概述
Tornado 是 FriendFeed 使用的可扩展的非阻塞式 web 服务器及其相关工具的开源版本。这个 Web 框架看起来有些像web.py 或者 Google 的 webapp,不过为了能有效利用非阻塞式服务器环境,这个 Web 框架还包含了一些相关的有用工具 和优化。
Tornado 和现在的主流 Web 服务器框架(包括大多数 Python 的框架)有着明显的区别:它是非阻塞式服务器,而且速度相当快。得利于其 非阻塞的方式和对 epoll 的运用,Tornado 每秒可以处理数以千计的连接,这意味着对于实时 Web 服务来说,Tornado 是一个理想的 Web 框架。我们开发这个 Web 服务器的主要目的就是为了处理 FriendFeed 的实时功能 ——在 FriendFeed 的应用里每一个活动用户都会保持着一个服务器连接。(关于如何扩容 服务器,以处理数以千计的客户端的连接的问题,请参阅 C10K problem。)
下载安装:
|
1
2
3
4
|
pip3 install tornado源码安装https://pypi.python.org/packages/source/t/tornado/tornado-4.3.tar.gz |
框架使用
一、快速上手
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
|
#!/usr/bin/env python# -*- coding:utf-8 -*- import tornado.ioloopimport tornado.web class MainHandler(tornado.web.RequestHandler): def get(self): self.write("Hello, world") application = tornado.web.Application([ (r"/index", MainHandler),]) if __name__ == "__main__": application.listen(8888) tornado.ioloop.IOLoop.instance().start() |
执行过程:
- 第一步:执行脚本,监听 8888 端口
- 第二步:浏览器客户端访问 /index --> http://127.0.0.1:8888/index
- 第三步:服务器接受请求,并交由对应的类处理该请求
- 第四步:类接受到请求之后,根据请求方式(post / get / delete ...)的不同调用并执行相应的方法
- 第五步:方法返回值的字符串内容发送浏览器
#!/usr/bin/env python # -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
import tornado.ioloop import tornado.web from tornado import httpclient from tornado.web import asynchronous from tornado import gen import uimodules as md import uimethods as mt class MainHandler(tornado.web.RequestHandler): @asynchronous @gen.coroutine def get(self): print ‘start get ‘ http = httpclient.AsyncHTTPClient() http.fetch("http://127.0.0.1:8008/post/", self.callback) self.write(‘end‘) def callback(self, response): print response.body settings = { ‘template_path‘: ‘template‘, ‘static_path‘: ‘static‘, ‘static_url_prefix‘: ‘/static/‘, ‘ui_methods‘: mt, ‘ui_modules‘: md, } application = tornado.web.Application([ (r"/index", MainHandler), ], **settings) if __name__ == "__main__": application.listen(8009) tornado.ioloop.IOLoop.instance().start()
二、路由系统
路由系统其实就是 url 和 类 的对应关系,这里不同于其他框架,其他很多框架均是 url 对应 函数,Tornado中每个url对应的是一个类。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
|
#!/usr/bin/env python# -*- coding:utf-8 -*- import tornado.ioloopimport tornado.web class MainHandler(tornado.web.RequestHandler): def get(self): self.write("Hello, world") class StoryHandler(tornado.web.RequestHandler): def get(self, story_id): self.write("You requested the story " + story_id) class BuyHandler(tornado.web.RequestHandler): def get(self): self.write("buy.wupeiqi.com/index") application = tornado.web.Application([ (r"/index", MainHandler), (r"/story/([0-9]+)", StoryHandler),]) application.add_handlers(‘buy.wupeiqi.com$‘, [ (r‘/index‘,BuyHandler),]) if __name__ == "__main__": application.listen(80) tornado.ioloop.IOLoop.instance().start() |
Tornado中原生支持二级域名的路由,如:
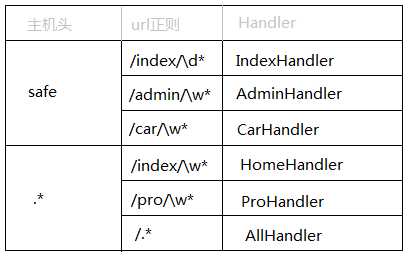
三、模板引擎
Tornao中的模板语言和django中类似,模板引擎将模板文件载入内存,然后将数据嵌入其中,最终获取到一个完整的字符串,再将字符串返回给请求者。
Tornado 的模板支持“控制语句”和“表达语句”,控制语句是使用 {% 和 %} 包起来的 例如 {% if len(items) > 2 %}。表达语句是使用 {{ 和 }} 包起来的,例如 {{ items[0] }}。
控制语句和对应的 Python 语句的格式基本完全相同。我们支持 if、for、while 和 try,这些语句逻辑结束的位置需要用 {% end %} 做标记。还通过 extends 和 block 语句实现了模板继承。这些在 template 模块 的代码文档中有着详细的描述。
注:在使用模板前需要在setting中设置模板路径:"template_path" : "tpl"
1、基本使用

