标签:obj 概念 return 比较 false 简单的 语句 浅拷贝 实现继承
js对象与其它面向对象编程语言的差异
-- JAVA与C++等语言中的对象,是先构造一个类抽象事物,再通过类实例化一个个对象。但javascript中,中不区分类和实例的概念,而是通过原型(prototype)来实现面向对象的封装,继承和多态,从而实现面向对象编程。
什么是面向对象编程?
什么是js原型?
什么是构造函数?
new运算符,就能生成实例,并且this变量会绑定在实例对象上什么是原型链?
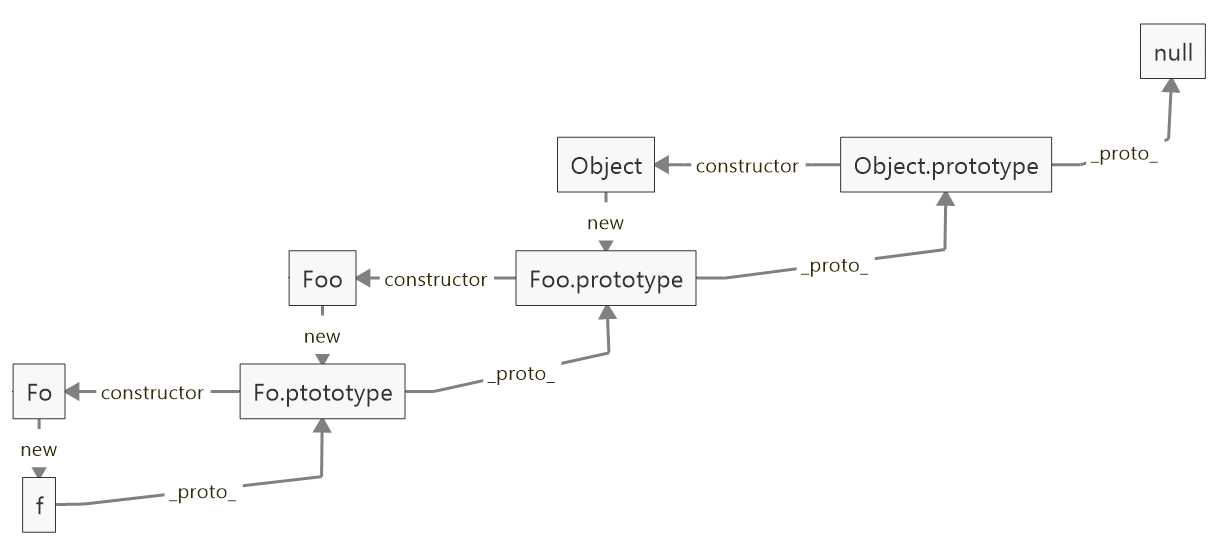
-- 构造函数有prototype属性,会指向一个原型对象,这样通过构造函数生成的实例就会继承来自原型对象的属性和方法,而原型对象又是它所属构造函数形成的实例,会继承来自它的原型对象的属性和方法,这样层层继承,直到原型顶部为null为止,这样原型层层连接起来,就构成了原型链。 如下图所示
什么是封装
--就是将属性和方法封装成一个对象,隐藏属性和方法的实现细节,仅对外公开接口。
js如何封装
简单的封装--原始模式生成实例对象
缺点:
eg:
<script> // 创建一个cat原型对象 // 把两个属性封装在一个对象里面 var Cat = { name: ‘‘, color: ‘‘ }; // 生成两个实例对象 var cat1 = {}; // 创建一个空对象 cat1.name = "大毛"; // 按照原型对象的属性赋值 cat1.color = "黄色"; var cat2 = {}; cat2.name = "二毛"; cat2.color = "黑色"; </script>
原始模式--用函数生成实例对象
优点:
缺点:
eg:
<script> function Cat(name, color) { return { name: name, color: color }; } var cat1 = Cat("大毛","黄色"); //调用函数生成实例对象 var cat2 = Cat("二毛","黑色"); </script>
构造函数模式
优点:
缺点:
<script> function Cat(name, color) { this.name = name; this.color = color; } var cat1 = new Cat("大毛", "黄色"); var cat2 = new Cat("二毛", "黑色"); alert(cat1.name); // 大毛 alert(cat1.color); // 黄色 alert(cat1.constructor === Cat); //true alert(cat2.constructor === Cat); //true alert(cat1.hasOwnProperty("constructor")); //false; alert(cat1.__proto__.hasOwnProperty("constructor")); //true //constructor属性在原型中指向构造函数 </script>
Prototype模式
优点:
将不变的属性和方法,直接定义在prototype对象上
<script> function Cat(name, color) { this.name = name; this.color = color; } Cat.prototype.type = "动物"; Cat.prototype.eat = function () { alert("吃鱼"); }; var cat1 = new Cat("大毛", "黄色"); var cat2 = new Cat("二毛", "黑色"); alert(cat1.type); // 动物 cat1.eat(); // 吃鱼 alert(Cat.prototype.isPrototypeOf(cat1)); //true alert(Cat.prototype.isPrototypeOf(cat2)); //true alert(cat1.hasOwnProperty("name")); // true alert(cat1.hasOwnProperty("type")); // false alert("name" in cat1); // true alert("type" in cat1); // true </script>
继承:子类可以使用父类的所有功能,并且对这些功能进行扩展。继承的过程,就是从一般到特殊的过程。
使用构造函数继承:
一 构造函数绑定
--用call或apply方法,将父对象的构造函数绑定在子对象,实现对父对象属性的继承
<script> function Animal() { this.type = "动物"; } function Cat(name, color) { this.name = name; this.color = color; } function Cat(name, color) { Animal.apply(this); this.name = name; this.color = color; } var cat1 = new Cat("大毛", "黄色"); alert(cat1.type); // 动物 alert(cat1.hasOwnProperty(‘type‘)); //true type已是实例中自身的属性 </script>
