标签:过程 stdout 修改时间 整理 0kb 创建文件 director 空目录 复杂
1. mkdir ##创建目录
命令 【参数】 路径文件
参数:
mkdir -p ##递归创建
mkdir -v ##显示创建目录的过程
示例:
[root@XM ~]# mkdir /data
[root@XM ~]# mkdir -pv test/{1..3}/{4..6} ##同时创建多个目录及子目录
mkdir: created directory `test‘
mkdir: created directory `test/1‘
mkdir: created directory `test/1/4‘
mkdir: created directory `test/1/5‘
mkdir: created directory `test/1/6‘
mkdir: created directory `test/2‘
mkdir: created directory `test/2/4‘
mkdir: created directory `test/2/5‘
mkdir: created directory `test/2/6‘
mkdir: created directory `test/3‘
mkdir: created directory `test/3/4‘
mkdir: created directory `test/3/5‘
mkdir: created directory `test/3/6‘
2. ls ##显示文件或目录
命令 【参数】 路径文件
参数:
ls -ld ##以长格式显示目录
ls -a ##显示隐藏文件,显示文件的索引号
ls -pF ##给不同类型文件结尾加不同的符号
ls -t ##按最近时间修改显示
ls -r ##翻转排序
ls -lrt ##显示最近创建的目录或文件
ls -u ##最后访问时间
示例:
[root@XM ~]# ls -ld /data
drwxr-xr-x. 2 root root 4096 Jan 23 13:48 /data
3. cd ##切换目录层次
cd - ##返回到上次目录
cd ~ ##切换到root的家目录
cd . ##当前目录
cd .. ##上级目录
4. pwd ##显示当前的路径
[root@XM 123]# pwd
/root/123
5. touch ##创建文件
示例1:
[root@GHJC ~]# touch ett.txt
[root@GHJC ~]# ll -d ett.txt
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 0 Apr 26 12:29 ett.txt
示例2:
[root@XM 123]# touch mm{1..5}
[root@XM 123]# ll
total 0
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 Jan 2 13:35 mm1
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 Jan 2 13:35 mm2
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 Jan 2 13:35 mm3
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 Jan 2 13:35 mm4
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 Jan 2 13:35 mm5
6. echo ##打印输出内容(printf复杂的输出),配合“>或>>”可以为文件覆盖及追加内容,“>”意思为重定向,会清除文件里所有以前数据;“>>”为内容追加,文件结尾加入内容,不会删除己有的文件内容
命令 参数 " " 路径文件
参数:
echo -n ##不换行
echo -e ##可以指定特殊字符(\t,\n等)
>或1> 重定向,会清除文件里所有以前数据,增加新数据。
>>或1>> 追加输出重定向,文件结尾加入内容,不会删除己有文件内容。
<0 输入重定向
<<追加输入重定向
2> 错误重定向
2>> 错误追加重定向
标准输入(stdin):代码为0,使用<或<<数据流向从右向左。
正常输出(stdout):代码为1, 使用>或>>数据流向从左向右
错误输出(stderr):代码为2,使用2 >或2>>箭头的指向就是数据的流向
ech 111 1>xiaomi.txt 2>xiaomi1.txt //错误的ech 在xiaomi.txt
>/dev/null 2>&1 等价于 1>/dev/null 2>/dev/null
示例1:
[root@GHJC ~]# echo "123" >>ett.txt
[root@GHJC ~]# cat ett.txt
linuxxinshou
123
[root@NGINX-Y data]# echo "123"
123
7. cat ##查看文件内容
参数:
cat -n ##显示行号
[root@XM 123]# cat >>e.txt<<EOF
> 123
> 321
> 456
> 789
> EOF
8. xargs ##从标准输入获取内容
示例
[root@XM 123]# xargs -n2 <e.txt ##-n(几组几行)
123 321
456 789
[root@XM 123]# xargs -n1 <e.txt
123
321
456
789
[root@XM 123]# xargs -n3 <e.txt
123 321 456
789
示例:
[root@XM ~]# echo stu{1..10}|xargs -n1 >>1.txt
[root@XM ~]# cat 1.txt
1t 2t 3t 4t 5t 6t 7t 8t 9t 10t
stu1
stu2
stu3
stu4
stu5
stu6
stu7