#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
import tornado.ioloop
import tornado.web
class MainHandler(tornado.web.RequestHandler):
def get(self):
self.render("index.html", list_info = [11,22,33])
application = tornado.web.Application([
(r"/index", MainHandler),
])
if __name__ == "__main__":
application.listen(8888)
tornado.ioloop.IOLoop.instance().start()

<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8"/>
<title>老男孩</title>
<link href="{{static_url("css/common.css")}}" rel="stylesheet" />
</head>
<body>
<div>
<ul>
{% for item in list_info %}
<li>{{item}}</li>
{% end %}
</ul>
</div>
<script src="{{static_url("js/jquery-1.8.2.min.js")}}"></script>
</body>
</html>

在模板中默认提供了一些函数、字段、类以供模板使用: escape: tornado.escape.xhtml_escape 的別名 xhtml_escape: tornado.escape.xhtml_escape 的別名 url_escape: tornado.escape.url_escape 的別名 json_encode: tornado.escape.json_encode 的別名 squeeze: tornado.escape.squeeze 的別名 linkify: tornado.escape.linkify 的別名 datetime: Python 的 datetime 模组 handler: 当前的 RequestHandler 对象 request: handler.request 的別名 current_user: handler.current_user 的別名 locale: handler.locale 的別名 _: handler.locale.translate 的別名 static_url: for handler.static_url 的別名 xsrf_form_html: handler.xsrf_form_html 的別名
2、母版

<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8"/>
<title>老男孩</title>
<link href="{{static_url("css/common.css")}}" rel="stylesheet" />
{% block CSS %}{% end %}
</head>
<body>
<div class="pg-header">
</div>
{% block RenderBody %}{% end %}
<script src="{{static_url("js/jquery-1.8.2.min.js")}}"></script>
{% block JavaScript %}{% end %}
</body>
</html>

{% extends ‘layout.html‘%}
{% block CSS %}
<link href="{{static_url("css/index.css")}}" rel="stylesheet" />
{% end %}
{% block RenderBody %}
<h1>Index</h1>
<ul>
{% for item in li %}
<li>{{item}}</li>
{% end %}
</ul>
{% end %}
{% block JavaScript %}
{% end %}
3、导入

<div>
<ul>
<li>1024</li>
<li>42区</li>
</ul>
</div>

<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8"/>
<title>老男孩</title>
<link href="{{static_url("css/common.css")}}" rel="stylesheet" />
</head>
<body>
<div class="pg-header">
{% include ‘header.html‘ %}
</div>
<script src="{{static_url("js/jquery-1.8.2.min.js")}}"></script>
</body>
</html>
4、自定义UIMethod以UIModule
a. 定义

