标签:process isl row readline ascii 文件名 width tput comm
链接:https://gitee.com/iy2524/WordCount.git
| psp2.1 | psp阶段 |
估计耗时(分钟) |
实际耗时(分钟) |
| Planning | 计划 | 40 | 20 |
| · Estimate | · 估计这个任务需要多少时间 | 40 | 20 |
| Development | 开发 | 490 | 450 |
| · Analysis | · 需求分析 (包括学习新技术) | 30 | 30 |
| · Design Spec | · 生成设计文档 | 60 | 50 |
| · Design Review | · 设计复审 (和同事审核设计文档) | 60 | 50 |
| · Coding Standard | · 代码规范 (为目前的开发制定合适的规范) | 10 | 5 |
| · Design | · 具体设计 | 50 | 55 |
| · Coding | · 具体编码 | 130 | 100 |
| · Code Review | · 代码复审 | 60 | 60 |
| · Test | · 测试(自我测试,修改代码,提交修改) | 90 | 60 |
| Reporting | 报告 | 60 | 70 |
| · Test Report | · 测试报告 | 40 | 40 |
| · Size Measurement | · 计算工作量 | 10 | 5 |
|
· Postmortem & ProcessImprovement Plan |
· 事后总结, 并提出过程改进计划 | 10 | 25 |
| 合计 | 590 | 380 |
WordCount功能为统计文件中信息,主要涉及的知识为文件IO流和对字符串的处理。我选择熟悉的java来完成此项目。
一开始看程序预期运行效果和过程,对命令模式启动程序一无所知,百度后发现args中即存储的命令行。
程序测试的时候问题又来了,所需要的args参数该如何加入?百度后又得知在运行配置和调试配置中可以设置,在此,解决了绝大多数问题。
WordCount功能为统计文件中信息,则按照功能需求依次先完成各种数据的统计,以下是具体功能实现代码
所有对文件的统计方法写在此工具类中
涉及到的知识:对文件IO流的操作,对字符串的操作
以下是此类总览,详细见后面,具体完整代码点最上面码云链接
public class WordCount { private String input; private String output; private String stop; public static String result="resource/result.txt"; public WordCount(String input,String stop,String output) throws FileNotFoundException { this.input=input; if(output==null)//未指定输出文件 则默认为result { this.output=result; } else { this.output=output; } this.stop=stop; } //返回文件中的字符数 public void CountChars() throws IOException { ... } //返回文件中的总行数 public void CountLines() throws IOException { ... } //返回文件中的总单词数 public void CountWords() throws IOException { ... } //返回 代码行/空行/注释行 的行数 public void CountLinesByKind()throws IOException { ... } //使用停用词文件 统计单词个数 public void CountWordsWithLimite() throws IOException { ... } }
java对文件操作的方法有很多,此处主要用了BufferedInputStream和BufferedOutputStream,利用缓冲可以加快效率和速度
所有功能的操作都差不多:(1)读取文件信息(2)处理文件信息(3)将结果写入文件
下面是统计字符个数的完整代码
public void CountChars() throws IOException { BufferedInputStream input= new BufferedInputStream( new FileInputStream(this.input)); BufferedOutputStream output=new BufferedOutputStream( new FileOutputStream(this.output,true)); int count=0; int x=-1; char ch; while((x=input.read())!=-1) //流读取完的标志是返回-1 其他时候返回的为字符的ascii值 { ch=(char)x; if(ch!=‘\r‘&&ch!=‘\n‘)//换行\n和回车\r不统计为字符 { count++; } } input.close(); String str=this.input+",字符数:"+count; output.write(str.getBytes()); output.write("\r\n".getBytes()); //回车 /r和换行/n位置不可换 output.flush(); output.close(); }
