标签:注意 某月 unbound 获取 png 饼状图 职位 lse 公司
和聚合函数相似,但是对于每一组记录,无论多少行,聚合函数只返回一行值,而分析函数对其中每一行记录都返回值
这一组记录,称为分析函数的一个窗口(WINDOW)
由窗口决定了要处理数据的范围,该范围在物理上可以由指定的行数来确定,或者在逻辑上由相对偏移量来确定
分析函数总是在除了ORDER BY之外的其他子句运算后才执行的,所以它不能出现在 where、group by等子句中,只能出现在select列表和order by子句中
排名 相邻 统计
– 排名无并列,且每个排名与紧接着的下一个排名都是连续的
– 排名有并列,且并列的排名与紧接着的下一个排名不连续
– 排名有并列,且并列的排名与紧接着的下一个排名连续
– 如下例,对CNT列排序的结果,从左到右分别符合上述三种需求,结果即为:
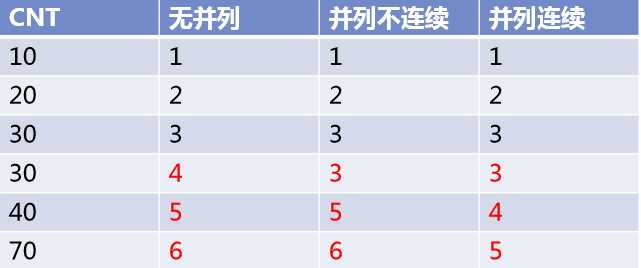
– 对cnt列的不同排名,sql如何写?
with t as (select rownum*10 cnt from dual connect by rownum<5 union all select rownum*4010 from dual connect by rownum<3) select cnt, row_number()over(order by cnt) rn, rank()over(order by cnt) rk, dense_rank()over(order by cnt) drk from t
– row_number – rank – dense_rank
select dept_id, sale_date, goods_type, sale_cnt, row_number()over(partition by
dept_id order by sale_cnt desc) rn, rank()over(partition by dept_id order by sale_cnt desc) rk,
dense_rank()over(partition by dept_id order by sale_cnt desc) drk from lw_sales where trunc(sale_date,‘MM‘)=date‘2013-04-01‘;
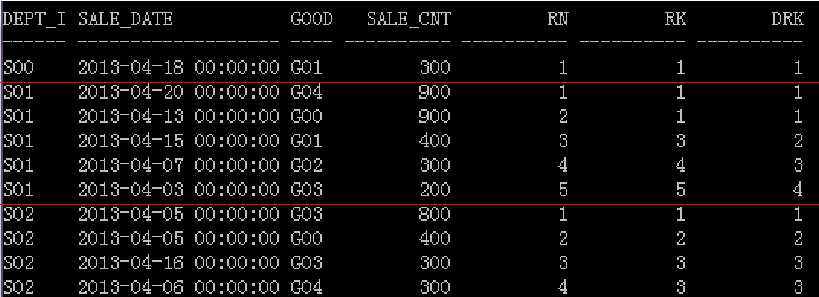
– 排名分析函数不需要参数
– 排名分析函数里的order by子句是必须的
– partition by 和 order by后均可跟多列
– 只在没有partition by 的情况下,rownum才能做到和row_number同样的事情
– 用于获取相邻行的数据,以便于进行相关计算,例如同比环比
– 实现重复数据只输出第一个的需求
– 实现重复数据只输出第一个和最后一个的需求
– LAG和LEAD用于获取相邻行的数据,以便于进行相关计算
– LAG 是取到排序后当前记录之前的记录
– LEAD 是取到排序后当前记录之后的记录
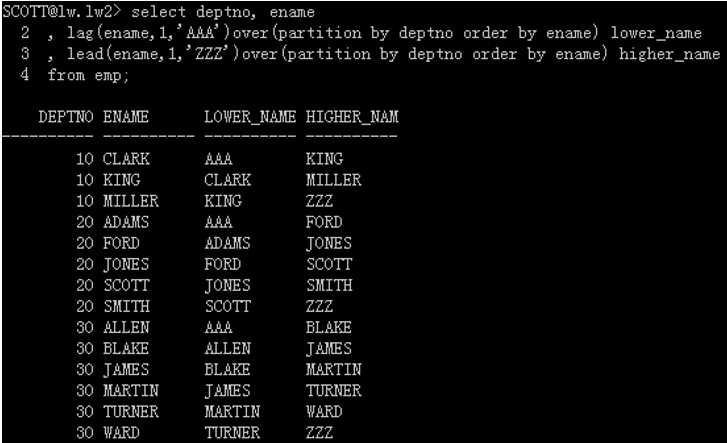
查出同部门按字母正序姓名比自己大和小的雇员姓名各是啥?没有比自己姓名小的设为AAA ,没有比自己姓名大的设为ZZZ。
select deptno, ename , lag(ename,1,‘AAA‘)over(partition by deptno order by ename) lower_name , lead(ename,1,‘ZZZ‘)over(partition by deptno order by ename) higher_name from emp;
在前例基础上,部门编号只输出一次
select (case when deptno= lag(deptno,1,-1)over(partition by deptno order by ename) then null else deptno end) deptno , ename , lag(ename,1,‘AAA‘)over(partition by deptno order by ename) lower_name , lead(ename,1,‘ZZZ‘)over(partition by deptno order by ename) higher_name from emp;
– LAG/LEAD(v, n, dv)里的n表示位移,必须是0或正整数,dv是在没有取到对应值时的默认值 。n默认是1,dv默认是null。
– 相邻类分析函数后面order by子句是必须的
