标签:取数 官网 ext city desc 有一个 body 描述 详细
一、单一代理流配置http://flume.apache.org/FlumeUserGuide.html#avro-source
通过一个通道将来源和接收器链接。需要列出源,接收器和通道,为给定的代理,然后指向源和接收器及通道。一个源的实例可以指定多个通道,但只能指定一个接收器实例。格式如下:
# list the sources, sinks and channels for the agent
<Agent>.sources = <Source>
<Agent>.sinks = <Sink>
<Agent>.channels = <Channel1> <Channel2>
# set channel for source
<Agent>.sources.<Source>.channels = <Channel1> <Channel2> ...
# set channel for sink
<Agent>.sinks.<Sink>.channel = <Channel1>实例解析:一个代理名为agent_foo,外部通过avro客户端,并且发送数据通过内存通道给hdfs。在配置文件foo.config的可能看起来像这样:
# list the sources, sinks and channels for the agent
agent_foo.sources = avro-appserver-src-1
agent_foo.sinks = hdfs-sink-1
agent_foo.channels = mem-channel-1
# set channel for source
agent_foo.sources.avro-appserver-src-1.channels = mem-channel-1
# set channel for sink
agent_foo.sinks.hdfs-sink-1.channel = mem-channel-1案例说明:这将使事件流从avro-appserver-src-1到hdfs-sink-1通过内存通道mem-channel-1。当代理开始foo.config作为其配置文件,它会实例化流。
配置单个组件
定义流之后,需要设置每个源,接收器和通道的属性。可以分别设定组件的属性值。
# properties for sources
<Agent>.sources.<Source>.<someProperty> = <someValue>
# properties for channels
<Agent>.channel.<Channel>.<someProperty> = <someValue>
# properties for sinks
<Agent>.sources.<Sink>.<someProperty> = <someValue>“type”属性必须为每个组件设置,以了解它需要什么样的对象。每个源,接收器和通道类型有其自己的一套,它所需的性能,以实现预期的功能。所有这些,必须根据需要设置。在前面的例子中,从hdfs-sink-1中的流到HDFS,通过内存通道mem-channel-1的avro-appserver-src-1源。下面是 一个例子,显示了这些组件的配置。
agent_foo.sources = avro-AppSrv-source
agent_foo.sinks = hdfs-Cluster1-sink
agent_foo.channels = mem-channel-1
# set channel for sources, sinks
# properties of avro-AppSrv-source
agent_foo.sources.avro-AppSrv-source.type = avro
agent_foo.sources.avro-AppSrv-source.bind = localhost
agent_foo.sources.avro-AppSrv-source.port = 10000
# properties of mem-channel-1
agent_foo.channels.mem-channel-1.type = memory
agent_foo.channels.mem-channel-1.capacity = 1000
agent_foo.channels.mem-channel-1.transactionCapacity = 100
# properties of hdfs-Cluster1-sink
agent_foo.sinks.hdfs-Cluster1-sink.type = hdfs
agent_foo.sinks.hdfs-Cluster1-sink.hdfs.path = hdfs://namenode/flume/webdata
#...通过flume来监控一个目录,当目录中有新文件时,将文件内容输出到控制台。
创建一个test01.conf的文件:
#配置一个agent,agent的名称可以自定义(如a1)
#指定agent的sources(如s1)、sinks(如k1)、channels(如c1)
#分别指定agent的sources,sinks,channels的名称 名称可以自定义
a1.sources = s1
a1.sinks = k1
a1.channels = c1
#描述source
#配置目录scource
a1.sources.s1.type = spooldir
a1.sources.s1.spoolDir = /opt/flume/logs
a1.sources.s1.fileHeader= true
a1.sources.s1.channels =c1
#配置sink
a1.sinks.k1.type = logger
a1.sinks.k1.channel = c1
#配置channel(内存做缓存)
a1.channels.c1.type = memory启动命令
./bin/flume-ng agent --conf conf --conf-file ./conf/test1.conf --name a1 -Dflume.root.logger=INFO,console测试 Flume
重新打开一个终端,我们将123.log移动到logs目录
$ cp test.log logs/原始的Flume终端将在日志消息中输出事件:
2018-11-03 03:54:54,207 (pool-3-thread-1) [INFO - org.apache.flume.client.avro.ReliableSpoolingFileEventReader.readEvents(ReliableSpoolingFileEventReader.java:324)] Last read took us just up to a file boundary. Rolling to the next file, if there is one.
