标签:sele ica persist 持久 dea username this field col
Spring负责管理项目中的所有对象。Spring是一站式框架,仅仅使用Spring足以完成Web项目。
二、Spring项目搭建以及测试
环境为IDEA,Spring项目创建:
创建一个对象:
public class User { private String name; public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } }
配置文件(建议放到src下面):
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"> <!--将user对象交给Spring容器--> <bean id="user" class="domain.User"> <property name="name" value="helloworld"></property> </bean> </beans>
测试代码:
public class Main { public static void main(String[] args){ //创建容器对象 //ApplicationContext对象在加载 spring-config.xml(容器启动)时候就会创建 ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring-config.xml"); //向容器要user对象 User user = (User) context.getBean("user"); System.out.println(user.getName()); } }
运行结果:helloworld
三、IOC和DI
IOC:Inverse Of Control反转控制。即将我们创建对象的方式反转,以前对象的创建和依赖关系是我们自己维护。使用Spring之后,对象的创建以及依赖关系可以由Spring完成创建以及注入。
DI:Dependency Injection依赖注入,实现IOC思想需要DI做支持,注入方式:set方式注入、构造方式注入、字段注入。注入类型:值类型注入、引用类型注入。
public class User { public User() { } private String name; public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } }
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"> <!--创建方式1:空参构造创建--> <bean name="user" class="domain.User"> <property name="name" value="naruto"></property> </bean> </beans>
public class UserFactory { public static User createUser(){ System.out.println("静态工厂创建User"); return new User(); } }
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"> <!-- 创建方式2:静态工厂创建 调用UserFactory的createUser方法创建名为user2的对象.放入容器 --> <bean name="user2" class="domain.UserFactory" factory-method="createUser" > </bean> </beans>
public class UserFactory { public User createUser2(){ System.out.println("实例工厂创建User"); return new User(); } }
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"> <!-- 创建方式3:实例工厂创建 调用UserFactory对象的createUser2方法创建名为user3的对象.放入容器 --> <bean name="user3" factory-bean="userFactory" factory-method="createUser2" > </bean> <bean name="userFactory" class="domain.UserFactory" > </bean> </beans>
Scpoe即Bean的作用范围:
singleton :默认值,单例的。
prototype :多例的
request :WEB 项目中,Spring 创建一个 Bean 的对象,将对象存入到 request 域中。
session :WEB 项目中,Spring 创建一个 Bean 的对象,将对象存入到 session 域中。(了解即可)
globalSession :WEB 项目中,应用在 Porlet 环境.如果没有 Porlet 环境那么 globalSession 相当于 session。(了解即可)
在一个配置文件中包含另一个配置文件:
<import resource="applicationContext2.xml"></import>
User对象:
public class User { public User() { } private String name; private Car car; public Car getCar() { return car; } public void setCar(Car car) { this.car = car; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } @Override public String toString() { return "User{" + "name=‘" + name + ‘\‘‘ + ", car=" + car + ‘}‘; } }
Car对象:
public class Car { private String color; public String getColor() { return color; } public void setColor(String color) { this.color = color; } @Override public String toString() { return "Car{" + "color=‘" + color + ‘\‘‘ + ‘}‘; } }
注入容器:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.spring framework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"> <!--set方式注入--> <bean name="user6" class="domain.User"> <!--为User对象中名为name的属性注入naruto--> <property name="name" value="naruto"></property> <property name="car" ref="car"></property> </bean> <!--将car对象配置到容器中--> <bean name="car" class="domain.Car"> <!--为car对象中名为color的属性注入yellow--> <property name="color" value="yellow"></property> </bean> </beans>
运行测试:
public class Main { public static void main(String[] args){ ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring-config.xml"); User user = (User) context.getBean("user6"); System.out.println(user.toString()); } }
运行结果:User{name=’naruto’, car=Car{color=’yellow’}}
User对象:
public class User { public User() { } private String name; private Car car; public User(Car car, String name) { this.car = car; this.name = name; } public Car getCar() { return car; } public void setCar(Car car) { this.car = car; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } @Override public String toString() { return "User{" + "name=‘" + name + ‘\‘‘ + ", car=" + car + ‘}‘; } }!
