标签:sklearn tree 表示 tick 指定 translate cut 重复 聚类
《Python数据分析与挖掘实战》书中本章无原始数据,文中仅展示了聚类分析了各人群聚集区特征(商圈特征,做营销策划住宅区、CBD商场、办公楼这还用聚类分析吗,直接肉眼也能辨别吧,这就是所有的人流特征和规律?)也是没什么实际用处,而且数据源数据预处理过程才是挖掘重点吧,避重就轻。
归一化:无量纲化,提升模型的收敛速度、精度;需考虑标准化前后模型是否同解等价
正则化:一般是为解决模型过拟合问题,除降低特征维度外可选用的方法就是给模型目标函数加入正则化项(即惩罚项,如L1范数(如Lasso),L2范数(如ridge))
离差标准化(0-1标准化/max-min标准化)

Z标准化(标准差标准化,Z-score标准化)
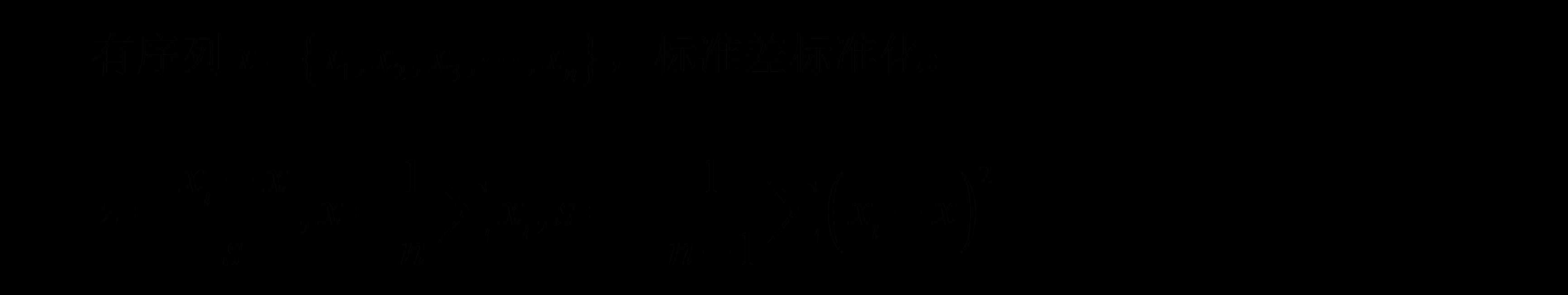
小数定点标准化,归一化

比较经典的有k-means和层次聚类法。
层次聚类法
层次聚类法基本过程如下:
层次聚类不指定具体的簇数,而只关注簇之间的远近,最终会形成一个树形图。
sklearn模块中
1 from sklearn.cluster import AgglomerativeClustering as AC 2 #sklearn.cluster.AgglomerativeClustering(n_clusters=2, affinity=‘euclidean‘, memory=None, connectivity=None, compute_full_tree=‘auto‘, linkage=‘ward‘) 3 #affinity距离算法 4 #linkage合并的策略 5 model=AC(n_clusters=3,linkage=‘ward‘) 6 #linkage : {“ward”, “complete”, “average”}, optional, default: “ward” 7 # “euclidean”, “l1”, “l2”, “manhattan”, “cosine”, or ‘precomputed’. If linkage is “ward”, only “euclidean” is accepted 8 model.fit(data_normal)
linkage criteria 确定用于合并的策略的度量:
scipy模块中
from scipy.cluster.hierarchy import linkage,dendrogram # scipy中的层次聚类 Z=linkage(data_normal,method=‘ward‘,metric=‘euclidean‘) #method={ ‘single’,‘complete’, ‘average’, ‘weighted’, ‘centroid’, ‘median’,‘ward’ } #metric={ ‘braycurtis’, ‘canberra’, ‘chebyshev’, ‘cityblock’, ‘correlation’, ‘cosine’, ‘dice’, ‘euclidean’, ‘hamming’, ‘jaccard’, ‘kulsinski’, ‘mahalanobis’, ‘matching’, ‘minkowski’, ‘rogerstanimoto’, ‘russellrao’, ‘seuclidean’, ‘sokalmichener’, ‘sokalsneath’, ‘sqeuclidean’, ‘yule’} P=dendrogram(Z,0) #系统树图 plot.show() # 画出聚类图
K-means聚类法
k-means通常被称为 Lloyd’s algorithm(劳埃德算法),其中的k就是最终聚集的簇数。k-means基本过程如下:
sklearn模块中
1 sklearn.cluster.KMeans(n_clusters=8, init=‘k-means++‘, n_init=10, max_iter=300, tol=0.0001, precompute_distances=‘auto‘, verbose=0, random_state=None, copy_x=True, n_jobs=1, algorithm=‘auto‘) 2 3 from sklearn.cluster import KMeans 4 kmeans = KMeans(n_clusters=2, random_state=0).fit(X) 5 kmeans.labels_ #kmeans[1] 6 kmeans.cluster_centers_ #kmeans[0]
