标签:ide 情况 http 客户端 使用 服务端 close ima 变化
关于TCP的数据拆包、粘包的介绍,我在上一篇文章里面已经有过介绍。
想要了解一下的,请点击这里 Chick Here!
今天我们要讲解的是Netty提供的两种解决方案:
(1)使用StringDecoder之前
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {
try {
ByteBuf in = (ByteBuf) msg;
String str = in.toString(CharsetUtil.UTF_8);
System.out.println("Client:"+str);
} finally {
ReferenceCountUtil.release(msg);
}
}(2)使用StringDecoder之后
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {
try {
String str = (String) msg;
System.out.println("Client:"+str);
} finally {
ReferenceCountUtil.release(msg);
}
}关于Decoder
decoder:n. 解码器
在我看来,Netty数据的解析方式大概为:
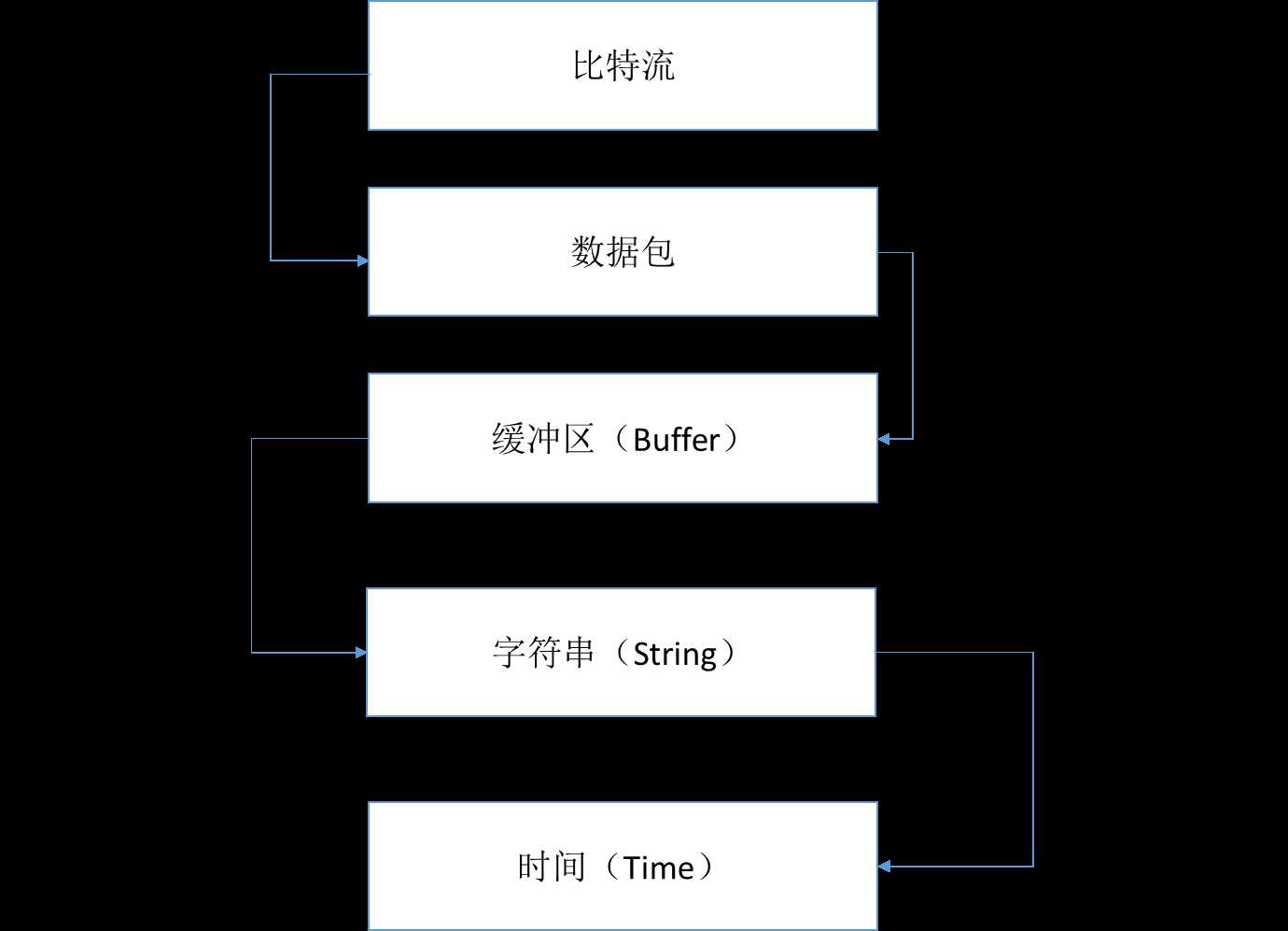
发送过程:Buffer------>数据报------>比特流
接受过程:Buffer<------数据报<------比特流
所以我们接受到的msg是一个ButeBuf
使用了Decoder(这里使用StringDecoder举例)之后:
发送过程:Buffer------>数据报------>比特流
接受过程:String<------Buffer<------数据报<------比特流
相当于ByteBuf按照StringDecoder的解码规则,把msg翻译成为了一个字符串。
如何使用Decoder
(1)实际代码演示:
package com.xm.netty.demo02;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import io.netty.bootstrap.ServerBootstrap;
import io.netty.channel.Channel;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelFuture;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelInitializer;
import io.netty.channel.EventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioServerSocketChannel;
import io.netty.handler.codec.string.StringDecoder;
public class Server {
private final int port;
public Server(int port) {
this.port = port;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int port = 8989;
try {
new Server(port).start();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
private void start() throws InterruptedException {
EventLoopGroup g1 = new NioEventLoopGroup();
EventLoopGroup g2 = new NioEventLoopGroup();
try {
ServerBootstrap bootstrap = new ServerBootstrap();
bootstrap
.group(g1,g2)
.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class)
.localAddress(new InetSocketAddress( port))
.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(Channel ch) throws Exception {
ch.pipeline().addLast(new StringDecoder());
ch.pipeline().addLast(new ServerHandler());
}
});
ChannelFuture future = bootstrap.bind().sync();
future.channel().closeFuture().sync();
} finally {
g1.shutdownGracefully().sync();
g2.shutdownGracefully().sync();
}
}
}代码改动:
ch.pipeline().addLast(new StringDecoder());
?? ch.pipeline().addLast(new ServerHandler());
(2)多个Decoder的使用顺序:
从前往后,依次解码
?
假设我们有个通过字符串变化为时间的TimeDecoder:
ch.pipeline().addLast(new StringDecoder());
ch.pipeline().addLast(new TimeDecoder());
? ch.pipeline().addLast(new ServerHandler());
解析规则为:
关于DelimiterBasedFrameDecoder
其实很简单,就是在一个缓冲区的末尾添加一个结束字符。
在规定了最大长度的缓冲区里,遇到一个特殊字符,就截取一次。
原理类似于String的split()方法。
代码实现
(1)服务端Server
package com.xm.netty.demo03;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import io.netty.bootstrap.ServerBootstrap;