stu8
stu9
stu10
9. cp ##拷贝文件或目录
参数:
cp -a ##拷贝目录,相当于-apr
cp -d ##若源文件为链接文件(link file),则复制链接文件属性而非档案本身
cp -f ##强制,若目标档案已经存在且无法开启,则移除后再尝试
cp -i ##若目标文件已经存在,在覆盖时会先询问
cp -p ##连同档案的属性一起复制过去,而非使用默认属性
cp -r ##递归,用于复制目录
cp -u ##若目标文件存在,则目标文件比源文件旧时才复制
示例:
[root@XM 123]# cp e.txt /tmp/
[root@XM 123]# ll /tmp/e.txt
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 16 Jan 2 14:07 /tmp/e.txt
10. mv ##移动单个目录或文件
参数;
mv -i:如果目的文件已存在,询问是否覆盖
mv -f:强制执行
mv -u:若目的文件存在,则比源文件新才会移动
11. rm ##删除文件或目录
参数:
rm -f ##强制删除文件
rm -r ##递归删除,用于删除目录
rm -fr ##强制删除指定的目录或文件
rmdir ##删除空目录
12. find ##在指定目录下查找文件
参数:
find / -type ## -type 文件类型
find / -type f ## f 文件
find / -type d ## d 目录
find / -type c ## c 是字符设备
find / -type b ## b 块设备、磁盘
find / -type s ## s 网络
find / -type l ## l 链接文件
基于目录深度搜索
find / -maxdepth 2 -type d ##搜索2级目录
find / -maxdepth 2 -type f ##搜索当前目录及下一级目录的所有文件
访问时间(-atime/天,-amin/分钟):最后访问时间
修改时间(-mtime/天,mmin/分钟):文件最后一次修改时间
变化时间(-ctime/天,cmin/分钟):文件数据元(例如权限)状态改变时间
find / -type f -atime -7 ##搜索7天内被访问的所有文件
find / -type f -atime 7 ##搜索7天当天被访问的所有文件
find / -type f -atime +7 ##搜索7天以前被访问的所有文件
find / -type f -amin +10 ##搜索访问时间超过10分钟的所有文件
根据文件大小进行匹配
文件大小单元 -size
b ##块(512字节)
c ##字节
w ##字(2字节)
k ##千字节
M ##兆字节
G ##G字节
find . -type f -size +10k ##搜索大于10KB的文件
find . -type f -size 10k ##搜索等于10KB的文件
find . -type f -size -10k ##搜索小于10KB的文件
根据文件权限进行匹配
find / -type d -perm 777 ##搜索出权限为777的目录
find / -type f -perm 666 ## 搜索出权限为666的文件
find / -type f -name "*.php" ! -perm 644 ##搜索出权限不是644的php文件
借助-exec选项与其他目录结合使用
示例1: -ok会提示,-exec不会提示
[root@XM ~]# find . -type d -name "*3" -ok rm {} \;
< rm ... ./123 > ? y
rm: cannot remove ‘./123’: Is a directory
[root@XM ~]# find . -type d -name "*3" -exec rm -fr {} \;
find: ‘./123’: No such file or directory
示例2:
[root@XM ~]# find . -type f -name "*.txt"|xargs ls -l
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 343 Dec 22 16:40 ./name.txt
13. grep ##按行过滤
参数:
grep -v ##排除,不接参数按行过滤自己想要的
grep -E ##同时过滤多个字符串;
grep -vE ##同时排除多个字符串
grep -i ##不区分大小写
grep -Ei ##不区分大小写的过滤中间用|隔开等价于小写的egrep
示例:
[root@XM ~]# xargs -n1 <1.txt
1t
2t
3t
4t
5t
6t
7t
8t
9t
10t
[root@XM ~]# xargs -n1 <1.txt|grep -Ev "1|2"
3t
4t
5t
6t
7t
8t
9t
[root@NGINX-Y ~]# grep 20 -A 10 ett.txt #(先打印出20,再打印之后的10行)-A除了显示匹配的一行之外,并显示该行之后的num行
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
[root@NGINX-Y ~]# grep 25 -C 5 ett.txt ##先匹配25行,再把25行前后的5行打印出来。 (-C除了显示匹配的一行之外,并显示该行之前后的num行)
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
[root@NGINX-Y ~]# grep 30 -B 10 ett.txt #(先打印出30,再打印之前的10行)-B除了显示匹配的一行之外,并显示该行之前的num行
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
14. head ##显示文件头部,不接参数默认显示前十行
-n ##行数
