标签:res 双向遍历 rest 内部类 条件 strong code inf iter
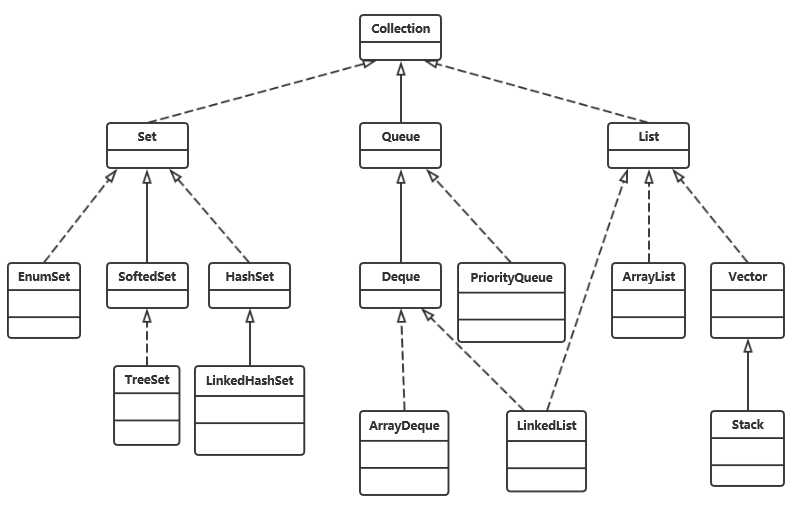
区别如下:
Collection接口定义的操作集合的方法有:
Java8为Iterator接口新增的forEach默认方法
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.HashSet;
public class CollectionTest {
public void each() {
Collection<String> books = new HashSet<>();
books.add("aaaaaa");
books.add("bbbbbb");
//1.使用Collection提供的方法
books.forEach(str -> System.out.println(str));每个集合都以内部类的方式实现了Iterator接口,Iterator替代了Enumeration,其更加安全,因为其遍历集合时会阻止其他线程修改集合
ListIterator继承了Iterator接口,它用于遍历List集合的元素,由于是双向遍历,不仅可以删除元素,还可以添加和修改元素
Java8增强的Iterator提供的方法如下:
void forEachRemaining(Consumer action)
//2使用iterator的方法
Iterator<String> iterator = books.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
//需要强制转换
String str = (String) iterator.next();
if("aaaaaa".equals(str))
iterator.remove();
}
//3.使用lambda表达式遍历
iterator.forEachRemaining(str -> System.out.println(str));
}
}books.removeIf(str -> ((String)str).length() < 10); public void stream() {
//1.使用流的builder类方法创建对应的Builder
//2.重复调用add()方法向流中添加元素
//3.调用builder的build()方法获取对应的Stream
IntStream is = IntStream.builder()
.add(1)
.add(2)
.add(3)
.add(5)
.build();
//4.调用Stream的聚集方法(很多),每次只能调用一个,调用完流即不可用
//如System.out.println(is.sum());
//将is映射成新的newIs流
IntStream newIs = is.map(ele -> ele * 2 + 1);
//使用方法引用的方式遍历集合元素
newIs.forEach(System.out::println);
} public void preStream() {
Collection<String> books = new HashSet<>();
books.add("java");
books.add("myjava");
books.add("JAVA");
System.out.println(books.stream().filter(ele -> ((String)ele).contains("java")).count());
//1.先调用Collection对象的stream方法将集合转换为Stream
//2.再调用Stream的mapToInt方法获取原有的Stream对应的IntStream
//3.再调用forEach方法遍历IntStream中的元素
books.stream().mapToInt(ele -> ((String)ele).length()).forEach(System.out::println);
}int expectedModCount = modCount;,modCount表示修改次数,迭代器会通过checkForComodification()方法判断modCount和expectedModCount 是否相等,如果不相等就表示已经有线程修改了集合结构。标签:res 双向遍历 rest 内部类 条件 strong code inf iter
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/pycrab/p/8926772.html