配置:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"> <!--将car对象配置到容器中--> <bean name="car" class="domain.Car"> <!--为car对象中名为color的属性注入yellow--> <property name="color" value="yellow"></property> </bean> <!--构造方法注入--> <bean name="user66" class="domain.User"> <!--为User对象中名为name的属性注入naruto--> <constructor-arg name="name" value="long" index="1"></constructor-arg> <constructor-arg name="car" ref="car"></constructor-arg> </bean> </beans>
运行测试:
public class Main { public static void main(String[] args){ ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring-config.xml"); User user = (User) context.getBean("user66"); System.out.println(user.toString()); } }
创建一个复杂对象:
public class CollectionBean { private Object[] arr;//数组类型注入 private List list;//list/set 类型注入 private Map map;//map类型注入 private Properties prop;//properties类型注入 public Object[] getArr() { return arr; } public void setArr(Object[] arr) { this.arr = arr; } public List getList() { return list; } public void setList(List list) { this.list = list; } public Map getMap() { return map; } public void setMap(Map map) { this.map = map; } public Properties getProp() { return prop; } public void setProp(Properties prop) { this.prop = prop; } @Override public String toString() { return "CollectionBean [arr=" + Arrays.toString(arr) + ", list=" + list + ", map=" + map + ", prop=" + prop + "]"; } }
配置:
<!-- ============================================================= --> <!-- 复杂类型注入 --> <bean name="cb" class="domain.CollectionBean" > <!-- 如果数组中只准备注入一个值(对象),直接使用value|ref即可 <property name="arr" value="tom" ></property> --> <!-- array注入,多个元素注入 --> <property name="arr"> <array> <value>tom</value> <value>jerry</value> <ref bean="user6" /> </array> </property> <!-- 如果List中只准备注入一个值(对象),直接使用value|ref即可 <property name="list" value="jack" ></property>--> <property name="list" > <list> <value>jack</value> <value>rose</value> <ref bean="user3" /> </list> </property> <!-- map类型注入 --> <property name="map" > <map> <entry key="url" value="jdbc:mysql:///crm" ></entry> <entry key="user" value-ref="user6" ></entry> <entry key-ref="user3" value-ref="user2" ></entry> </map> </property> <!-- prperties 类型注入 --> <property name="prop" > <props> <prop key="driverClass">com.jdbc.mysql.Driver</prop> <prop key="userName">root</prop> <prop key="password">1234</prop> </props> </property> </bean>
配置监听器:
<!-监听器:服务器启动,Spring对象创建,服务器销毁,Spring对象销毁。--> <listener> <listener-class>org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener</listenerclass> </listener> <!--指定加载Spring配置文件的位置。--> <context-param> <param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name> <param-value>classpath:applicationContext.xml</param-value> </context-param>
Spring将容器放入ServletContext中去了,即可以从Application域中获取Spring对象。
配置XML文件:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd"> <!--扫描指定包及其子包下所有类中的注解--> <context:component-scan base-package="domain"></context:component-scan> </beans>
将car对象注入到Spring中:
@Component("car2")
public class Car {
@Value("yellow")
private String color;
public void setColor(String color) {
this.color = color;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Car{" +
"color=‘" + color + ‘\‘‘ +
‘}‘;
}
}
将user对象注入到Spring中:
//对象名为user,将其放入Spring容器中 @Component("user") //@Service("user") //service层 //@Controller("user") //web层 //@Repository("user") //dao层 //@Scope(scopeName = "protoType") //指定对象作用范围:多例 public class User { @Value("long") //通过反射的Field赋值,破坏了封装性 private String name; //@Autowired //自动装配 //自动装配问题:如果匹配多个类型一致的对象,将无法选择具体注入哪一个对象 //@Qualifier("car2") 使用Qualifier注解告诉Spring容器自动装配哪个名称的对象 //使用Resource注解手动注入,指定注入哪个名称的对象(推荐) @Resource(name="car2") private Car car; @PostConstruct //在对象被创建后调用 public void init(){ System.out.println("我是初始化方法"); } @PreDestroy //在对象被销毁之前调用 public void destroy(){ System.out.println("我是销毁方法"); } public Car getCar() { return car; } public void setCar(Car car) { this.car = car; } public String getName() { return name; } //@Value("long") //通过set方法赋值(推荐) public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } @Override public String toString() { return "User{" + "name=‘" + name + ‘\‘‘ + ", car=" + car + ‘}‘; } }