– partition by 和 order by后均可跟多列
– 当年各月的累计销售额
– 每名销售人员当月的销售额与平均每名销售人员销售额的差值
– XX货物每月的最高和最低销售额对应的部门
– 获取相邻行内最近的一个非空值
– ……
– SUM
– AVG
– MAX/MIN
– FIRST_VALUE/LAST_VALUE
– ……
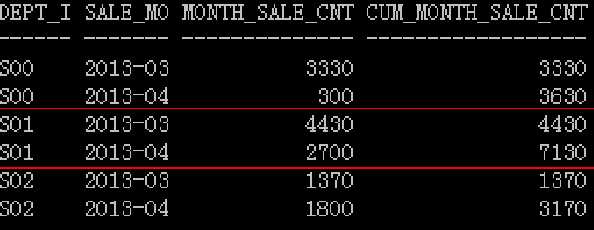
求出每个部门按月的累计销售额
with t as (select dept_id, to_char(sale_date,‘YYYY-MM‘) sale_month, sum(sale_cnt) month_sale_cnt from lw_sales group by dept_id, to_char(sale_date,‘YYYY-MM‘)) select dept_id, sale_month, month_sale_cnt, sum(month_sale_cnt)over(partition by dept_id order by sale_month) cum_month_sale_cnt from t;
求出每个部门按售出货物类别的累计销售额(按货物类别代码正序排列)以及每个货物按部门 的累计销售额(按部门编号正序排列)
with t as (select dept_id, goods_type, sum(sale_cnt) goods_sale_cnt from lw_sales group by dept_id, goods_type) select dept_id, goods_type, goods_sale_cnt, sum(goods_sale_cnt)over(partition by dept_id order by goods_type) cum_gsc_goods, sum(goods_sale_cnt)over(partition by goods_type order by dept_id) cum_gsc_dept from t;
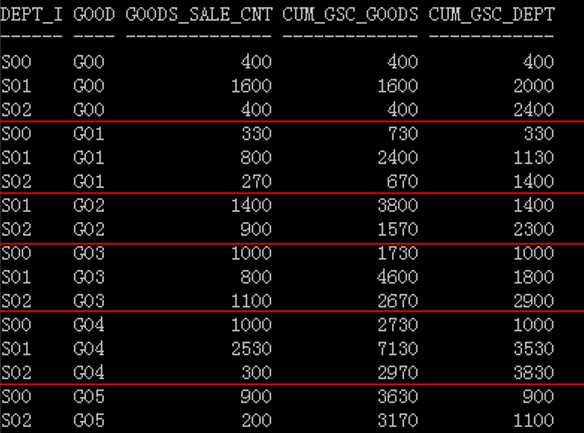
排序规则=select中排在最后的规则
求出每个部门每种货物的销售额与该货物在公司各部门平均销售额之间的差值
分析函数写法:
with t as (select dept_id, goods_type, sum(sale_cnt) goods_sale_cnt from lw_sales group by dept_id, goods_type) select dept_id, goods_type, goods_sale_cnt, round(AVG(goods_sale_cnt)over(partition by goods_type),2) avg_goods_sale_cnt ,goods_sale_cnt-round(AVG(goods_sale_cnt) over(partition by goods_type),2) dv_goods_sale_cnt from t;
传统方式写法:
with t as (select dept_id, goods_type, sum(sale_cnt) goods_sale_cnt from lw_sales group by dept_id, goods_type) ,t1 as (select goods_type, round(avg(goods_sale_cnt),2) avg_goods_sale_cnt from t group by goods_type) select a.dept_id, a.goods_type, goods_sale_cnt, avg_goods_sale_cnt, goods_sale_cnt-avg_goods_sale_cnt dv_goods_sale_cnt from t a, t1 b where a.goods_type=b.goods_type order by 2,1;
不同写法的比较

一般情况下,分析函数性能优于传统写法
货物G01每月的最高和最低销售额对应的部门(如有多个部门按部门ID列出最小的一个,如某部门某月无销售额则不做统计)
传统方式写法:
with t as (select dept_id , to_char(sale_date,‘YYYY-MM‘) sale_month, sum(sale_cnt) goods_sale_cnt from lw_sales where goods_type=‘G01‘ group by dept_id, to_char(sale_date,‘YYYY-MM‘)) , t1 as (select sale_month, max(goods_sale_cnt) max_gsc, min(goods_sale_cnt) min_gsc from t group by sale_month)