# uimethods.py
def tab(self):
return ‘UIMethod‘

#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
from tornado.web import UIModule
from tornado import escape
class custom(UIModule):
def render(self, *args, **kwargs):
return escape.xhtml_escape(‘<h1>wupeiqi</h1>‘)
#return escape.xhtml_escape(‘<h1>wupeiqi</h1>‘)
b. 注册

#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
import tornado.ioloop
import tornado.web
from tornado.escape import linkify
import uimodules as md
import uimethods as mt
class MainHandler(tornado.web.RequestHandler):
def get(self):
self.render(‘index.html‘)
settings = {
‘template_path‘: ‘template‘,
‘static_path‘: ‘static‘,
‘static_url_prefix‘: ‘/static/‘,
‘ui_methods‘: mt,
‘ui_modules‘: md,
}
application = tornado.web.Application([
(r"/index", MainHandler),
], **settings)
if __name__ == "__main__":
application.listen(8009)
tornado.ioloop.IOLoop.instance().start()
c. 使用

<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head lang="en">
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title></title>
<link href="{{static_url("commons.css")}}" rel="stylesheet" />
</head>
<body>
<h1>hello</h1>
{% module custom(123) %}
{{ tab() }}
</body>
四、静态文件
对于静态文件,可以配置静态文件的目录和前段使用时的前缀,并且Tornaodo还支持静态文件缓存。

#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
import tornado.ioloop
import tornado.web
class MainHandler(tornado.web.RequestHandler):
def get(self):
self.render(‘home/index.html‘)
settings = {
‘template_path‘: ‘template‘,
‘static_path‘: ‘static‘,
‘static_url_prefix‘: ‘/static/‘,
}
application = tornado.web.Application([
(r"/index", MainHandler),
], **settings)
if __name__ == "__main__":
application.listen(80)
tornado.ioloop.IOLoop.instance().start()

<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head lang="en">
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title></title>
<link href="{{static_url("commons.css")}}" rel="stylesheet" />
</head>
<body>
<h1>hello</h1>
</body>
</html>
注:静态文件缓存的实现

def get_content_version(cls, abspath):
"""Returns a version string for the resource at the given path.
This class method may be overridden by subclasses. The
default implementation is a hash of the file‘s contents.
.. versionadded:: 3.1
"""
data = cls.get_content(abspath)
hasher = hashlib.md5()
if isinstance(data, bytes):
hasher.update(data)
else:
for chunk in data:
hasher.update(chunk)
return hasher.hexdigest()
五、cookie
Tornado中可以对cookie进行操作,并且还可以对cookie进行签名以放置伪造。
1、基本操作

class MainHandler(tornado.web.RequestHandler):
def get(self):
if not self.get_cookie("mycookie"):
self.set_cookie("mycookie", "myvalue")
self.write("Your cookie was not set yet!")
else:
self.write("Your cookie was set!")
2、加密cookie(签名)
Cookie 很容易被恶意的客户端伪造。加入你想在 cookie 中保存当前登陆用户的 id 之类的信息,你需要对 cookie 作签名以防止伪造。Tornado 通过 set_secure_cookie 和 get_secure_cookie 方法直接支持了这种功能。 要使用这些方法,你需要在创建应用时提供一个密钥,名字为 cookie_secret。 你可以把它作为一个关键词参数传入应用的设置中:

class MainHandler(tornado.web.RequestHandler):
def get(self):
if not self.get_secure_cookie("mycookie"):
self.set_secure_cookie("mycookie", "myvalue")
self.write("Your cookie was not set yet!")
else:
self.write("Your cookie was set!")
application = tornado.web.Application([
(r"/", MainHandler),
], cookie_secret="61oETzKXQAGaYdkL5gEmGeJJFuYh7EQnp2XdTP1o/Vo=")