2018-11-03 03:54:54,207 (pool-3-thread-1) [INFO - org.apache.flume.client.avro.ReliableSpoolingFileEventReader.rollCurrentFile(ReliableSpoolingFileEventReader.java:433)] Preparing to move file /opt/flume/logs/test.log to /opt/flume/logs/test.log.COMPLETED
2.6 NetCat Source案例2:实时模拟从web服务器中读取数据到hdfs中
此处使用 exec source 详细参考 上一节里面的 2.3 Exec Source 介绍
单个Flume代理可以包含几个独立的流。你可以在一个配置文件中列出多个源,接收器和通道。这些组件可以连接形成多个流。
# list the sources, sinks and channels for the agent
<Agent>.sources = <Source>
<Agent>.sinks = <Sink>
<Agent>.channels = <Channel1> <Channel2>
# set channel for source
<Agent>.sources.<Source>.channels = <Channel1> <Channel2> ...
# set channel for sink
<Agent>.sinks.<Sink>.channel = <Channel1>可以连接源和接收器到其相应的通道,设置两个不同的流。例如,如果需要设置一个agent_foo代理两个流,一个从外部Avro客户端到HDFS,另外一个是tail的输出到Avro接收器,然后在这里是做一个配置。
# list the sources, sinks and channels in the agent
agent_foo.sources = avro-AppSrv-source1 exec-tail-source2
agent_foo.sinks = hdfs-Cluster1-sink1 avro-forward-sink2
agent_foo.channels = mem-channel-1 file-channel-2
# flow #1 configuration
agent_foo.sources.avro-AppSrv-source1.channels = mem-channel-1
agent_foo.sinks.hdfs-Cluster1-sink1.channel = mem-channel-1
# flow #2 configuration
agent_foo.sources.exec-tail-source2.channels = file-channel-2
agent_foo.sinks.avro-forward-sink2.channel = file-channel-2设置一个多层的流,需要有一个指向下一跳avro源的第一跳的avro 接收器。这将导致第一Flume代理转发事件到下一个Flume代理。例如,如果定期发送的文件,每个事件(1文件)AVRO客户端使用本地Flume 代理,那么这个当地的代理可以转发到另一个有存储的代理。
配置如下:
Weblog agent config:
# list sources, sinks and channels in the agent
agent_foo.sources = avro-AppSrv-source
agent_foo.sinks = avro-forward-sink
agent_foo.channels = file-channel
# define the flow
agent_foo.sources.avro-AppSrv-source.channels = file-channel
agent_foo.sinks.avro-forward-sink.channel = file-channel
# avro sink properties
agent_foo.sinks.avro-forward-sink.type = avro
agent_foo.sinks.avro-forward-sink.hostname = 10.1.1.100
agent_foo.sinks.avro-forward-sink.port = 10000
# configure other pieces
#...HDFS agent config:
# list sources, sinks and channels in the agent
agent_foo.sources = avro-collection-source
agent_foo.sinks = hdfs-sink
agent_foo.channels = mem-channel
# define the flow
agent_foo.sources.avro-collection-source.channels = mem-channel
agent_foo.sinks.hdfs-sink.channel = mem-channel
# avro source properties
agent_foo.sources.avro-collection-source.type = avro
agent_foo.sources.avro-collection-source.bind = 10.1.1.100
