标签:string 简单 怎么 分析 参数 复杂 col png builder
leetcode(使用的是中文网站:领扣):83
给定一个排序链表,删除所有含有重复数字的节点,只保留原始链表中 没有重复出现 的数字。
示例 1:
输入: 1->2->3->3->4->4->5 输出: 1->2->5
示例 2:
输入: 1->1->1->2->3 输出: 2->3
package leetcode.LinkedList83; /** * Definition for singly-linked list. * public class ListNode { * int val; * ListNode next; * ListNode(int x) { val = x; } * } */ class Solution { public ListNode deleteDuplicates(ListNode head) { if(head == null) { return null; } //原链表的当前节点 ListNode cur = head.next; //创建一个新的链表 ListNode newHead = new ListNode(head.val); ListNode newList_cur = newHead; while(cur!=null){ //如果新的链表中没有这个节点,那么就添加进去 if(!contains(newHead,cur.val)){ newList_cur.next = new ListNode(cur.val); newList_cur = newList_cur.next; } cur = cur.next; } return newHead; } //检测链表中是否包含某个元素 boolean contains(ListNode head,int val){ while(head != null){ if(head.val == val){ return true; } else { head = head.next; } } return false; } public static void main(String[] args) { int arr[] = {1,2,3,4,3,5,6}; ListNode head = new ListNode(arr); System.out.println(head); ListNode ret = (new Solution()).deleteDuplicates(head); System.out.println("最终结果:"+ret); } }
这里为了测试代码,我们这里可以写一个将数组转化成链表的函数
本地测试用代码(后面的代码测试也是用的这个):
package leetcode.LinkedList83; /** * 用于本地测试 */ class ListNode { int val; ListNode next; ListNode(int x) { val = x; } // 链表节点的构造函数 // 使用arr为参数,创建一个链表,当前的ListNode为链表头结点 ListNode(int[] arr){ if(arr == null || arr.length == 0){ throw new IllegalArgumentException("arr can not be empty"); } this.val = arr[0]; ListNode cur = this; for (int i = 1; i < arr.length; i++) { cur.next = new ListNode(arr[i]); cur = cur.next; } } @Override public String toString(){ StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(); ListNode cur = this; while(cur != null){ sb.append(cur.val); sb.append("->"); cur = cur.next; } sb.append("NULL"); return sb.toString(); } }
解法二(这里才用到题目的已经排序的条件):
思路:使用递归,在递推之后回归的过程中我们可以比较当前链表和子链的值是否相等,相等的话就直接返回子链,否则就返回当前链表。
链表的递归,可以想象成不断的把问题交给子链去解决,最后返回的时候也是不断的返回子链的结果。
package leetcode.LinkedList83;
public class Solution2 { public ListNode deleteDuplicates(ListNode head) { if(head == null || head.next == null) { return head; } else { // ListNode res = deleteDuplicates(head.next); // if(head.val == head.next.val){ // return res; // } else { // head.next = res; // return head; // } head.next = deleteDuplicates(head.next); return head.val == head.next.val ? head.next:head; } } public static void main(String[] args) { int arr[] = {1,2,3,3,5,6}; ListNode head = new ListNode(arr); System.out.println(head); ListNode ret = (new Solution2()).deleteDuplicates(head); System.out.println("最终结果:"+ret); } }
简单的画个图表示一下(用res更好理解一点):
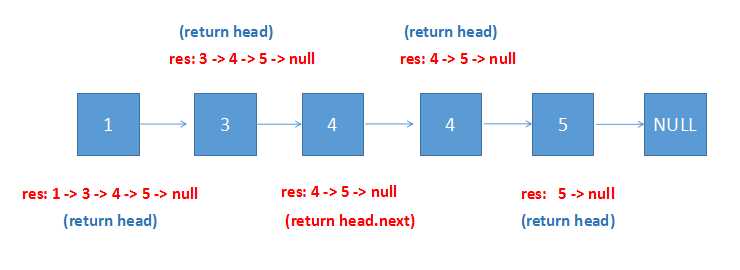
最后是官方给出的使用迭代的方法:
解法三:
思路:每一次都比较当前节点和下一个节点的值,如果不同,就将当前节点后移,如果相同,就不改变当前节点,直至下一个节点的值与当前节点的值不相等。
public ListNode deleteDuplicates(ListNode head) { ListNode current = head; while (current != null && current.next != null) { if (current.next.val == current.val) { current.next = current.next.next; } else { current = current.next; } } return head; }
标签:string 简单 怎么 分析 参数 复杂 col png builder
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/bax-life/p/9693635.html