def _create_signature_v1(secret, *parts):
hash = hmac.new(utf8(secret), digestmod=hashlib.sha1)
for part in parts:
hash.update(utf8(part))
return utf8(hash.hexdigest())
# 加密
def _create_signature_v2(secret, s):
hash = hmac.new(utf8(secret), digestmod=hashlib.sha256)
hash.update(utf8(s))
return utf8(hash.hexdigest())
def create_signed_value(secret, name, value, version=None, clock=None,
key_version=None):
if version is None:
version = DEFAULT_SIGNED_VALUE_VERSION
if clock is None:
clock = time.time
timestamp = utf8(str(int(clock())))
value = base64.b64encode(utf8(value))
if version == 1:
signature = _create_signature_v1(secret, name, value, timestamp)
value = b"|".join([value, timestamp, signature])
return value
elif version == 2:
# The v2 format consists of a version number and a series of
# length-prefixed fields "%d:%s", the last of which is a
# signature, all separated by pipes. All numbers are in
# decimal format with no leading zeros. The signature is an
# HMAC-SHA256 of the whole string up to that point, including
# the final pipe.
#
# The fields are:
# - format version (i.e. 2; no length prefix)
# - key version (integer, default is 0)
# - timestamp (integer seconds since epoch)
# - name (not encoded; assumed to be ~alphanumeric)
# - value (base64-encoded)
# - signature (hex-encoded; no length prefix)
def format_field(s):
return utf8("%d:" % len(s)) + utf8(s)
to_sign = b"|".join([
b"2",
format_field(str(key_version or 0)),
format_field(timestamp),
format_field(name),
format_field(value),
b‘‘])
if isinstance(secret, dict):
assert key_version is not None, ‘Key version must be set when sign key dict is used‘
assert version >= 2, ‘Version must be at least 2 for key version support‘
secret = secret[key_version]
signature = _create_signature_v2(secret, to_sign)
return to_sign + signature
else:
raise ValueError("Unsupported version %d" % version)
# 解密
def _decode_signed_value_v1(secret, name, value, max_age_days, clock):
parts = utf8(value).split(b"|")
if len(parts) != 3:
return None
signature = _create_signature_v1(secret, name, parts[0], parts[1])
if not _time_independent_equals(parts[2], signature):
gen_log.warning("Invalid cookie signature %r", value)
return None
timestamp = int(parts[1])
if timestamp < clock() - max_age_days * 86400:
gen_log.warning("Expired cookie %r", value)
return None
if timestamp > clock() + 31 * 86400:
# _cookie_signature does not hash a delimiter between the
# parts of the cookie, so an attacker could transfer trailing
# digits from the payload to the timestamp without altering the
# signature. For backwards compatibility, sanity-check timestamp
# here instead of modifying _cookie_signature.
gen_log.warning("Cookie timestamp in future; possible tampering %r",
value)
return None
if parts[1].startswith(b"0"):
gen_log.warning("Tampered cookie %r", value)
return None
try:
return base64.b64decode(parts[0])
except Exception:
return None
def _decode_fields_v2(value):
def _consume_field(s):
length, _, rest = s.partition(b‘:‘)
n = int(length)
field_value = rest[:n]
# In python 3, indexing bytes returns small integers; we must
# use a slice to get a byte string as in python 2.
if rest[n:n + 1] != b‘|‘:
raise ValueError("malformed v2 signed value field")
rest = rest[n + 1:]
return field_value, rest
rest = value[2:] # remove version number
key_version, rest = _consume_field(rest)
timestamp, rest = _consume_field(rest)
name_field, rest = _consume_field(rest)
value_field, passed_sig = _consume_field(rest)
return int(key_version), timestamp, name_field, value_field, passed_sig
def _decode_signed_value_v2(secret, name, value, max_age_days, clock):
try:
key_version, timestamp, name_field, value_field, passed_sig = _decode_fields_v2(value)
except ValueError:
return None
signed_string = value[:-len(passed_sig)]
if isinstance(secret, dict):
try:
secret = secret[key_version]
except KeyError:
return None
expected_sig = _create_signature_v2(secret, signed_string)
if not _time_independent_equals(passed_sig, expected_sig):
return None
if name_field != utf8(name):
return None
timestamp = int(timestamp)
if timestamp < clock() - max_age_days * 86400:
# The signature has expired.
return None
try:
return base64.b64decode(value_field)
except Exception:
return None
def get_signature_key_version(value):
value = utf8(value)
version = _get_version(value)
if version < 2:
return None
try:
key_version, _, _, _, _ = _decode_fields_v2(value)
except ValueError:
return None
return key_version
签名Cookie的本质是:
写cookie过程:
- 将值进行base64加密
- 对除值以外的内容进行签名,哈希算法(无法逆向解析)
- 拼接 签名 + 加密值
读cookie过程:
- 读取 签名 + 加密值
- 对签名进行验证
- base64解密,获取值内容
注:许多API验证机制和安全cookie的实现机制相同。