agent_foo.sources.avro-collection-source.port = 10000
# configure other pieces
#...这里连接从weblog-agent的avro-forward-sink 到hdfs-agent的avro-collection-source收集源。最终结果从外部源的appserver最终存储在HDFS的事件。
创建一个case_avro.conf的文件:
a1.sources = s1
a1.sinks = k1
a1.channels = c1
a1.sources.s1.type = avro
a1.sources.s1.channels = c1
a1.sources.s1.bind = localhost
a1.sources.s1.port = 22222
a1.channels.c1.type = memory
a1.channels.c1.capacity = 1000
a1.channels.c1.transactionCapacity = 100
a1.sinks.k1.type = logger
a1.sinks.k1.channel = c1创建一个case_avro_sink.conf的文件:
a2.sources = s1
a2.sinks = k1
a2.channels = c1
a2.sources.s1.type = syslogtcp
a2.sources.s1.channels = c1
a2.sources.s1.host = 192.168.123.102
a2.sources.s1.port = 33333
a2.channels.c1.type = memory
a2.channels.c1.capacity = 1000
a2.channels.c1.transactionCapacity = 100
a2.sinks.k1.type = avro
a2.sinks.k1.hostname = 192.168.123.102
a2.sinks.k1.port = 22222
a2.sinks.k1.channel = c1说明:case_avro_sink.conf是前面的Agent,case_avro.conf是后面的Agent
先启动Avro的Source,监听端口
$ ./bin/flume-ng agent --conf conf --conf-file ./conf/case_avro.conf --name a1 -Dflume.root.logger=DEBUG,console -Dorg.apache.flume.log.printconfig=true -Dorg.apache.flume.log.rawdata=true再启动Avro的Sink
$ ./bin/flume-ng agent --conf conf --conf-file ./conf/case_avro_sink.conf --name a2 -Dflume.root.logger=DEBUG,console -Dorg.apache.flume.log.printconfig=true -Dorg.apache.flume.log.rawdata=true可以看到已经建立连接
在Avro Sink上生成测试log
$ echo "hello flume avro sink" | nc 192.168.1.102 33333查看结果: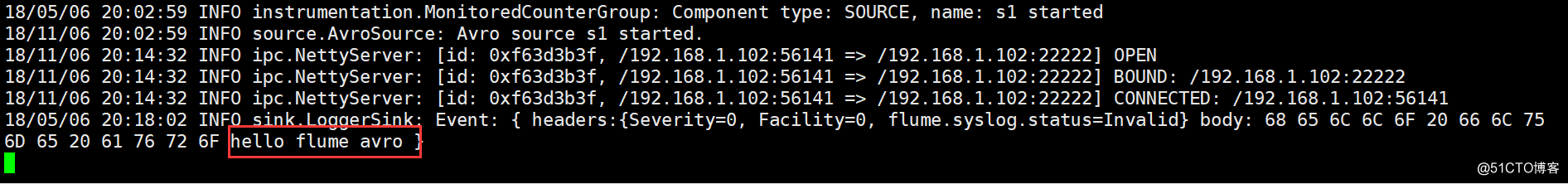
Flume支持扇出流从一个源到多个通道。有两种模式的扇出,复制和复用。在复制流的事件被发送到所有的配置通道。在复用的情况下,事件被发送到合格的渠 道只有一个子集。扇出流,需要指定源和扇出通道的规则。这是通过添加一个通道“选择”,可以复制或复用。再进一步指定选择的规则,如果它是一个多路。如果你 不指定一个选择,则默认情况下它复制。
# list the sources, sinks and channels for the agent
<Agent>.sources = <Source>
<Agent>.sinks = <Sink>
<Agent>.channels = <Channel1> <Channel2>
# set channel for source
<Agent>.sources.<Source>.channels = <Channel1> <Channel2> ...
# set channel for sink
<Agent>.sinks.<Sink>.channel = <Channel1>复用的选择集的属性进一步分叉。这需要指定一个事件属性映射到一组通道。选择配置属性中的每个事件头检查。如果指定的值相匹配,那么该事件被发送到所有的通道映射到该值。如果没有匹配,那么该事件被发送到设置为默认配置的通道。
# Mapping for multiplexing selector
<Agent>.sources.<Source1>.selector.type = multiplexing
<Agent>.sources.<Source1>.selector.header = <someHeader>
<Agent>.sources.<Source1>.selector.mapping.<Value1> = <Channel1>
<Agent>.sources.<Source1>.selector.mapping.<Value2> = <Channel1> <Channel2>
<Agent>.sources.<Source1>.selector.mapping.<Value3> = <Channel2>
#...