二、 prototype模式
<script> function Animal() { this.type = "动物"; } function Cat(name, color) { this.name = name; this.color = color; } Cat.prototype = new Animal(); // 替换prototype对象(原先值被删除,被赋予一个新值) // 此时Cat.prototype.constructor也变为Animal Cat.prototype.constructor = Cat; // 将constructor属性指回原来的构造函数 // 防止继承链的紊乱 var cat1 = new Cat("大毛", "黄色"); alert(cat1.type); // 动物 alert(cat1.hasOwnProperty(‘type‘)); //false //type继承Animal一个实例属性, //Animal的一个实例为cat1原型 alert(Animal.isPrototypeOf(cat1)); //false alert(Cat.prototype.isPrototypeOf(cat1)); //true </script>
三 直接继承prototype
优点:效率比较高(不用执行和建立Animal的实例了),节省内存
缺点:Cat.prototype和Animal.prototype现在指向了同一个对象,那么任何对Cat.prototype的修改,都会反映到Animal.prototype。
<script> function Animal() {} Animal.prototype.type = "动物"; function Cat(name, color) { this.name = name; this.color = color; } Cat.prototype = Animal.prototype; //不用new Animal(); Cat.prototype.constructor = Cat; //隐士改变Animal的构造函数变Cat var cat1 = new Cat("大毛", "黄色"); alert(cat1.type); // 动物 alert(cat1.hasOwnProperty(‘type‘)); //false alert(Animal.prototype.isPrototypeOf(cat1)); //true alert(Animal.prototype.constructor); // Cat(){} //确认Animal的构造函数变为Cat </script>
四、 利用空对象作为中介
<script> function Animal() {} Animal.prototype.type = "动物"; function Cat(name, color) { this.name = name; this.color = color; } function extend(Child, Parent) { // YUI库如何实现继承的方法 var F = function () {}; // 创建一个空函数对象 F.prototype = Parent.prototype; Child.prototype = new F(); Child.prototype.constructor = Child; Child.uber = Parent.prototype; // 备用属性指向父对象的prototype属性 // 实现继承的完备性 } extend(Cat, Animal); var cat1 = new Cat("大毛", "黄色"); alert(cat1.type); // 动物 alert(cat1.hasOwnProperty(‘type‘)); // false alert(Animal.prototype.isPrototypeOf(cat1)); // true alert(Animal.prototype.constructor); // Animal(){} </script>
五、 拷贝继承
-- 把父对象的所有属性和方法,拷贝进子对象,去实现继承
<script> function Animal() {} Animal.prototype.type = "动物"; function Cat(name, color) { this.name = name; this.color = color; }
//父对象的prototype属性一一拷贝给子对象的prototype属性中 function extend2(Child, Parent) { var p = Parent.prototype; var c = Child.prototype; for (var i in p) { c[i] = p[i]; } c.uber = p; } extend2(Cat, Animal); var cat1 = new Cat("大毛", "黄色"); alert(cat1.type); // 动物 alert(cat1.hasOwnProperty(‘type‘)); //false alert(Animal.prototype.isPrototypeOf(cat1)); //false alert(Cat.prototype.isPrototypeOf(cat1)); //true alert(Animal.prototype.constructor); // Animal(){}