#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
import tornado.ioloop
import tornado.web
class MainHandler(tornado.web.RequestHandler):
def get(self):
login_user = self.get_secure_cookie("login_user", None)
if login_user:
self.write(login_user)
else:
self.redirect(‘/login‘)
class LoginHandler(tornado.web.RequestHandler):
def get(self):
self.current_user()
self.render(‘login.html‘, **{‘status‘: ‘‘})
def post(self, *args, **kwargs):
username = self.get_argument(‘name‘)
password = self.get_argument(‘pwd‘)
if username == ‘wupeiqi‘ and password == ‘123‘:
self.set_secure_cookie(‘login_user‘, ‘武沛齐‘)
self.redirect(‘/‘)
else:
self.render(‘login.html‘, **{‘status‘: ‘用户名或密码错误‘})
settings = {
‘template_path‘: ‘template‘,
‘static_path‘: ‘static‘,
‘static_url_prefix‘: ‘/static/‘,
‘cookie_secret‘: ‘aiuasdhflashjdfoiuashdfiuh‘
}
application = tornado.web.Application([
(r"/index", MainHandler),
(r"/login", LoginHandler),
], **settings)
if __name__ == "__main__":
application.listen(8888)
tornado.ioloop.IOLoop.instance().start()

#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
import tornado.ioloop
import tornado.web
class BaseHandler(tornado.web.RequestHandler):
def get_current_user(self):
return self.get_secure_cookie("login_user")
class MainHandler(BaseHandler):
@tornado.web.authenticated
def get(self):
login_user = self.current_user
self.write(login_user)
class LoginHandler(tornado.web.RequestHandler):
def get(self):
self.current_user()
self.render(‘login.html‘, **{‘status‘: ‘‘})
def post(self, *args, **kwargs):
username = self.get_argument(‘name‘)
password = self.get_argument(‘pwd‘)
if username == ‘wupeiqi‘ and password == ‘123‘:
self.set_secure_cookie(‘login_user‘, ‘武沛齐‘)
self.redirect(‘/‘)
else:
self.render(‘login.html‘, **{‘status‘: ‘用户名或密码错误‘})
settings = {
‘template_path‘: ‘template‘,
‘static_path‘: ‘static‘,
‘static_url_prefix‘: ‘/static/‘,
‘cookie_secret‘: ‘aiuasdhflashjdfoiuashdfiuh‘,
‘login_url‘: ‘/login‘
}
application = tornado.web.Application([
(r"/index", MainHandler),
(r"/login", LoginHandler),
], **settings)
if __name__ == "__main__":
application.listen(8888)
tornado.ioloop.IOLoop.instance().start()
3、JavaScript操作Cookie
由于Cookie保存在浏览器端,所以在浏览器端也可以使用JavaScript来操作Cookie。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
/*设置cookie,指定秒数过期 */function setCookie(name,value,expires){ var temp = []; var current_date = new Date(); current_date.setSeconds(current_date.getSeconds() + 5); document.cookie = name + "= "+ value +";expires=" + current_date.toUTCString();} |
对于参数:
- domain 指定域名下的cookie
- path 域名下指定url中的cookie
- secure https使用
注:jQuery中也有指定的插件 jQuery Cookie 专门用于操作cookie,猛击这里
六、CSRF
Tornado中的夸张请求伪造和Django中的相似,跨站伪造请求(Cross-site request forgery)

settings = {
"xsrf_cookies": True,
}
application = tornado.web.Application([
(r"/", MainHandler),
(r"/login", LoginHandler),
], **settings)