<Agent>.sources.<Source1>.selector.default = <Channel2>映射允许每个值通道可以重叠。默认值可以包含任意数量的通道。下面的示例中有一个单一的流复用两条路径。代理有一个单一的avro源和连接道两个接收器的两个通道。
# list the sources, sinks and channels in the agent
agent_foo.sources = avro-AppSrv-source1
agent_foo.sinks = hdfs-Cluster1-sink1 avro-forward-sink2
agent_foo.channels = mem-channel-1 file-channel-2
# set channels for source
agent_foo.sources.avro-AppSrv-source1.channels = mem-channel-1 file-channel-2
# set channel for sinks
agent_foo.sinks.hdfs-Cluster1-sink1.channel = mem-channel-1
agent_foo.sinks.avro-forward-sink2.channel = file-channel-2
# channel selector configuration
agent_foo.sources.avro-AppSrv-source1.selector.type = multiplexing
agent_foo.sources.avro-AppSrv-source1.selector.header = State
agent_foo.sources.avro-AppSrv-source1.selector.mapping.CA = mem-channel-1
agent_foo.sources.avro-AppSrv-source1.selector.mapping.AZ = file-channel-2
agent_foo.sources.avro-AppSrv-source1.selector.mapping.NY = mem-channel-1 file-channel-2
agent_foo.sources.avro-AppSrv-source1.selector.default = mem-channel-1“State”作为Header的选择检查。如果值是“CA”,然后将其发送到mem-channel-1,如果它的“AZ”的,那么jdbc- channel-2,如果它的“NY”那么发到这两个。如果“State”头未设置或不匹配的任何三个,然后去默认的mem-channel-1通道。
case_replicate_sink.conf
a1.sources = s1
a1.sinks = k1 k2
a1.channels = c1 c2
a1.sources.s1.type = syslogtcp
a1.sources.s1.channels = c1 c2
a1.sources.s1.host = 192.168.1.102
a1.sources.s1.port = 6666
a1.sources.s1.selector.type = replicating
a1.channels.c1.type = memory
a1.channels.c1.capacity = 1000
a1.channels.c1.transactionCapacity = 100
a1.channels.c2.type = memory
a1.channels.c2.capacity = 1000
a1.channels.c2.transactionCapacity = 100
a1.sinks.k1.type = avro
a1.sinks.k1.hostname = 192.168.1.102
a1.sinks.k1.port = 7777
a1.sinks.k1.channel = c1
a1.sinks.k1.type = avro
a1.sinks.k1.hostname = 192.168.1.102
a1.sinks.k1.port = 7777
a1.sinks.k1.channel = c2case_replicate_s1.conf
a2.sources = s1
a2.sinks = k1
a2.channels = c1
a2.sources.s1.type = avro
a2.sources.s1.channels = c1
a2.sources.s1.host = 192.168.1.102
a2.sources.s1.port = 7777
a2.channels.c1.type = memory
a2.channels.c1.capacity = 1000
a2.channels.c1.transactionCapacity = 100
a2.sinks.k1.type = logger
a2.sinks.k1.channel = c1case_replicate_s2.conf
a3.sources = s1
a3.sinks = k1
a3.channels = c1
a3.sources.s1.type = avro
a3.sources.s1.channels = c1
a3.sources.s1.host = 192.168.1.102
a3.sources.s1.port = 7777
a3.channels.c1.type = memory
a3.channels.c1.capacity = 1000
a3.channels.c1.transactionCapacity = 100
a3.sinks.k1.type = logger
a3.sinks.k1.channel = c1先启动Avro的Source,监听端口
$ ./bin/flume-ng agent --conf conf --conf-file ./conf/case_replicate_s1.conf --name a2 -Dflume.root.logger=DEBUG,console -Dorg.apache.flume.log.printconfig=true -Dorg.apache.flume.log.rawdata=true$ ./bin/flume-ng agent --conf conf --conf-file ./conf/case_replicate_s2.conf --name a3 -Dflume.root.logger=DEBUG,console -Dorg.apache.flume.log.printconfig=true -Dorg.apache.flume.log.rawdata=true再启动Avro的Sink