scipy模块中
from scipy.cluster.vq import vq, kmeans, whiten whitened = whiten(features) # kmeans聚类前对每个属性特征标准化,除以各自标准差(列) codebook, distortion = kmeans(whitened, 2) # 标准化后数据及需要聚成类个数 # 返回两个量分别是类中心和损失 label=vq(whitened,codebook)[0] #vq函数根据聚类中心对所有数据进行分类,[0]表示返回两维中的类别
1 # -*- coding: utf-8 -*- 2 """ 3 Created on Mon Oct 1 00:20:30 2018 4 5 @author: Luove 6 """ 7 8 import os 9 import pandas as pd 10 import numpy as np 11 from scipy.cluster.hierarchy import linkage,dendrogram # scipy中的层次聚类 12 from sklearn.cluster import AgglomerativeClustering as AC # sklearn中的层次聚类 13 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt 14 import scipy.cluster.vq 15 os.getcwd() 16 os.chdir(‘D:/Analyze/Python Matlab/Python/BookCodes/Python数据分析与挖掘实战/图书配套数据、代码/chapter14/demo/code‘) 17 filepath=‘../data/business_circle.xls‘ 18 19 data=pd.read_excel(filepath) 20 data.head() 21 data=data.iloc[:,1:] 22 data_normal=(data-data.min())/(data.max()-data.min()) # 离差标准化 23 24 Z=linkage(data_normal,method=‘ward‘,metric=‘euclidean‘) 25 P=dendrogram(Z,0) 26 plot.show() 27 28 model=AC(n_clusters=3,linkage=‘ward‘) 29 model.fit(data_normal) 30 data_1=pd.concat([data_normal,pd.Series(model.labels_,index=data.index)],axis=1) 31 data_1.columns=list(data_normal.columns)+[‘聚类类别‘] 32 data_1.shape 33 # 正确显示 中文及负号 34 plt.rcParams[‘font.sans-serif‘]=[‘SimHei‘] 35 plt.rcParams[‘axes.unicode_minus‘]=False 36 37 style=[‘bo-‘,‘ro-‘,‘go-‘] 38 xlabels=[‘工作日人均停留时间‘,‘凌晨人均停留时间‘,‘周末人均停留时间‘,‘日均人流量‘] 39 40 for i in range(3): 41 plt.figure() 42 tmp=data_1[data_1[‘聚类类别‘]==i].iloc[:,:4] 43 for j in range(len(tmp)): 44 plt.plot(range(1,5),tmp.iloc[j,:],style[i]) 45 plt.xticks(range(1,5),xlabels,rotation=20) 46 plt.subplots_adjust(bottom=0.15) 47
Ref:
sklearn.cluster.AgglomerativeClustering
《数据分析与挖掘实战》:源代码及数据需要可自取:https://github.com/Luove/Data
标签:sklearn tree 表示 tick 指定 translate cut 重复 聚类
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/amoor/p/9733973.html