<form action="/new_message" method="post">
{{ xsrf_form_html() }}
<input type="text" name="message"/>
<input type="submit" value="Post"/>
</form>

function getCookie(name) {
var r = document.cookie.match("\\b" + name + "=([^;]*)\\b");
return r ? r[1] : undefined;
}
jQuery.postJSON = function(url, args, callback) {
args._xsrf = getCookie("_xsrf");
$.ajax({url: url, data: $.param(args), dataType: "text", type: "POST",
success: function(response) {
callback(eval("(" + response + ")"));
}});
};
注:Ajax使用时,本质上就是去获取本地的cookie,携带cookie再来发送请求
七、上传文件
1、Form表单上传

<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8"/>
<title>上传文件</title>
</head>
<body>
<form id="my_form" name="form" action="/index" method="POST" enctype="multipart/form-data" >
<input name="fff" id="my_file" type="file" />
<input type="submit" value="提交" />
</form>
</body>
</html>

#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
import tornado.ioloop
import tornado.web
class MainHandler(tornado.web.RequestHandler):
def get(self):
self.render(‘index.html‘)
def post(self, *args, **kwargs):
file_metas = self.request.files["fff"]
# print(file_metas)
for meta in file_metas:
file_name = meta[‘filename‘]
with open(file_name,‘wb‘) as up:
up.write(meta[‘body‘])
settings = {
‘template_path‘: ‘template‘,
}
application = tornado.web.Application([
(r"/index", MainHandler),
], **settings)
if __name__ == "__main__":
application.listen(8000)
tornado.ioloop.IOLoop.instance().start()
2、AJAX上传

<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head lang="en">
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title></title>
</head>
<body>
<input type="file" id="img" />
<input type="button" onclick="UploadFile();" />
<script>
function UploadFile(){
var fileObj = document.getElementById("img").files[0];
var form = new FormData();
form.append("k1", "v1");
form.append("fff", fileObj);
var xhr = new XMLHttpRequest();
xhr.open("post", ‘/index‘, true);
xhr.send(form);
}
</script>
</body>
</html>

<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head lang="en">
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title></title>
</head>
<body>
<input type="file" id="img" />
<input type="button" onclick="UploadFile();" />
<script>
function UploadFile(){
var fileObj = $("#img")[0].files[0];
var form = new FormData();
form.append("k1", "v1");
form.append("fff", fileObj);
$.ajax({
type:‘POST‘,
url: ‘/index‘,
data: form,
processData: false, // tell jQuery not to process the data
contentType: false, // tell jQuery not to set contentType
success: function(arg){
console.log(arg);
}
})
}
</script>
</body>
</html>

<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head lang="en">
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title></title>
</head>
<body>
<form id="my_form" name="form" action="/index" method="POST" enctype="multipart/form-data" >
<div id="main">
<input name="fff" id="my_file" type="file" />
<input type="button" name="action" value="Upload" onclick="redirect()"/>
<iframe id=‘my_iframe‘ name=‘my_iframe‘ src="" class="hide"></iframe>
</div>
</form>
<script>
function redirect(){
document.getElementById(‘my_iframe‘).onload = Testt;
document.getElementById(‘my_form‘).target = ‘my_iframe‘;
document.getElementById(‘my_form‘).submit();
}
function Testt(ths){
var t = $("#my_iframe").contents().find("body").text();
console.log(t);
}
</script>
</body>
</html>

