写入文件 部分 字符 blob
实现一个自动生成小学四则运算题目的命令行程序.
1. 使用 -n 参数控制生成题目的个数
2. 使用 -r 参数控制题目中数值(自然数、真分数和真分数分母)的范围
3.使用 -e,-a参数对给定的题目文件和答案文件,判定答案中的对错并进行数量统计
4.程序应能支持一万道题目的生成
分为3个块内容,第一个是生成表达式,第二个是写入文件以及读取文件,第三个是命令行控制
通过上一次的作业,储备了知识,使我对字符串的处理能力有所提升,处理带分数和假分数的相互转换比较方便,
但是在添加括号的处理以及解析题目文件计算答案还是花了挺多时间的。 其他的基本就按照设计图的思路按部就班的进行。
主要的函数有:
getSymbol():#获得符号列表
getNumerical(i,r):#获得数值列表
calculate(a,b,c):#计算
cf(fraction):#真分数的表达
rcf(fra):#真分数转化为分数
writeFormula(symbol,numerical,syb):#算术表达式
getFormula(n,r):#生成题目和答案列表
text_save(filename, data):#filename为写入文件的路径,data为要写入数据列表.
answers_read(filename):#解析答案文件
exercises_read(filename):#解析题目文件
checkAnswer(a,e,ra,re):#检查答案
controlParameter():#命令行控制模块
if __name__ == ‘__main__‘:#主函数
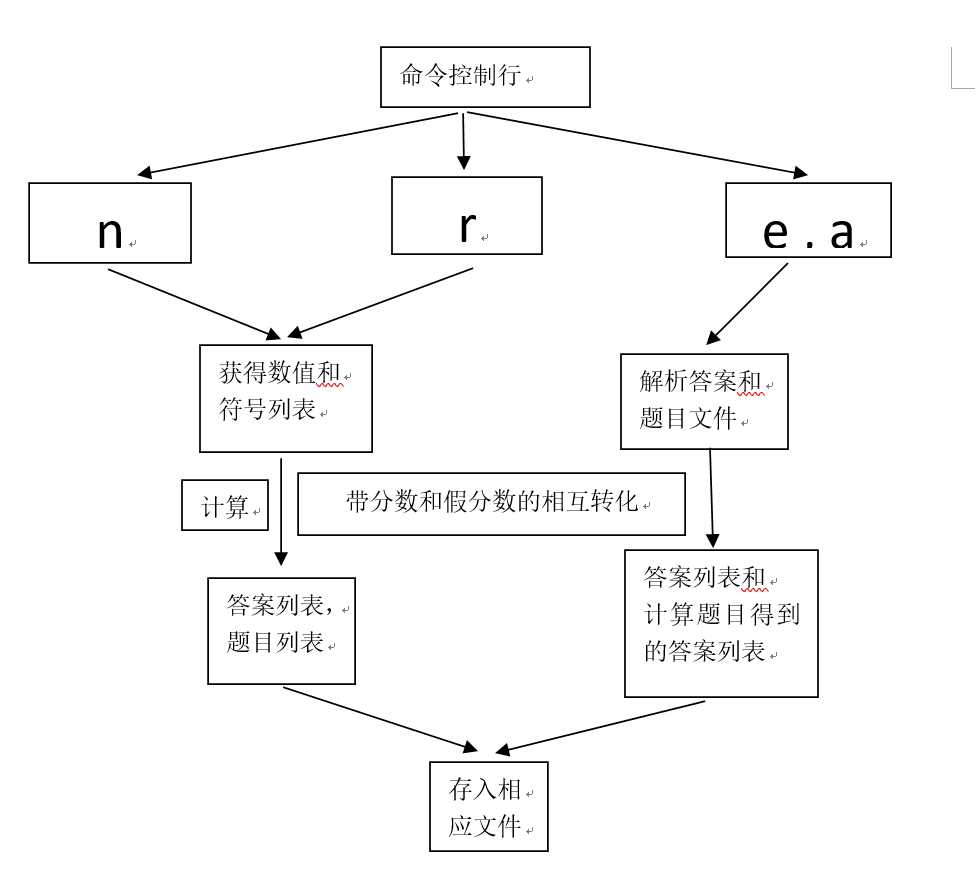
usage: Myapp.py [-h] [-n N] [-r R] [-e E] [-a A]
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
-n N 题目数量
-r R 题目中数值的范围
-e E 题目文件
-a A 答案文件
所有的功能函数:
def getSymbol():#获得符号列表 symbol=[] syb=0 i=random.randint(1, 3) for x in range(i): sy=random.choice([‘+‘,‘-‘,‘ב,‘÷‘]) if sy==‘+‘or sy==‘-‘: syb +=10**(i-x-1) else : syb += 2 * (10 ** (i - x - 1)) symbol.append(sy) return symbol,i,syb def getNumerical(i,r):#获得数值列表 numerical,n,m=[],1,0 if r < 10: n = int(10 / r) if n==1: while m <= i: numerical.append(Fraction(random.randint(1, r), random.randint(1, r))) m+=1 else: while m <= i: nu = Fraction(random.randint(1, r * n), random.randint(1, r * n)) if nu<=r: numerical.append(nu) m += 1 return numerical def calculate(a,b,c):#计算 answer=0 if c==‘+‘: answer=a+b elif c==‘-‘: if a>=b:answer=a-b else:answer=-1 elif c==‘ב: answer=a*b else:answer=a/b return answer def cf(fraction):#真分数的表达 if fraction.numerator%fraction.denominator==0: return ‘%d‘%(fraction.numerator/fraction.denominator) elif fraction.numerator>fraction.denominator: a=int(fraction.numerator/fraction.denominator) b, c = fraction.numerator - a * fraction.denominator, fraction.denominator return ‘%d%s%d%s%d‘ % (a,‘’‘,b,‘/‘,c) else: b, c = fraction.numerator, fraction.denominator return ‘%d%s%d‘ % (b,‘/‘,c) def rcf(fra):#真分数转化为分数 line = re.sub(r‘[\’\/]‘, ‘ ‘, fra) wo = line.split(‘ ‘) # 空格分割单词 wo = [int(x) for x in wo] i=len(wo) if i==1: return wo[0] elif i==2: return Fraction(wo[0], wo[1]) else:return Fraction(wo[0]*wo[2]+wo[1], wo[2]) def writeFormula(symbol,numerical,syb):#算术表达式 s=‘‘ if syb>100: if syb == 112 or syb ==212: s = ‘(%s %s %s %s %s) %s %s = ‘ % (cf(numerical[0]), symbol[0], cf(numerical[1]),symbol[1], cf(numerical[2]), symbol[2], cf(numerical[3])) elif syb == 121 or syb ==122: s = ‘(%s %s %s) %s %s %s %s = ‘ % (cf(numerical[0]), symbol[0], cf(numerical[1]),symbol[1], cf(numerical[2]), symbol[2], cf(numerical[3])) else: s = ‘%s %s %s %s %s %s %s = ‘ % (cf(numerical[0]), symbol[0], cf(numerical[1]),symbol[1], cf(numerical[2]), symbol[2], cf(numerical[3])) elif syb>10: if syb == 12: s = ‘(%s %s %s)%s %s = ‘ % (cf(numerical[0]), symbol[0], cf(numerical[1]), symbol[1], cf(numerical[2])) else: s = ‘%s %s %s %s %s = ‘ % (cf(numerical[0]), symbol[0], cf(numerical[1]), symbol[1], cf(numerical[2])) else : s =‘%s %s %s = ‘ % (cf(numerical[0]),symbol[0],cf(numerical[1])) return s def getFormula(n,r):#生成题目和答案列表 Exercises,Answers,Exercises1,Exercises2=[],[],[],[] x=1 while x<n+1: symbol,i,syb=getSymbol() numerical=getNumerical(i,r) answer = numerical[0] legal = True for y in range(i): cal=calculate(answer,numerical[y+1],symbol[y]) if cal>=0:#判断算式是否合法 answer=cal else: legal=False break if legal:#判断是否重复题目 try: num=Answers.index(answer)#第一个重复答案的索引 if operator.eq(Exercises1[num],symbol) and operator.eq(Exercises2[num],numerical): pass except