下面是其他方法的关键代码
//返回文件中的总行数 public void CountLines() throws IOException {
... int count=0; int x=-1; while((x=input.read())!=-1) { if((char)x==‘\n‘)//遇到换行符表示一行结束 { count++; } } count++; ... }
//返回文件中的总单词数 public void CountWords() throws IOException { ... int count=0; int x=-1; boolean InWord=false;//是否读取到某个单词中 char ch=‘0‘; while(true) { x=input.read(); ch=(char)x; if(Character.isLetter(ch)&&InWord==false)//第一次读取到字母 则读取进入到单词中 { InWord=true; } else if(!Character.isLetter(ch)&&InWord==true)//读取到单词中时 读取到第一个非字母的字符 则读完一个单词 { count++; InWord=false; } if(x==-1) { break; } } ... }
//返回 代码行/空行/注释行 的行数 public void CountLinesByKind()throws IOException { ... int all_lines=0; int blank_lines=0; int note_lines=0; int code_lines=0; String strLine=null; boolean InNoteLines=false; //bug:若文件末尾有多个回车 则尾不可读 导致总行数少1 未解决 while((strLine=input.readLine())!=null) { all_lines++; strLine.replaceAll("\r", "");//去除换行符和空格 便于后面操作 strLine.replaceAll("\n", ""); strLine=strLine.trim(); strLine.replaceAll(" ", ""); if(InNoteLines==true) { note_lines++; if(strLine.endsWith("*/")||strLine.endsWith("*/}")) { InNoteLines=false; } } else if(strLine.startsWith("/*")||strLine.startsWith("{/*")) //进入注释行 { note_lines++; if(!strLine.endsWith("*/")&&!strLine.endsWith("*/}"))//本行未注释结束 { InNoteLines=true; } } else if(strLine.startsWith("//")||strLine.startsWith("{//")) { note_lines++; } else if(strLine.equals("")||strLine.equals("{")||strLine.equals("}")) { blank_lines++; } } code_lines=all_lines-blank_lines-note_lines;
...
}
//使用停用词文件 统计单词个数 public void CountWordsWithLimite() throws IOException {
... int count=0; int x=-1; char ch; String stopStr=""; String str=""; List<String> stopList =new ArrayList<>(); boolean InWord=false; //取出停用词装到stopList while(true) { x=stop.read(); if(x==-1) { stopList.add(stopStr); stopStr=""; stop.close(); break; } ch=(char)x; if(ch==‘ ‘) { stopList.add(stopStr); stopStr=""; } else { stopStr+=ch; } } while(true) { x=input.read(); ch=(char)x; if(Character.isLetter(ch)&&InWord==false)//第一次读取到字母 则读取进入到单词中 { InWord=true; str+=ch; } else if(!Character.isLetter(ch)&&InWord==true)//读取到单词中时 读取到第一个非字母的字符 则读完一个单词 { if(!stopList.contains(str))//不在停用词中 { count++; } InWord=false; str=""; } else if(InWord==true)//读取字母在单词中 { str+=ch; } if(x==-1) { break; } }
...
}
主函数及其类中方法如下:
主函数:得到用户的指令(存储在args中的字符串数组)调用analyseCommand()来处理