select a.sale_month, min(case when goods_sale_cnt=max_gsc then dept_id end) max_dept_id, min(case when goods_sale_cnt=min_gsc then dept_id end) min_dept_id
from t a, t1 b where a.sale_month=b.sale_month and (goods_sale_cnt=min_gsc or goods_sale_cnt=max_gsc ) group by a.sale_month;
分析函数写法:
with t as (select dept_id , to_char(sale_date,‘YYYY-MM‘) sale_month, sum(sale_cnt) goods_sale_cnt, max(sum(sale_cnt))over(partition by to_char(sale_date,‘YYYY-MM‘)) max_gsc,
min(sum(sale_cnt))over(partition by to_char(sale_date,‘YYYY-MM‘)) min_gsc from lw_sales where goods_type=‘G01‘ group by dept_id, to_char(sale_date,‘YYYYMM‘))
select a.sale_month, min(case when goods_sale_cnt=max_gsc then dept_id end) max_dept_id, min(case when goods_sale_cnt=min_gsc then dept_id end) min_dept_id
from t a where (goods_sale_cnt=min_gsc or goods_sale_cnt=max_gsc ) group by a.sale_month;
最直接的写法:
with t as (select dept_id , to_char(sale_date,‘YYYY-MM‘) sale_month, sum(sale_cnt) goods_sale_cnt from lw_sales where goods_type=‘G01‘ group by dept_id, to_char(sale_date,‘YYYY-MM‘)) select a.sale_month, min(dept_id)keep(dense_rank first order by goods_sale_cnt desc) max_dept_id, min(dept_id)keep(dense_rank first order by goods_sale_cnt) min_dept_id from t a group by a.sale_month;
在这种写法里,MAX/MIN是作为聚合函数而不是分析函数去用的,后面的FIRST函数也是聚合函数
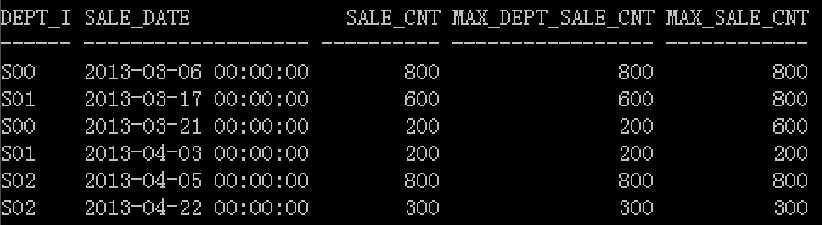
查出货物G03在销售当天及前十二天的最大销售额(按部门和整个公司分别求出)
select dept_id, sale_date,sale_cnt, max(sale_cnt)over(partition by dept_id order by sale_date range interval ‘12‘ day preceding) max_dept_sale_cnt, max(sale_cnt)over(order by sale_date range numtodsinterval(12, ‘DAY‘) preceding) max_sale_cnt from lw_sales where goods_type=‘G03‘;
货物G01每月的最高和最低销售额对应的部门(如有多个部门按部门ID列出最小的一个,如某部门某月无销售额则不做统计)
with t as (select dept_id , to_char(sale_date,‘YYYY-MM‘) sale_month, sum(sale_cnt) goods_sale_cnt from lw_sales where goods_type=‘G01‘ group by dept_id, to_char(sale_date,‘YYYY-MM‘)),