ValueError as e:#可以写入 Answers.append(answer) Exercises1.append(symbol) Exercises2.append(numerical) Exercises.append(‘%d. %s‘%(x,writeFormula(symbol,numerical,syb))) x+=1 else:pass return Exercises,Answers def text_save(filename, data):#filename为写入文件的路径,data为要写入数据列表. file = open(filename,‘a‘) file.seek(0) file.truncate() # 清空文件 for x in data: x=‘%s\n‘%(x) file.write(x) file.close() print(‘%s文件保存成功‘%filename) def answers_read(filename): file = open(filename) read = file.readlines() answers=[] for line in read: line = re.sub(r‘\n‘, ‘‘, line) answers.append(line.split(‘ ‘)[1])#字符串 return answers def exercises_read(filename): file = open(filename) read = file.readlines() answers2= [] for line in read: line = re.sub(r‘[\.\(\)\=\s]+‘, ‘ ‘, line) line = line.strip() # 除去左右的空格 wo = line.split( ) # 空格分割单词 del wo[0] sy,nu=[],[] for x in range(len(wo)): if x%2: sy.append(wo[x]) else:nu.append(rcf(wo[x])) ans = nu[0] for y in range(len(sy)): ans = calculate(ans, nu[y + 1], sy[y]) answers2.append(ans) return answers2 def checkAnswer(a,e,ra,re): correct,wrong=[],[] for x in range(len(ra)): if operator.eq(ra[x],cf(re[x])): correct.append(x+1) else:wrong.append(x+1) file = open(‘Grade.txt‘, ‘a‘) file.seek(0) file.truncate() # 清空文件 x1=‘Correct:%d%s\n‘%(len(correct),correct) x2=‘Wrong:%d%s‘%(len(wrong),wrong) file.write(x1) file.write(x2) file.close() print(‘题目文件%s与答案文件%s比对成功,结果已存入Grade.txt‘%(e,a)) def controlParameter():#命令行控制模块 parser = argparse.ArgumentParser() parser.add_argument(‘-n‘, help=‘题目数量‘,type=int) parser.add_argument(‘-r‘, help=‘题目中数值的范围‘,type=int) parser.add_argument(‘-e‘, help=‘题目文件‘,type=str) parser.add_argument(‘-a‘, help=‘答案文件‘,type=str) return parser.parse_args()
主函数:
if __name__ == ‘__main__‘:#主函数 n=10#设置默认值 args=controlParameter() if args.n: n=args.n if args.r: r=args.r Exercises, Answers=getFormula(n,r) for x in range(n): Answers[x]=‘%d. %s‘%(x+1,cf(Answers[x])) print(‘n,r两个参数的值为%d,%d:‘%(n,r)) text_save(‘Exercises.txt‘,Exercises) text_save(‘Answers.txt‘,Answers) if args.e and args.a:#‘Answers.txt‘,‘Exercises.txt‘ Answers1=args.a Exercises1=args.e checkAnswer(Answers1,Exercises1,answers_read(Answers1), exercises_read(Exercises1))
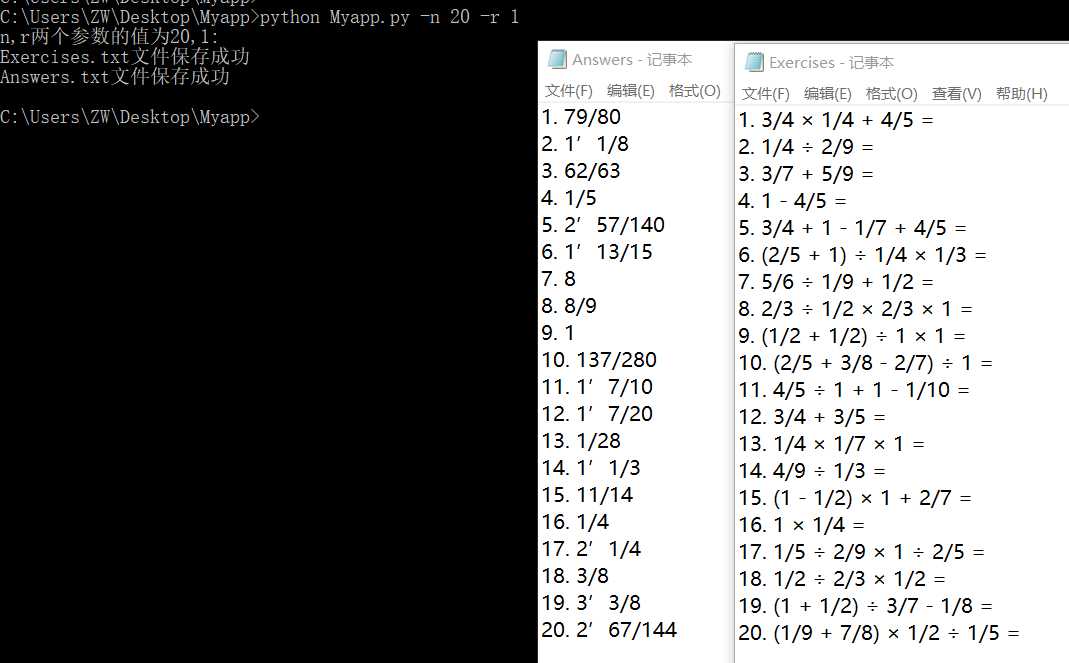
普通-n,-r参数测试
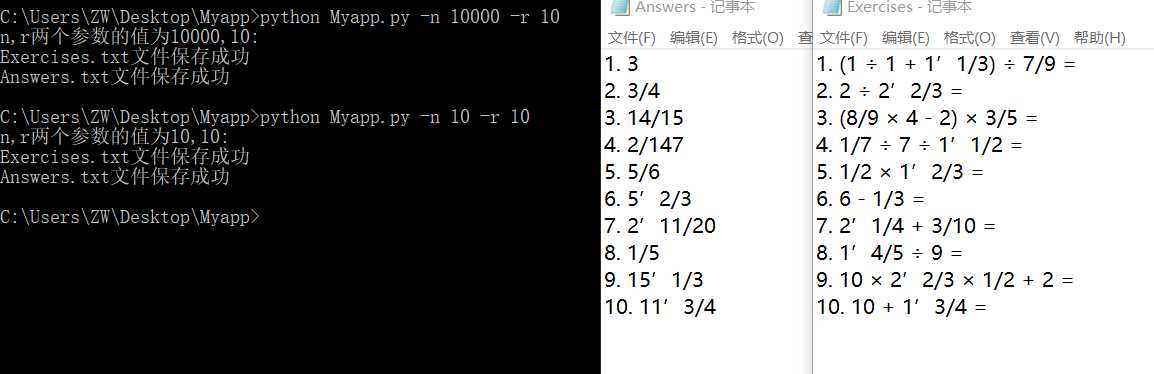
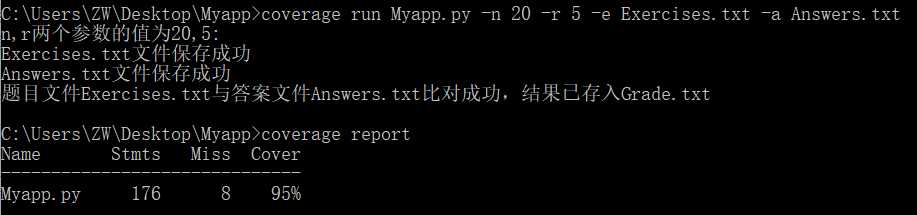
一万道题目测试,经过了稍微久一点的等待:
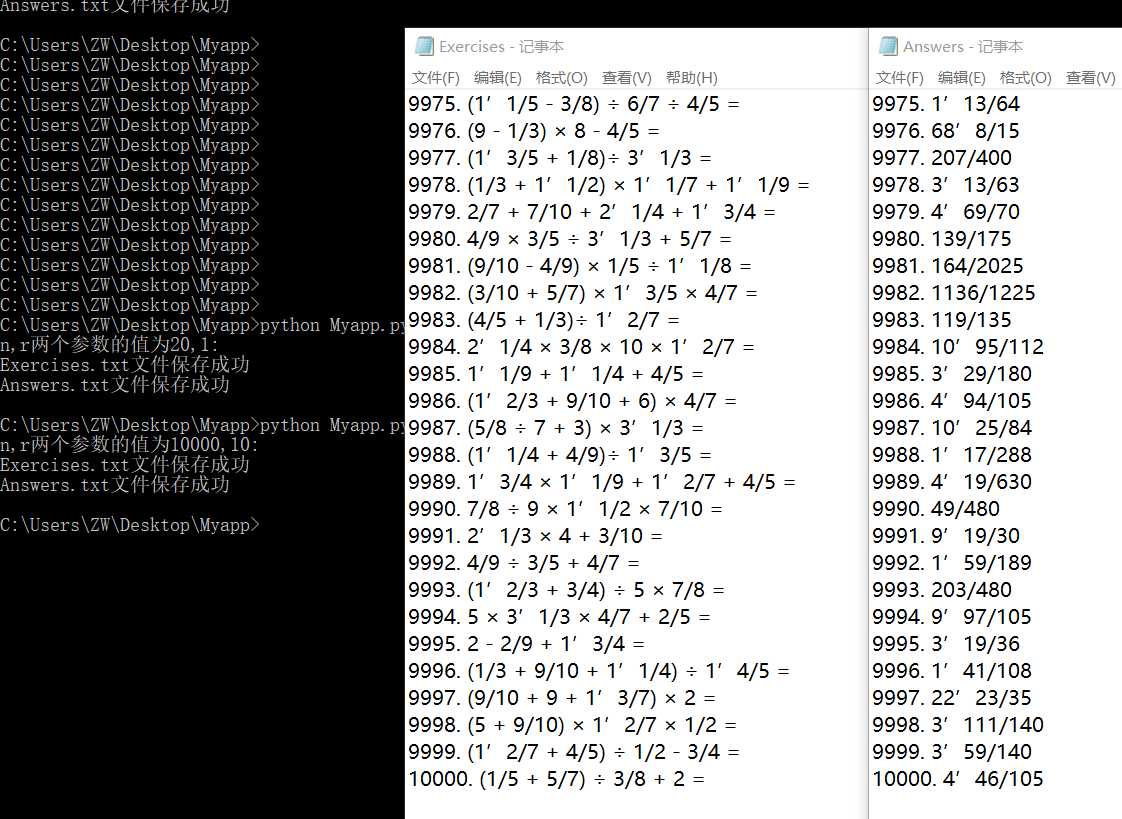
当r=1时:
-e,-a 测试:
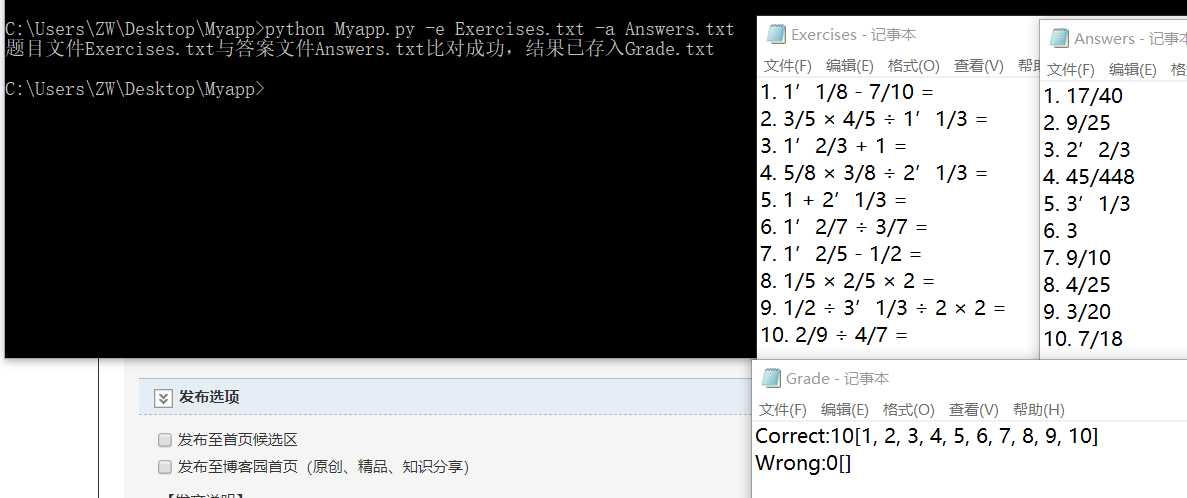
全部功能测试:
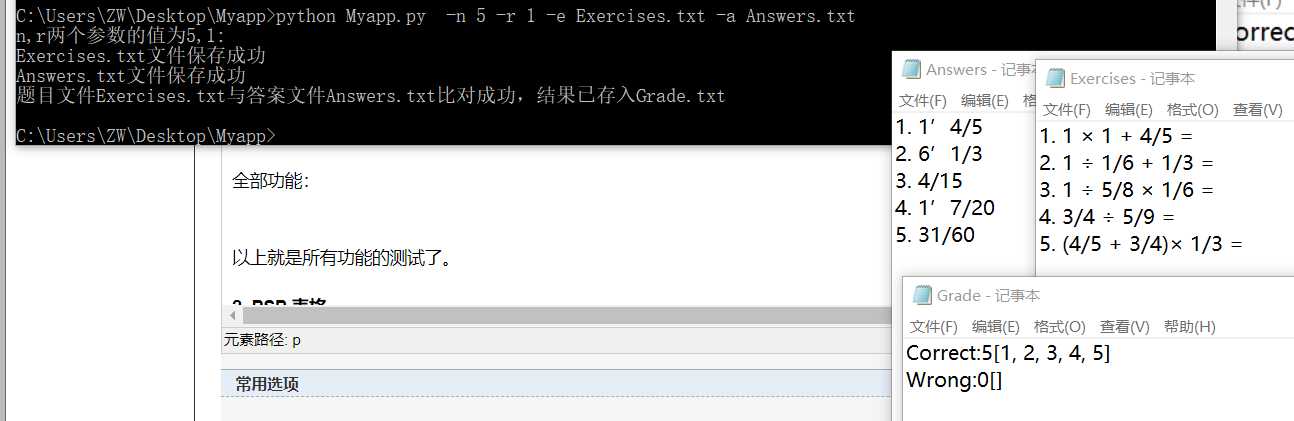
以上就是所有功能的测试了。
|
PSP2.1 |
Personal Software Process Stages |
预估耗时(分钟) |
实际耗时(分钟) |
|
Planning |
计划 |
5 |
5 |
|
· Estimate |
· 估计这个任务需要多少时间 |
800 |
930 |
|
Development |
开发 |
480 |
610 |
|
· Analysis |
· 需求分析 (包括学习新技术) |
60 |
60 |
|
· Design Spec |
· 生成设计文档 |
60 |
60 |
|
· Design Review |
· 设计复审 (和同事审核设计文档) |
30 |
30 |
|
· Coding Standard |
· 代码规范 (为目前的开发制定合适的规范) |
30 |
10 |
|
· Design |
· 具体设计 |
30 |
60 |
|
· Coding |
· 具体编码 |
120 |
480 |
|
· Code Review |
· 代码复审 |
30 |
30 |
|
· Test |
· 测试(自我测试,修改代码,提交修改) |
120 |
120 |
|
Reporting |
报告 |
120 |
120 |
|
· Test Report |
· 测试报告 |
60 |
60 |
|
· Size Measurement |
· 计算工作量 |
30 |
30 |
|
· Postmortem & Process Improvement Plan |
· 事后总结, 并提出过程改进计划 |
30 |
30 |
|
合计 |
800 |
975 |
通过这次作业,思路比较清晰,做的比较快,首先和伙伴交流了思路,然后就开始做。
3个部分刚好用了三天。最后一个命令行因为之前没有实现,所以花了时间去学习如何使用argparse模块,挺有收获的。
虽然写的过程中有遇到挺多的bug,但是我们都逐一克服了,也总结了经验的教训,这样下次可以写出更加优质的代码。
两个人一起处理工作,两双眼睛可以使得工作更加细致,解决问题的能力大大提高,汲取伙伴的好思路,做到1+1>2,事半功倍。
同时这次的课程设计也慢慢的提高我的python理解,只有不断的练习才能更加熟练。
标签:else 一起 文件的 evel orm 写入文件 部分 字符 blob
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/fengoxiao/p/9677697.html