标签:return 异常类 __call des rip 交互 而且 elf 实例化
1.反射:
1.1定义:通过字符串映射或修改程序运行时的状态、属性、方法
1.2有以下四个方法:
(1)hasattr(object,str) 判断object对象中是否有对应的方法或属性,返回值:True·、False
class People(object): ‘‘‘this is the description of People‘‘‘ def __init__(self,name,sex,age): self.name = name self.sex = sex self.age = age def eat(self): print("%s is eating...."%self.name) def piao(self): print("%s is piaoing..."%self.name) def __call__(self, *args, **kwargs): print("My name is Mr Wu") def __str__(self): return "hello world" man = People("dog","male",19) if hasattr(man,"name") and hasattr(man,"eat"): print("hello world!") #output:hello world!
(2)func = getattr(object,str)根据str去获取object对象中的对应的方法的内存地址或属性的值(调用:func(argument))
class People(object): ‘‘‘this is the description of People‘‘‘ def __init__(self,name,sex,age): self.name = name self.sex = sex self.age = age def eat(self): print("%s is eating...."%self.name) def piao(self): print("%s is piaoing..."%self.name) def __call__(self, *args, **kwargs): print("My name is Mr Wu") def __str__(self): return "hello world" man = People("dog","male",19) func = getattr(man,"eat") func() #dog is eating.... name = getattr(man,"name") print(name) #dog
(3)delattr(object,str) 删除object对象中的str对应的方法或属性
class People(object): ‘‘‘this is the description of People‘‘‘ def __init__(self,name,sex,age): self.name = name self.sex = sex self.age = age def eat(self): print("%s is eating...."%self.name) def piao(self): print("%s is piaoing..."%self.name) def __call__(self, *args, **kwargs): print("My name is Mr Wu") def __str__(self): return "hello world" man = People("dog","male",19) delattr(man,"name") print(man.name) #AttributeError: ‘People‘ object has no attribute ‘name‘ delattr(man,"eat") man.eat()#AttributeError: eat
(4)setattr(x,y,v)相当于x.y = v,设置新的属性或方法(可修改原有的属性和方法)
class People(object): ‘‘‘this is the description of People‘‘‘ def __init__(self,name,sex,age): self.name = name self.sex = sex self.age = age def eat(self): print("%s is eating...."%self.name) def piao(self): print("%s is piaoing..."%self.name) def sleep(self): print("%s is sleeping...."%(self.name)) name = "Mr Wu" man = People("dog","male",19) setattr(man,"sleep",sleep) man.sleep(man) #dog is sleeping.... setattr(man,"name",name) print(man.name) #Mr Wu
2.异常处理
2.1 概述:
Python的异常处理能力是很强大的,可向用户准确反馈出错信息。在Python中,异常也是对象,可对它进行操作。所有异常都是基类Exception的成员。所有异常都从基类Exception继承,而且都在exceptions模块中定义。Python自动将所有异常名称放在内建命名空间中,所以程序不必导入exceptions模块即可使用异常。一旦引发而且没有捕捉SystemExit异常,程序执行就会终止。如果交互式会话遇到一个未被捕捉的SystemExit异常,会话就会终止。
2.2 python中所有的标准异常类
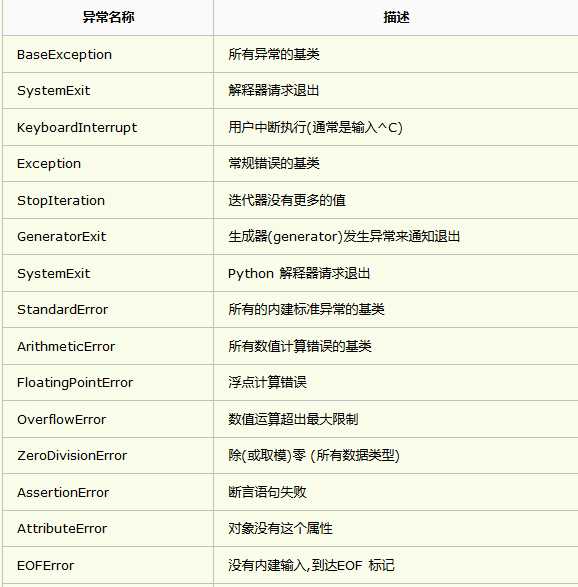

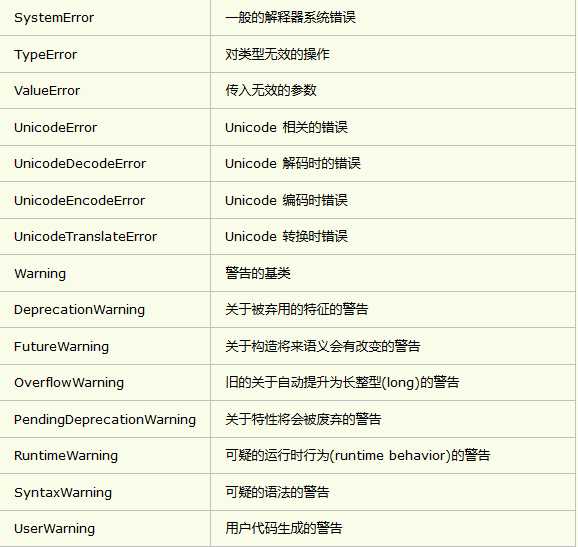
2.2 语法格式
try:
代码块
except 异常名称 as e:
print(e) #输出异常的内容
except 异常名称 as e:
print(e) #输出异常处理
...............
特别地:
except Exception as e:
#如果不知道异常具体是什么类型,可以使用Exception
else:
#如果没有出现前面的异常则执行这条语句
finally:
#不管有没有出现前面的异常都会执行这条语句
注:如果已经捕获到了try下的一条异常,那么就不会再捕获其他异常了
代码实例:
names = ["Mr Wu","Ms Li"] dict_names = {"name":"Mr Wu","age":19} try: print(names[3]) dict_names["Mr Wang"] except IndexError as e: print("出错了:",e) except KeyError as e: print("出错了:",e) except Exception as e: print("未知错误:",e) #output:出错了: list index out of range
names = ["Mr Wu","Ms Li"] dict_names = {"name":"Mr Wu","age":19} try: print(names[3]) dict_names["Mr Wang"] #except IndexError as e: # print("出错了:",e) #except KeyError as e: # print("出错了:",e) except Exception as e: print("未知错误:",e) #output:未知错误: list index out of range
2.3 自定义异常
我们可以自己定义异常类,并且触发执行这个异常。
注:自定义的异常必须继承异常类基类Exception,并通过raise语句实例化这个类
class AlexException(Exception): def __init__(self,msg): self.message = msg try: raise AlexException("\033[1;41m数据库连接失败\033[0m") except AlexException as e: print(e) #output:数据库连接失败
标签:return 异常类 __call des rip 交互 而且 elf 实例化
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/BUPT-MrWu/p/9889060.html