#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
import tornado.ioloop
import tornado.web
class MainHandler(tornado.web.RequestHandler):
def get(self):
self.render(‘index.html‘)
def post(self, *args, **kwargs):
file_metas = self.request.files["fff"]
# print(file_metas)
for meta in file_metas:
file_name = meta[‘filename‘]
with open(file_name,‘wb‘) as up:
up.write(meta[‘body‘])
settings = {
‘template_path‘: ‘template‘,
}
application = tornado.web.Application([
(r"/index", MainHandler),
], **settings)
if __name__ == "__main__":
application.listen(8000)
tornado.ioloop.IOLoop.instance().start()

<script type="text/javascript">
$(document).ready(function () {
$("#formsubmit").click(function () {
var iframe = $(‘<iframe name="postiframe" id="postiframe" style="display: none"></iframe>‘);
$("body").append(iframe);
var form = $(‘#theuploadform‘);
form.attr("action", "/upload.aspx");
form.attr("method", "post");
form.attr("encoding", "multipart/form-data");
form.attr("enctype", "multipart/form-data");
form.attr("target", "postiframe");
form.attr("file", $(‘#userfile‘).val());
form.submit();
$("#postiframe").load(function () {
iframeContents = this.contentWindow.document.body.innerHTML;
$("#textarea").html(iframeContents);
});
return false;
});
});
</script>
<form id="theuploadform">
<input id="userfile" name="userfile" size="50" type="file" />
<input id="formsubmit" type="submit" value="Send File" />
</form>
<div id="textarea">
</div>

$(‘#upload_iframe‘).load(function(){
var iframeContents = this.contentWindow.document.body.innerText;
iframeContents = JSON.parse(iframeContents);
})

function bindChangeAvatar1() {
$(‘#avatarImg‘).change(function () {
var file_obj = $(this)[0].files[0];
$(‘#prevViewImg‘)[0].src = window.URL.createObjectURL(file_obj)
})
}
function bindChangeAvatar2() {
$(‘#avatarImg‘).change(function () {
var file_obj = $(this)[0].files[0];
var reader = new FileReader();
reader.readAsDataURL(file_obj);
reader.onload = function (e) {
$(‘#previewImg‘)[0].src = this.result;
};
})
}
function bindChangeAvatar3() {
$(‘#avatarImg‘).change(function () {
var file_obj = $(this)[0].files[0];
var form = new FormData();
form.add(‘img_upload‘, file_obj);
$.ajax({
url: ‘‘,
data: form,
processData: false, // tell jQuery not to process the data
contentType: false, // tell jQuery not to set contentType
success: function (arg) {
}
})
})
}
function bindChangeAvatar4() {
$(‘#avatarImg‘).change(function () {
$(this).parent().submit();
$(‘#upload_iframe‘).load(function () {
var iframeContents = this.contentWindow.document.body.innerText;
iframeContents = JSON.parse(iframeContents);
if (iframeContents.status) {
$(‘#previewImg‘).attr(‘src‘, ‘/‘ + iframeContents.data);
}
})
})
}
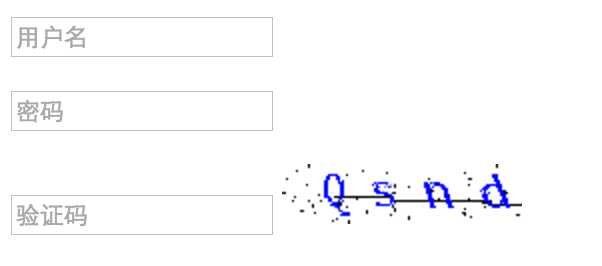
八、验证码
验证码原理在于后台自动创建一张带有随机内容的图片,然后将内容通过img标签输出到页面。
安装图像处理模块:
|
1
|
pip3 install pillow |
示例截图:
验证码Demo源码下载:猛击这里
九、异步非阻塞
1、基本使用
装饰器 + Future 从而实现Tornado的异步非阻塞
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
|
class AsyncHandler(tornado.web.RequestHandler): @gen.coroutine def get(self): future = Future() future.add_done_callback(self.doing) yield future # 或 # tornado.ioloop.IOLoop.current().add_future(future,self.doing) # yield future def doing(self,*args, **kwargs): self.write(‘async‘) self.finish() |
当发送GET请求时,由于方法被@gen.coroutine装饰且yield 一个 Future对象,那么Tornado会等待,等待用户向future对象中放置数据或者发送信号,如果获取到数据或信号之后,就开始执行doing方法。
异步非阻塞体现在当在Tornaod等待用户向future对象中放置数据时,还可以处理其他请求。
注意:在等待用户向future对象中放置数据或信号时,此连接是不断开的。
2、同步阻塞和异步非阻塞对比