测试:
public class Main { public static void main(String[] args){ ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring-config.xml"); User bean = (User) context.getBean("user"); System.out.println(bean.toString()); } }
运行结果:
我是初始化方法
User{name=’long’, car=Car{color=’yellow’}}
十、Spring中的AOP
Spring能够为容器中管理的对象生成动态代理对象。
Spring实现Aop的原理:Spring封装了动态代理和cglib代理
动态代理局限性:被代理对象必须要有接口,才能产生代理对象。
cglib代理:第三方代理技术,可以对任何类生成代理。代理的原理是对目标对象进行继承代理。如果目标对象被final修饰,那么该类无法被cglib代理。
使用动态代理:
UserService:
public interface UserService { void save(); void delete(); void update(); void find(); }
UserServiceImpl:
public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService { @Override public void save() { System.out.println("保存用户!"); //int i = 1/0; } @Override public void delete() { System.out.println("删除用户!"); } @Override public void update() { System.out.println("更新用户!"); } @Override public void find() { System.out.println("查找用户!"); } }
生成代理:
public class UserServiceProxyFactory implements InvocationHandler { public UserServiceProxyFactory(UserService us) { super(); this.us = us; } private UserService us; public UserService getUserServiceProxy(){ //生成动态代理 UserService usProxy = (UserService) Proxy.newProxyInstance(UserServiceProxyFactory.class.getClassLoader(), UserServiceImpl.class.getInterfaces(), //被代理对象实现的接口 this); //返回 return usProxy; } @Override public Object invoke(Object arg0, Method method, Object[] arg2) throws Throwable { System.out.println("打开事务!"); Object invoke = method.invoke(us, arg2); System.out.println("提交事务!"); return invoke; } }
测试:
public class Demo { @Test //动态代理 public void fun1(){ UserService us = new UserServiceImpl(); //传入代理对象 UserServiceProxyFactory factory = new UserServiceProxyFactory(us); UserService usProxy = factory.getUserServiceProxy(); usProxy.save(); //代理对象与被代理对象实现了相同的接口 //代理对象 与 被代理对象没有继承关系 System.out.println(usProxy instanceof UserServiceImpl );//false } }
运行结果:
打开事务!
保存用户!
提交事务!
false
2、动态代理
什么是代理(中介)
目标对象/被代理对象 —— 房主:真正的租房的方法
代理对象 ——- 黑中介:有租房子的方法(调用房主的租房的方法)
执行代理对象方法的对象 —- 租房的人
流程:我们要租房—–>中介(租房的方法)——>房主(租房的方法)
抽象:调用对象—–>代理对象——>目标对象
动态代理的API:
在jdk的API中存在一个Proxy中存在一个生成动态代理的的方法newProxyInstance:
newProxyInstance(ClassLoader loader, Class<?>[] interfaces, InvocationHandler h)
返回值:Object就是代理对象
参数:loader:代表与目标对象相同的类加载器—–目标对象.getClass().getClassLoader()
interfaces:代表与目标对象实现的所有的接口字节码对象数组
h:具体的代理的操作,InvocationHandler接口
栗子1:
目标对象接口:
public interface TargetInterface { public void method1(); public String method2(); public int method3(int x); }
目标对象:
//目标对象 public class Target implements TargetInterface{ @Override public void method1() { System.out.println("method1 running..."); } @Override public String method2() { System.out.println("method2 running..."); return "method2"; } @Override public int method3(int x) { return x; } }
代理对象:
//代理对象 public class ProxyTest { @Test public void test1(){ //获得动态的代理对象----在运行时 在内存中动态的为Target创建一个虚拟的代理对象 //objProxy是代理对象 根据参数确定到底是谁的代理对象 TargetInterface objProxy = (TargetInterface) Proxy.newProxyInstance( Target.class.getClassLoader(), //与目标对象相同的类加载器 new Class[]{TargetInterface.class}, new InvocationHandler() { //invoke 代表的是执行代理对象的方法 @Override //method:代表目标对象的方法字节码对象 //args:代表目标对象的响应的方法的参数 public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable { System.out.println("目标方法前的逻辑"); //执行目标对象的方法 Object invoke = method.invoke(new Target(), args); System.out.println("目标方法后的逻辑"); return invoke; } } ); objProxy.method1(); String method2 = objProxy.method2(); //System.out.println(method2); } }
运行结果:
目标方法前的逻辑
method1 running…
目标方法后的逻辑
目标方法前的逻辑
method2 running…
目标方法后的逻辑