</script>
将两个非构造函数的普通对象形成继承关
object()方法:
<script> //将子对象的prototype属性,指向父对象 //让子对象与父对象连在一起。 function object(o) { function F() {} F.prototype = o; return new F(); } var Chinese = { nation: ‘中国‘ }; var Doctor = object(Chinese); Doctor.career = ‘医生‘; alert(Doctor.nation); //中国 </script>
<script> function SuperType() { this.colors = ["red", "blue", "green"]; } function SubType() { SuperType.call(this); //继承了SuperType } var instance1 = new SubType(); instance1.colors.push("black"); //实例1中,属性color加一属性值black alert(instance1.colors); //"red,blue,green,black" var instance2 = new SubType(); alert(instance2.colors); //"red,blue,green" </script>
构造函数模式的一些问题:
浅拷贝:只拷贝对象中基本类型的数据
<script> function extendCopy(p) { var c = {}; for (var i in p) { c[i] = p[i]; //复制成另一对象的一副本,且对象中的属 //性若是地址也会相同的复制过来,造成一些属性对象的享
//可能会影响到父对象属性, } c.uber = p; return c; } var Chinese = { nation: ‘中国‘ }; var Doctor = extendCopy(Chinese); Doctor.career = ‘医生‘; alert(Doctor.nation); // 中国 </script>
深拷贝:
<script> function deepCopy(c, p) { var c = c || {}; for (var i in p) { if (typeof p[i] === ‘object‘) { c[i] = (p[i].constructor === Array) ? [] : {}; deepCopy(p[i], c[i]); //递归调用"浅拷贝",确定对象最终的基本属性 } else { c[i] = p[i]; } } return c; } var Chinese = { nation: ‘中国‘ }; var Doctor = deepCopy(Chinese) </script>
原型链继承的一些问题:
eg:
<script> function SuperType() { this.colors = ["red", "blue", "green"]; } function SubType() {} //继承了SuperType SubType.prototype = new SuperType(); var instance1 = new SubType(); instance1.colors.push("black"); alert(instance1.colors); //"red,blue,green,black" var instance2 = new SubType(); alert(instance2.colors); //"red,blue,green,black" //这样SubType.prototype会有一个colors属性,这样所有的SubType会共享这一实例,造成一些错误,你不知道还好,一直到
</script>
六、 Prototype模式的验证方法
proptotype对象和某个实例之间的关系。 //SubType.prototype.isPrototypeOf(incetence1); //trueprototype对象的属性。// incetence1.hasOwnProperty("color"); // truein运算符可以用来判断,某个实例是否含有某个属性,不管是不是本地属性。"color" in inctence1 //true
标签:obj 概念 return 比较 false 简单的 语句 浅拷贝 实现继承
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/fermin/p/9103047.html