class SyncHandler(tornado.web.RequestHandler):
def get(self):
self.doing()
self.write(‘sync‘)
def doing(self):
time.sleep(10)

class AsyncHandler(tornado.web.RequestHandler):
@gen.coroutine
def get(self):
future = Future()
tornado.ioloop.IOLoop.current().add_timeout(time.time() + 5, self.doing)
yield future
def doing(self, *args, **kwargs):
self.write(‘async‘)
self.finish()
3、httpclient类库
Tornado提供了httpclient类库用于发送Http请求,其配合Tornado的异步非阻塞使用。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
|
#!/usr/bin/env python# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-import tornado.webfrom tornado import genfrom tornado import httpclient# 方式一:class AsyncHandler(tornado.web.RequestHandler): @gen.coroutine def get(self, *args, **kwargs): print(‘进入‘) http = httpclient.AsyncHTTPClient() data = yield http.fetch("http://www.google.com") print(‘完事‘,data) self.finish(‘6666‘)# 方式二:# class AsyncHandler(tornado.web.RequestHandler):# @gen.coroutine# def get(self):# print(‘进入‘)# http = httpclient.AsyncHTTPClient()# yield http.fetch("http://www.google.com", self.done)## def done(self, response):# print(‘完事‘)# self.finish(‘666‘)application = tornado.web.Application([ (r"/async", AsyncHandler),])if __name__ == "__main__": application.listen(8888) tornado.ioloop.IOLoop.instance().start() |

#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
"""
需要先安装支持异步操作Mysql的类库:
Tornado-MySQL: https://github.com/PyMySQL/Tornado-MySQL#installation
pip3 install Tornado-MySQL
"""
import tornado.web
from tornado import gen
import tornado_mysql
from tornado_mysql import pools
POOL = pools.Pool(
dict(host=‘127.0.0.1‘, port=3306, user=‘root‘, passwd=‘123‘, db=‘cmdb‘),
max_idle_connections=1,
max_recycle_sec=3)
@gen.coroutine
def get_user_by_conn_pool(user):
cur = yield POOL.execute("SELECT SLEEP(%s)", (user,))
row = cur.fetchone()
raise gen.Return(row)
@gen.coroutine
def get_user(user):
conn = yield tornado_mysql.connect(host=‘127.0.0.1‘, port=3306, user=‘root‘, passwd=‘123‘, db=‘cmdb‘,
charset=‘utf8‘)
cur = conn.cursor()
# yield cur.execute("SELECT name,email FROM web_models_userprofile where name=%s", (user,))
yield cur.execute("select sleep(10)")
row = cur.fetchone()
cur.close()
conn.close()
raise gen.Return(row)
class LoginHandler(tornado.web.RequestHandler):
def get(self, *args, **kwargs):
self.render(‘login.html‘)
@gen.coroutine
def post(self, *args, **kwargs):
user = self.get_argument(‘user‘)
data = yield gen.Task(get_user, user)
if data:
print(data)
self.redirect(‘http://www.oldboyedu.com‘)
else:
self.render(‘login.html‘)
application = tornado.web.Application([
(r"/login", LoginHandler),
])
if __name__ == "__main__":
application.listen(8888)
tornado.ioloop.IOLoop.instance().start()