import io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf;
import io.netty.buffer.Unpooled;
import io.netty.channel.Channel;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelFuture;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelInitializer;
import io.netty.channel.EventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioServerSocketChannel;
import io.netty.handler.codec.DelimiterBasedFrameDecoder;
import io.netty.handler.codec.string.StringDecoder;
public class Server {
private final int port;
public Server(int port) {
this.port = port;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int port = 8989;
try {
new Server(port).start();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
private void start() throws InterruptedException {
EventLoopGroup g1 = new NioEventLoopGroup();
EventLoopGroup g2 = new NioEventLoopGroup();
try {
ServerBootstrap bootstrap = new ServerBootstrap();
bootstrap
.group(g1,g2)
.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class)
.localAddress(new InetSocketAddress( port))
.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(Channel ch) throws Exception {
ByteBuf buf = Unpooled.copiedBuffer("$".getBytes());
ch.pipeline().addLast(new DelimiterBasedFrameDecoder(1024,buf));
ch.pipeline().addLast(new StringDecoder());
ch.pipeline().addLast(new ServerHandler());
}
});
ChannelFuture future = bootstrap.bind().sync();
future.channel().closeFuture().sync();
} finally {
g1.shutdownGracefully().sync();
g2.shutdownGracefully().sync();
}
}
}(2)服务端ServerHandler
package com.xm.netty.demo03;
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
import java.time.format.DateTimeFormatter;
import io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf;
import io.netty.buffer.Unpooled;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerAdapter;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext;
import io.netty.util.CharsetUtil;
public class ServerHandler extends ChannelHandlerAdapter {
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {
String str = (String) msg;
System.out.println("Server:"+str);
str = "服务器返回--->"+ str+"$";
ctx.writeAndFlush(Unpooled.copiedBuffer(str.getBytes()));
}
@Override
public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) throws Exception {
cause.printStackTrace();
ctx.close();
}
@Override
public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
System.out.println(DateTimeFormatter.ISO_LOCAL_DATE_TIME.format(LocalDateTime.now())+"一个客户端连接上服务器!");
}
}
(3)客户端Client
package com.xm.netty.demo03;
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
import java.time.format.DateTimeFormatter;
import io.netty.bootstrap.Bootstrap;
import io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf;
