标签:ima datasets type lse class .data 判断 and shape
4
用python实现K均值算法
x=np.random.randint(1,100,[20,1]) y=np.zeros(20) k=3
def initcenter(x,k): return x[:k] def nearest(kc,i): d = (abs(kc - i)) w = np.where(d ==np.min(d)) return w [0] [0] kc = initcenter(x,k) nearest(kc,14)

for i in range(x.shape[0]): print(nearest(kc,x[i]))
运行结果为:
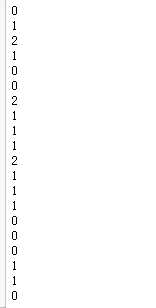
for i in range(x.shape[0]): y[i] = nearest(kc,x[i]) print(y)
运行结果为:
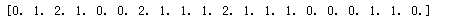
for i in range(x.shape[0]): y[i]=nearest(kc,x[i]) print(y)
运行结果为:
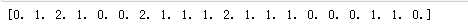
def initcenter(x,k): return x[:k] def nearest(kc, i): d = (abs(kc - 1)) w= np.where(d == np.min(d)) return w[0][0] def xclassify(x,y,kc): for i in range(x.shape[0]): y[i] = nearest(kc,x[i]) return y kc = initcenter(x,k) nearest(kc,93)
m = np.where(y == 0)
np.mean(x[m])
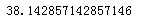
kc[0]=24
flag = True
import numpy as np from sklearn.datasets import load_iris iris = load_iris() x = iris.data[:,1] y = np.zeros(150) def nearest(kc,i): #初始聚类中心数组 return x[0:k] def nearest(kc,i): #数组中的值,与聚类中心最小距离所在类别的索引号 d = (abs(kc - i)) w = np.where(d == np.min(d)) return w[0][0] def kcmean(x, y, kc, k): #计算各聚类新均值 l =list(kc) flag = False for c in range(k): m = np.where(y == c) if m[0].shape != (0,): n = np.mean(x[m]) if l[c] != n: l[c] = n flag = True #聚类中心发生改变 return (np.array(1),flag) def xclassify(x,y,kc): for i in range(x.shape[0]): #对数组的每个值分类 y[i] = nearest(kc,x[i]) return y k = 3 kc = initcenter(x,k) falg = True print(x, y, kc, flag) while flag: y = xclassify(x, y, kc) xc, flag = kcmean(x, y, kc, k) print(y,kc)
运行结果为:
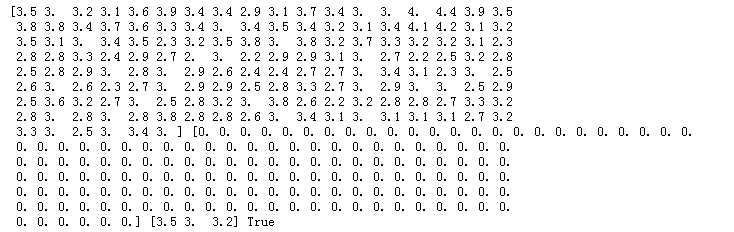
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt plt.scatter(x, x, c=y, s=50, cmap=‘rainbow‘,marker=‘p‘,alpha=0.5); plt.show()
运行结果为:
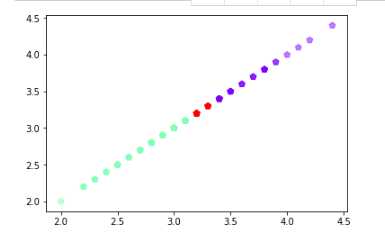
鸢尾花花瓣长度数据做聚类并用散点图显示。
import numpy as np from sklearn.datasets import load_iris iris = load_iris() x = iris.data[:,1] y = np.zeros(150) def initcenter(x,k): #初始聚类中心数组 return x[0:k].reshape(k) def nearest(kc,i): #数组中的值,与聚类中心最小距离所在类别的索引号 d = (abs(kc-i)) w = np.where(d == np.min(d)) return w[0][0] def xclassify(x,y,kc): for i in range(x.shape[0]): #对数组的每个值进行分类,shape[0]读取矩阵第一维度的长度 y[i] = nearest(kc,x[i]) return y def kcmean(x,y,kc,k): #计算各聚类新均值 l = list(kc) flag = False for c in range(k): print(c) m = np.where(y == c) n=np.mean(x[m]) if l[c] != n: l[c] = n flag = True #聚类中心发生变化 print(l,flag) return (np.array(l),flag) k = 3 kc = initcenter(x,k) flag = True print(x,y,kc,flag) #判断聚类中心和目标函数的值是否发生改变,若不变,则输出结果,若改变,则返回2 while flag: y = xclassify(x,y,kc) kc, flag = kcmean(x,y,kc,k) print(y,kc,type(kc)) print(x,y) import matplotlib.pyplot as plt plt.scatter(x,x,c=y,s=50,cmap="rainbow"); plt.show()
运行结果为:

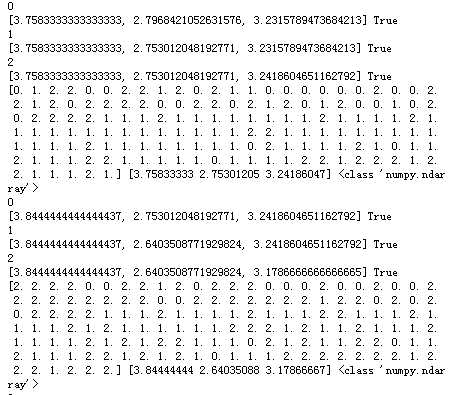

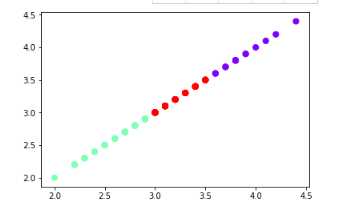
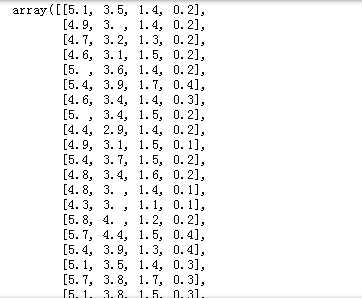
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import numpy as np from sklearn.datasets import load_iris iris = load_iris() X=iris.data X
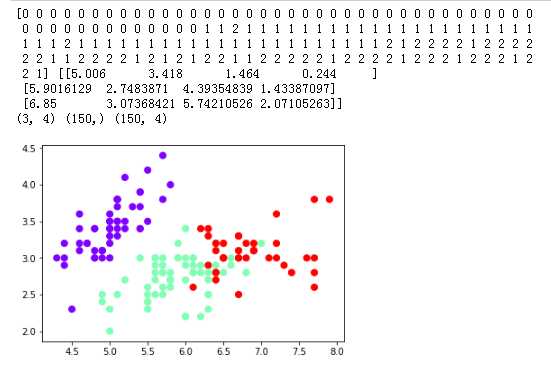
用sklearn.cluster.KMeans,鸢尾花花瓣长度数据做聚类并用散点图显示.
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import numpy as np from sklearn.datasets import load_iris iris = load_iris() X=iris.data X from sklearn.cluster import KMeans est = KMeans(n_clusters=3) est.fit(X) kc = est.cluster_centers_ y_kmeans = est.predict(X) #预测每个样本的聚类索引 print(y_kmeans,kc) print(kc.shape,y_kmeans.shape,X.shape) plt.scatter(X[:,0],X[:,1],c=y_kmeans, s=50, cmap=‘rainbow‘); plt.show()
运行结果为
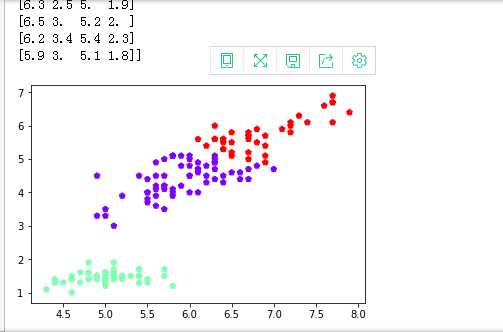
鸢尾花完整数据做聚类并用散点图显示.
from sklearn.cluster import KMeans import numpy as np from sklearn.datasets import load_iris import matplotlib.pyplot as plt data = load_iris() iris = data.data petal_len = iris print(petal_len) k_means = KMeans(n_clusters=3) #三个聚类中心 result = k_means.fit(petal_len) #Kmeans自动分类 kc = result.cluster_centers_ #自动分类后的聚类中心 y_means = k_means.predict(petal_len) #预测Y值 plt.scatter(petal_len[:,0],petal_len[:,2],c=y_means, marker=‘p‘,cmap=‘rainbow‘) plt.show()
运行结果为:
聚类--K均值算法:自主实现与sklearn.cluster.KMeans调用
标签:ima datasets type lse class .data 判断 and shape
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/fanfanfan/p/9862233.html