示例:
[root@XM ~]# head -2 1.txt
stu1
stu2
[root@XM ~]# head 1.txt
stu1
stu2
stu3
stu4
stu5
stu6
stu7
stu8
stu9
stu10
15. tail ##显示文件尾部,不接参数默认显示结尾十行
参数:
-n
tail -f ##跟踪显示文件的结尾
示例:
[root@XM ~]# tail -2 1.txt
stu9
stu10
16. sed ##擅长输出行,删除,替换,修改,添加
参数:
sed -n ##取消默认输出
sed -i ##替换文件内容
sed -e ##允许多项编辑
sed -r ##扩展正则
示例1:
[root@XM ~]# sed -n /li/p test.txt #把与li相关的打印出来
liyao
示例2:
[root@XM ~]# sed /oldboy/d test.txt 删除掉oldboy(不输出oldboy)
test
liyao
示例3:
[root@XM~]#sed -i ‘s#oldboylinux#oldboywindows#g‘ ett.txt ##替换
[root@XM ~]# cat ett.txt
oldboywindows
示例4:
[root@XM ~]# seq 100 >ett.txt ##输入
[root@XM ~]# sed -n ‘20,30p‘ e.txt ##打印20-30行的数据
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
示例5:
sed 把你想要的内容先保护起来(通过小括号),然后再使用它
[root@XM ~]# echo 123456|sed -r ‘s#(.*)#<\1>#g‘
<123456>
示例6:
[root@XM ~]# sed -n ‘1p;4p‘ e.txt
oldboy
xizi
[root@XM ~]# sed -nr ‘/^o.*|^x.*/p‘ e.txt
oldboy
xizi
17. awk ##擅长处理列
示例:
awk 逗号中算一个整体

awk 指定多个分隔符
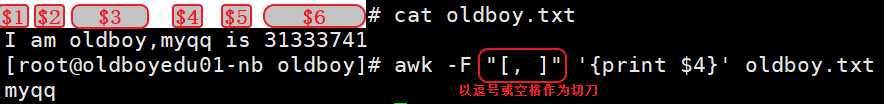
[root@oldboyedu-01 ~]# ifconfig eth0|awk ‘NR==2{print $2}‘
addr:10.0.0.200
[root@oldboyedu-01 ~]# ifconfig eth0|awk -F "[: ]+" ‘NR==2{print $4}‘
10.0.0.200
[root@NGINX-Y ~]# awk ‘NR>19&&NR<31‘ ett.txt
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
18. cp ##拷贝文件及目录(让覆盖文件不提示 加反斜线,\cp或/bin/cp这是cp的全路径)
参数:
cp -a ##拷贝目录,相当于-apr
cp -p ##连同档案的属性一起复制过去,而非使用默认属性
cp -r ##递归,用于复制目录
示例;
[root@GHJC ~]# cp ett.txt /mfg
[root@GHJC ~]# ll /mfg
total 4
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 17 Apr 26 14:30 ett.txt
19. alias ##查看和设置别名(别名的作用:通过给危险命令加一些包含参数,防止人为误操作。把很多复杂的字符串或命令变成一个简单的字符串或命令。)unalias cp ##删除cp 的别名(临时生效)
定义别名
/etc/profile ##全局生效
~/.bashrc ##当前用户生效
20. which ##查看目录所在的全路径
[root@XM ~]# which cp
alias cp=‘cp -i‘
/usr/bin/cp
21. seq ##打印
参数:
seq -s ##指定分隔符,横着打印
[root@XM ~]# seq 10
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
[root@XM ~]# seq -s ‘ ‘ 10
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
[root@XM ~]# seq -s ‘‘ 10
12345678910
22. uname
[root@XM ~]# uname -r ##查看内核
3.10.0-123.9.3.el7.x86_64
[root@XM ~]# uname -n ##显示主机名
XM
23. man ##适用于一般命令,非内置命令
help ##适用于内置命令
24. tree
tree -d ##只显示目录
tree -dL 1 ##显示指定的层次目录
[root@XM ~]# tree -dL 2
.
└── 11
└── 112
2 directories
[root@XM ~]# touch 1.ttt 11/
[root@XM ~]# tree -dL 2
.
└── 11
└── 112
2 directories
[root@XM ~]#
[root@XM ~]# tree -diL 2
.
11
112
25. ps -ef ##查看进程
26. useradd
27. passwd
28. history ##查看历史记录
history -d 5 ##删除指定历史记录
history -c ##清空所有
29. mount
30. df
df -h ##查看磁盘剩余空间
df -i ##查看磁盘inode
标签:过程 stdout 修改时间 整理 0kb 创建文件 director 空目录 复杂
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/Confusedren/p/9735905.html