import io.netty.buffer.Unpooled;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelFuture;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelInitializer;
import io.netty.channel.EventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.socket.SocketChannel;
import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioSocketChannel;
import io.netty.handler.codec.DelimiterBasedFrameDecoder;
import io.netty.handler.codec.string.StringDecoder;
public class Client {
private final int port;
private final String host;
public Client(int port, String host) {
this.port = port;
this.host = host;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
String host = "127.0.0.1";
int port = 8989;
try {
new Client(port, host).start();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
private void start() throws InterruptedException {
EventLoopGroup group = new NioEventLoopGroup();
try {
Bootstrap bootstrap = new Bootstrap();
bootstrap
.group(group)
.channel(NioSocketChannel.class)
.remoteAddress(host, port)
.handler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
ByteBuf buf = Unpooled.copiedBuffer("$".getBytes());
ch.pipeline().addLast(new DelimiterBasedFrameDecoder(1024,buf));
ch.pipeline().addLast(new StringDecoder());
ch.pipeline().addLast(new ClientHandler());
}
});
ChannelFuture future = bootstrap.connect().sync();
for(int i=10;i<20;i++) {
String str = DateTimeFormatter.ISO_LOCAL_DATE_TIME.format(LocalDateTime.now()) + "---- " +i+"<<<$";
future.channel().write(Unpooled.copiedBuffer(str.getBytes()));
}
future.channel().flush();
//future.channel().writeAndFlush(Unpooled.copiedBuffer("Hello Netty!".getBytes()));
future.channel().closeFuture().sync();
} finally {
group.shutdownGracefully().sync();
}
}
}
(4)客户端ClientHandler
package com.xm.netty.demo03;
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
import java.time.format.DateTimeFormatter;
import io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf;
import io.netty.buffer.Unpooled;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerAdapter;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext;
import io.netty.util.CharsetUtil;
import io.netty.util.ReferenceCountUtil;
public class ClientHandler extends ChannelHandlerAdapter {
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {
try {
String str = (String) msg;
System.out.println("Client:"+str);
} finally {
ReferenceCountUtil.release(msg);
}
}
@Override
public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) throws Exception {
cause.printStackTrace();
ctx.close();
}
@Override
public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
System.out.println(DateTimeFormatter.ISO_LOCAL_DATE_TIME.format(LocalDateTime.now())+"已连接服务器!");
}
}
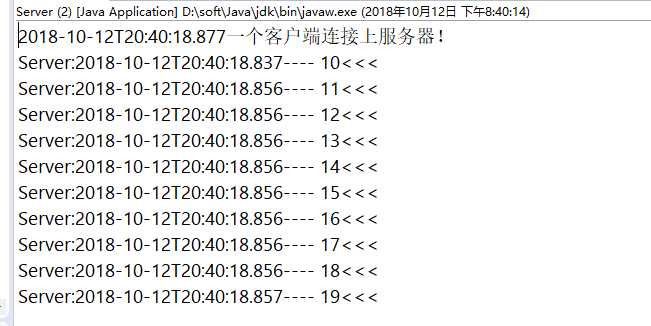
运行结果截图
(1)服务端运行结果:
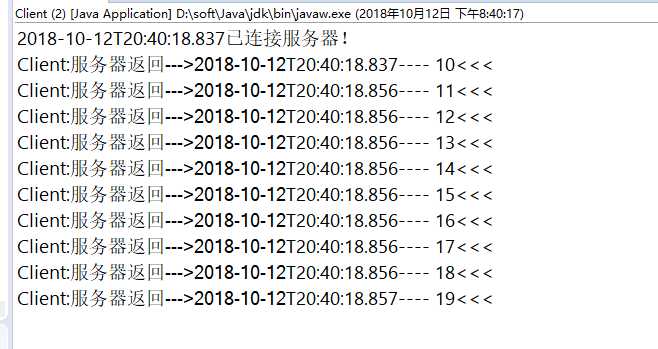