analyseCommand:首先处理命令是否有效,如参数应该为"-a"格式的字符串加字母形式;如果未文件名,文件是否存在;都满足时则将参数给commandAction执行具体功能。用户输入的信息为字符串数组,我将其放入到了字符串集合的集合中,这里有点绕,目的是便于后面处理指令参数,用户指令如 -c -w input.txt -e stop.txt -o output.txt,则将其分为三个字符串集合-c -w input.txt, -e stop.txt和-o output.txt,每个集合末尾装的是文件名,每个集合中的命令是针对自己文件的。
commandAction:先读取所有文件名,即遍历所有集合,取出集合末尾的字符串,判断其属性分别给到input,output和stop变量中。然后再便利所有指令集合执行相应功能。
public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) throws FileNotFoundException, IOException { analyseCommand(args); } public static void analyseCommand(String[] args) throws IOException { List<List<String>> commandsList =new ArrayList<>(); List<String> commands=new ArrayList<>(); if(args.length==0)//需要用户输出参数 { System.out.println("Command codes are needed !"); } else { for(int i=0;i<args.length;i++) { commands.add(args[i]); if(!args[i].matches("^-.*"))//不是命令符号 { if(args[i].contains("."))//是文件名或目录 { if(!new File(args[i]).exists())//文件不存在 { System.out.println("The file named "+args[i]+" does not exist"); System.exit(0); } else { commandsList.add(commands); commands=new ArrayList<>(); } } else//指令有错 { System.out.println("The "+(i+1)+"th code("+args[i]+") must begin with ‘-‘"); System.exit(0); } } } } commandAction(commandsList); } public static void commandAction(List<List<String>> commandList) throws IOException { String input=null,output=null,stop=null; for(List<String> commands:commandList) { if(commands.contains("-o")) { output=commands.get(commands.size()-1); } else if(commands.contains("-e")) { stop=commands.get(commands.size()-1); } else { input=commands.get(commands.size()-1); } } WordCount wc=new WordCount(input,stop,output); for(List<String> commands:commandList) { for(int i=0;i<commands.size()-1;i++) { switch(commands.get(i)) { case "-c":wc.CountChars(); break; case "-w":wc.CountWords(); break; case "-l":wc.CountLines(); break; case "-s":wc.CountLinesByKind(); break; case "-e":wc.CountWordsWithLimite(); break; case "-o":break; default:System.out.println("No such command code"); } } } } }
1.初步功能测试
使用此函数的main类文件作为input后测试看预期结果是否相同
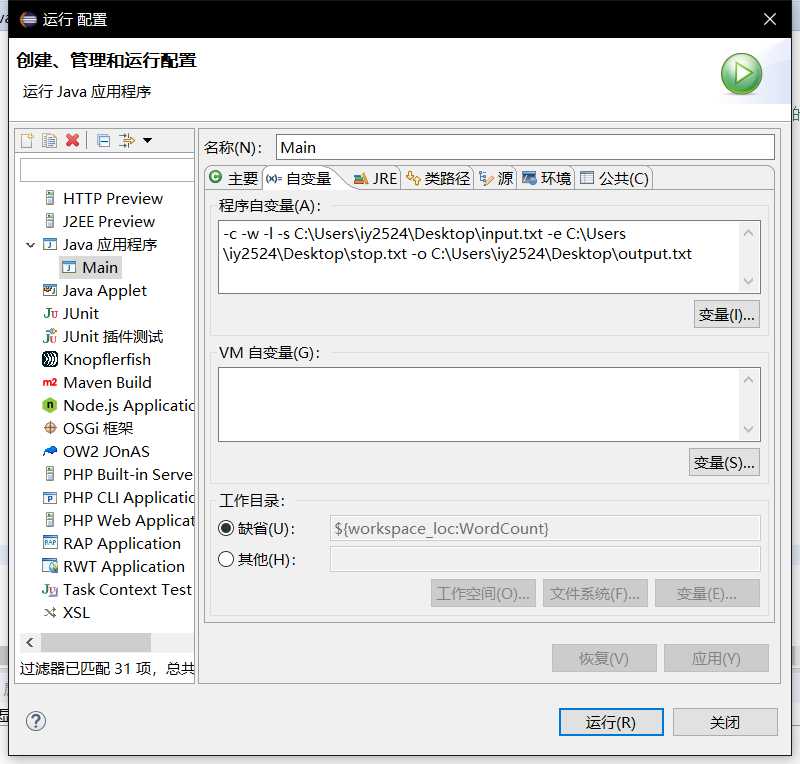
程序运行结果如下
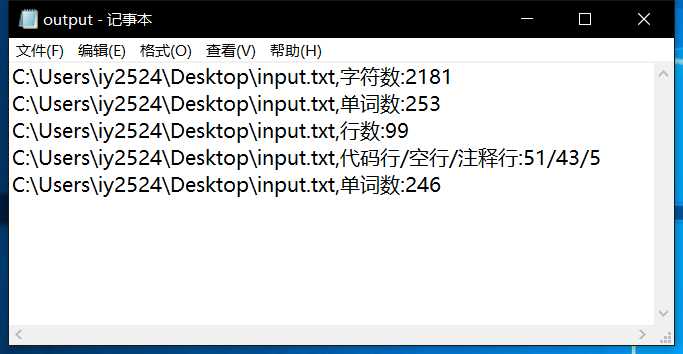
结果符合预期,大体功能实现。
2.进一步测试
准备一个标注的类文件(包含足够多的代码,注释等)
使用多种组合命令行
1).未指定输出目录的 默认为bin下的result.txt中
-c -w -l -s C:\Users\iy2524\Desktop\input.txt -e C:\Users\iy2524\Desktop\stop.txt
2).使用其他顺序组合命令
-w -c -s -l C:\Users\iy2524\Desktop\input.txt
...
3).输入不存在的命令 或者错误的文件名

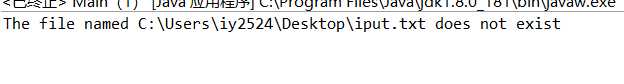
总结 :测试皆满足预期,未有出错
标签:process isl row readline ascii 文件名 width tput comm
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/xiaoyuge2524/p/9692457.html