t1 as (select a.sale_month, min(dept_id)keep(dense_rank first order by goods_sale_cnt desc) over(partition by a.sale_month) max_dept_id, min(dept_id)keep(dense_rank first order by goods_sale_cnt) over(partition by a.sale_month) min_dept_id from t a)
select sale_month, min(max_dept_id), min(min_dept_id) from t1 group by sale_month;
在这种写法里,MAX/MIN依然是作为聚合函数而不是分析函数去用的,但后面的FIRST函数是作为分析函数去用的
查出所有雇员的雇员职位、编号、姓名、薪水以及同职位上薪水最高和最低的雇员的雇员编号 (薪水相同的,按雇员编号倒序排列)
select job, empno, ename, sal, last_value(empno)over(partition by job order by sal, empno desc rows between unbounded preceding and unbounded following) lv, first_value(empno)over(partition by job order by sal, empno desc rows between unbounded preceding and unbounded following) fv from emp;
查出所有雇员的雇员职位、编号、姓名、薪水以及同职位上薪水最高和最低的雇员的雇员编号 (薪水相同的,按雇员编号倒序排列)
select job, empno, ename, sal, max(empno)keep(dense_rank last order by sal, empno desc)over(partition by job) lv, max(empno)keep(dense_rank first order by sal, empno desc)over(partition by job) fv from emp;
在"相邻"最后一例基础上,补全缺失的部门编号
with t as (select (case when deptno= lag(deptno,1,-1)over(partition by deptno order by ename) then null else deptno end) deptno , ename , lag(ename,1,‘AAA‘)over(partition by deptno order by ename) lower_name , lead(ename,1,‘ZZZ‘)over(partition by deptno order by ename) higher_name from emp) , t1 as (select t.*, rownum rn from t) select (case when deptno is not null then deptno else last_value(deptno ignore nulls)over(order by rn) end) deptno , ename, lower_name, higher_name from t1;
– 可以有partition by、order by和range/rows子句(此即windowing子句)
– 以上子句都不是必须出现的,但若出现windowing子句则其前必须出现order by子句
– 没有order by都就是分组统计,有order by就是分组累计
– FIRST/LAST这两个分析函数后面只能跟partition by子句
– FIRST_VALUE和LAST_VALUE用于获取一组有序的数据中的第一个和最后一个值,和 MAX/MIN以及FIRST/LAST函数很像,但要注意区别
– COUNT也可以作为分析函数,这和SUM/MAX等差不多,另外一个函数叫 RATIO_TO_REPORT,在做报表或饼状图的时候很有用,俩都自学吧!
标签:注意 某月 unbound 获取 png 饼状图 职位 lse 公司
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/lm970585581/p/9754355.html