$ ./bin/flume-ng agent --conf conf --conf-file ./confcase_replicate_sink.conf --name a1 -Dflume.root.logger=DEBUG,console -Dorg.apache.flume.log.printconfig=true -Dorg.apache.flume.log.rawdata=true生成测试log
$ echo "hello via channel selector" | nc 192.168.1.102 6666case_multi_sink.conf
#2个channel和2个sink的配置文件
a1.sources = r1
a1.sinks = k1 k2
a1.channels = c1 c2
# Describe/configure the source
a1.sources.r1.type = org.apache.flume.source.http.HTTPSource
a1.sources.r1.port = 5140
a1.sources.r1.host = 0.0.0.0
a1.sources.r1.selector.type = multiplexing
a1.sources.r1.channels = c1 c2
a1.sources.r1.selector.header = state
a1.sources.r1.selector.mapping.CZ = c1
a1.sources.r1.selector.mapping.US = c2
a1.sources.r1.selector.default = c1
# Describe the sink
a1.sinks.k1.type = avro
a1.sinks.k1.channel = c1
a1.sinks.k1.hostname = 192.168.1.102
a1.sinks.k1.port = 4545
a1.sinks.k2.type = avro
a1.sinks.k2.channel = c2
a1.sinks.k2.hostname = 192.168.1.102
a1.sinks.k2.port = 4545
# Use a channel which buffers events in memory
a1.channels.c1.type = memory
a1.channels.c1.capacity = 1000
a1.channels.c1.transactionCapacity = 100
a1.channels.c2.type = memory
a1.channels.c2.capacity = 1000
a1.channels.c2.transactionCapacity = 100case_ multi _s1.conf
# Name the components on this agent
a2.sources = r1
a2.sinks = k1
a2.channels = c1
# Describe/configure the source
a2.sources.r1.type = avro
a2.sources.r1.channels = c1
a2.sources.r1.bind = 192.168.1.102
a2.sources.r1.port = 4545
# Describe the sink
a2.sinks.k1.type = logger
a2.sinks.k1.channel = c1
# Use a channel which buffers events in memory
a2.channels.c1.type = memory
a2.channels.c1.capacity = 1000
a2.channels.c1.transactionCapacity = 100case_ multi _s2.conf
# Name the components on this agent
a3.sources = r1
a3.sinks = k1
a3.channels = c1
# Describe/configure the source
a3.sources.r1.type = avro
a3.sources.r1.channels = c1
a3.sources.r1.bind = 192.168.1.102
a3.sources.r1.port = 4545
# Describe the sink
a3.sinks.k1.type = logger
a3.sinks.k1.channel = c1
# Use a channel which buffers events in memory
a3.channels.c1.type = memory
a3.channels.c1.capacity = 1000
a3.channels.c1.transactionCapacity = 100先启动Avro的Source,监听端口
$ ./bin/flume-ng agent -c . -f ./conf/case_ multi _s1.conf -n a2 -Dflume.root.logger=INFO,console
$ ./bin/flume-ng agent -c . -f ./conf/case_ multi _s2.conf -n a3 -Dflume.root.logger=INFO,console再启动Avro的Sink
$ ./bin/lume-ng agent -c . -f ./conf/case_multi_sink.conf -n a1 -Dflume.root.logger=INFO,console根据配置文件生成测试的header 为state的POST请求
$ curl -X POST -d ‘[{ "headers" :{"state" : "CZ"},"body" : "TEST1"}]‘ http://localhost:5140
$ curl -X POST -d ‘[{ "headers" :{"state" : "US"},"body" : "TEST2"}]‘ http://localhost:5140
$ curl -X POST -d ‘[{ "headers" :{"state" : "SH"},"body" : "TEST3"}]‘ http://localhost:5140标签:取数 官网 ext city desc 有一个 body 描述 详细
原文地址:http://blog.51cto.com/13525470/2315517