(2)客户端运行结果:
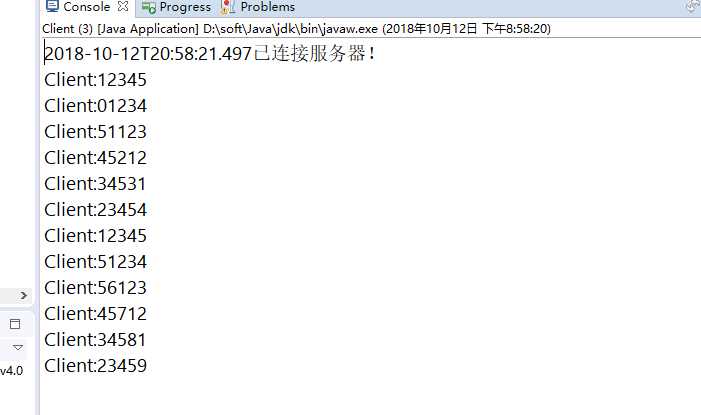
关于FixedLengthFrameDecoder
其实很简单,就是对规定的发送的数据进行限制长度,
当符合这个长度的情况下,就可以解析。
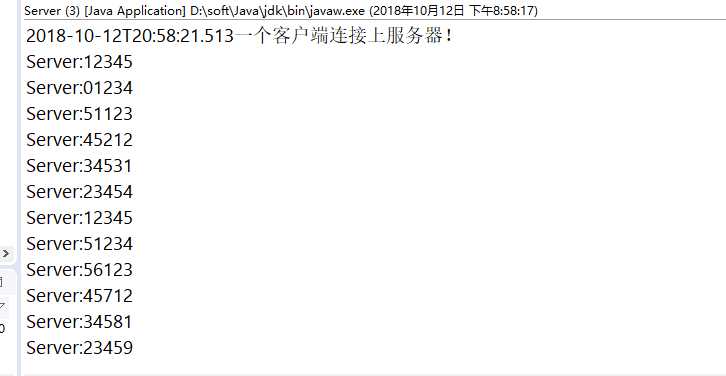
假设你发送一个’123456‘,’654321‘
那么解析的状况为’12345‘,’66543‘
代码实现
(1)服务端Server
package com.xm.netty.demo04;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import io.netty.bootstrap.ServerBootstrap;
import io.netty.channel.Channel;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelFuture;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelInitializer;
import io.netty.channel.EventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioServerSocketChannel;
import io.netty.handler.codec.FixedLengthFrameDecoder;
import io.netty.handler.codec.string.StringDecoder;
public class Server {
private final int port;
public Server(int port) {
this.port = port;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int port = 8989;
try {
new Server(port).start();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
private void start() throws InterruptedException {
EventLoopGroup g1 = new NioEventLoopGroup();
EventLoopGroup g2 = new NioEventLoopGroup();
try {
ServerBootstrap bootstrap = new ServerBootstrap();
bootstrap
.group(g1,g2)
.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class)
.localAddress(new InetSocketAddress( port))
.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(Channel ch) throws Exception {
ch.pipeline().addLast(new FixedLengthFrameDecoder(5));
ch.pipeline().addLast(new StringDecoder());
ch.pipeline().addLast(new ServerHandler());
}
});
ChannelFuture future = bootstrap.bind().sync();
future.channel().closeFuture().sync();
} finally {
g1.shutdownGracefully().sync();
g2.shutdownGracefully().sync();
}
}
}(2)服务端ServerHandler
package com.xm.netty.demo04;
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
import java.time.format.DateTimeFormatter;
import io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf;
import io.netty.buffer.Unpooled;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerAdapter;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext;
import io.netty.util.CharsetUtil;
public class ServerHandler extends ChannelHandlerAdapter {
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {
String str = (String) msg;
System.out.println("Server:"+str);
ctx.writeAndFlush(Unpooled.copiedBuffer(str.getBytes()));
}
@Override
public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) throws Exception {
cause.printStackTrace();
ctx.close();
}
@Override
public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
System.out.println(DateTimeFormatter.ISO_LOCAL_DATE_TIME.format(LocalDateTime.now())+"一个客户端连接上服务器!");
}
}
(3)客户端Client
package com.xm.netty.demo04;
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
import java.time.format.DateTimeFormatter;
import io.netty.bootstrap.Bootstrap;
import io.netty.buffer.Unpooled;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelFuture;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelInitializer;
import io.netty.channel.EventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.socket.SocketChannel;
import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioSocketChannel;
import io.netty.handler.codec.FixedLengthFrameDecoder;
import io.netty.handler.codec.string.StringDecoder;
public class Client {
private final int port;
private final String host;
public Client(int port, String host) {
this.port = port;
this.host = host;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
String host = "127.0.0.1";
int port = 8989;
try {
new Client(port, host).start();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
private void start() throws InterruptedException {
EventLoopGroup group = new NioEventLoopGroup();
try {
Bootstrap bootstrap = new Bootstrap();
bootstrap
.group(group)
.channel(NioSocketChannel.class)
.remoteAddress(host, port)
.handler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
ch.pipeline().addLast(new FixedLengthFrameDecoder(5));
ch.pipeline().addLast(new StringDecoder());
ch.pipeline().addLast(new ClientHandler());
}
});
ChannelFuture future = bootstrap.connect().sync();
for(int i=123450;i<123460;i++) {
String str = ""+i;
future.channel().write(Unpooled.copiedBuffer(str.getBytes()));
}
future.channel().flush();
//future.channel().writeAndFlush(Unpooled.copiedBuffer("Hello Netty!".getBytes()));
future.channel().closeFuture().sync();
} finally {
group.shutdownGracefully().sync();
}
}
}
(4)客户端ClientHandler
package com.xm.netty.demo04;
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
import java.time.format.DateTimeFormatter;
import io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf;
import io.netty.buffer.Unpooled;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerAdapter;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext;
import io.netty.util.CharsetUtil;
import io.netty.util.ReferenceCountUtil;
public class ClientHandler extends ChannelHandlerAdapter {
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {
try {
String str = (String) msg;
System.out.println("Client:"+str);
} finally {
ReferenceCountUtil.release(msg);
}
}
@Override
public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) throws Exception {
cause.printStackTrace();
ctx.close();
}
@Override
public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
System.out.println(DateTimeFormatter.ISO_LOCAL_DATE_TIME.format(LocalDateTime.now())+"已连接服务器!");
}
}
运行结果截图
(1)服务端运行结果:
(2)客户端运行结果:
标签:ide 情况 http 客户端 使用 服务端 close ima 变化
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/TimerHotel/p/netty03.html