package com.proxy; import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler; import java.lang.reflect.Method; import java.lang.reflect.Proxy; public class ProxyTest2 { public static void main(String[] args) { final Target target = new Target(); //动态创建代理对象 TargetInterface proxy = (TargetInterface) Proxy.newProxyInstance( target.getClass().getClassLoader(), target.getClass().getInterfaces(), new InvocationHandler() { @Override //被执行几次?------- 看代理对象调用方法几次 //代理对象调用接口相应方法 都是调用invoke /* * proxy:是代理对象 * method:代表的是目标方法的字节码对象 * args:代表是调用目标方法时参数 */ public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable { //反射知识点 Object invoke = method.invoke(target, args);//目标对象的相应方法 //retrun返回的值给代理对象 return invoke; } } ); //调用invoke---Method:目标对象的method1方法 args:null 返回值null proxy.method1(); //调用invoke---Method:目标对象的method2方法 args:null 返回值method2 String method2 = proxy.method2(); ////调用invoke-----Method:目标对象的method3方法 args:Object[]{100} 返回值100 int method3 = proxy.method3(100); System.out.println(method2); System.out.println(method3); } }
运行结果:
method1 running…
method2 running…
method2
100
public class EncodingFilter implements Filter{ @Override public void doFilter(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response, FilterChain chain) throws IOException, ServletException { final HttpServletRequest req = (HttpServletRequest) request; //使用动态代理完成全局编码 HttpServletRequest enhanceRequset = (HttpServletRequest) Proxy.newProxyInstance( req.getClass().getClassLoader(), req.getClass().getInterfaces(), new InvocationHandler() { @Override public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable { //对getParameter方法进行增强 String name = method.getName();//获得目标对象的方法名称 if("getParameter".equals(name)){ String invoke = (String) method.invoke(req, args);//乱码 //转码 invoke = new String(invoke.getBytes("iso8859-1"),"UTF-8"); return invoke; } return method.invoke(req, args); } } ); chain.doFilter(enhanceRequset, response); } @Override public void destroy() { } @Override public void init(FilterConfig filterConfig) throws ServletException { } }
public class UserServiceProxyFactory2 implements MethodInterceptor { public UserService getUserServiceProxy(){ //帮我们生成代理对象 Enhancer en = new Enhancer(); //设置对谁进行代理 en.setSuperclass(UserServiceImpl.class); //代理要做什么 en.setCallback(this); //创建代理对象 UserService us = (UserService) en.create(); return us; } @Override public Object intercept(Object prxoyobj, Method method, Object[] arg, MethodProxy methodProxy) throws Throwable { //打开事务 System.out.println("打开事务!"); //调用原有方法 Object returnValue = methodProxy.invokeSuper(prxoyobj, arg); //提交事务 System.out.println("提交事务!"); return returnValue; } }
代码测试:
@Test public void fun2(){ UserServiceProxyFactory2 factory = new UserServiceProxyFactory2(); UserService usProxy = factory.getUserServiceProxy(); usProxy.save(); //判断代理对象是否属于被代理对象类型 //代理对象继承了被代理对象=>true System.out.println(usProxy instanceof UserServiceImpl ); //true }
运行结果:
打开事务!
保存用户!
提交事务!
true
JoinPoint(连接点):目标对象中所有可以增强的方法。
PointCut(切入点):目标对象,已经增强的方法。
Advice(通知 / 增强):增强的代码。
Target(目标对象):被代理对象。
Weaving(织入):将通知应用到切入点的过程。
Proxy(代理):将通知织入到目标对象之后形成代理对象。
Aspect(切面):切入点+通知
创建通知类:
//表示该类是一个通知类 public class MyAdvice { //前置通知 public void before(){ System.out.println("这是前置通知!!"); } //后置通知 public void afterReturning(){ System.out.println("这是后置通知(如果出现异常不会调用)!!"); } //环绕通知 public Object around(ProceedingJoinPoint pjp) throws Throwable { System.out.println("这是环绕通知之前的部分!!"); Object proceed = pjp.proceed();//调用目标方法 System.out.println("这是环绕通知之后的部分!!"); return proceed; } //异常通知 public void afterException(){ System.out.println("出事啦!出现异常了!!"); } //后置通知 public void after(){ System.out.println("这是后置通知(出现异常也会调用)!!"); } }
XML文件中进行配置:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd"> <!--扫描指定包及其子包下所有类中的注解--> <context:component-scan base-package="domain"></context:component-scan> <context:component-scan base-package="aop"></context:component-scan> <!--1、配置目标对象,得到的是代理的对象--> <bean name="userServiceTarget" class="aop.service.UserServiceImpl"></bean> <!--2、配置通知对象--> <bean name="myAdvice" class="aop.advice.MyAdvice"></bean> <!--3、配置将通知织入目标对象--> <aop:config> <!-- 配置切入点 public void cn.long.service.UserServiceImpl.save() void cn.long.service.UserServiceImpl.save() * cn.long.service.UserServiceImpl.save() * cn.long.service.UserServiceImpl.*() * cn.long.service.*ServiceImpl.*(..) * cn.long.service..*ServiceImpl.*(..) --> <aop:pointcut id="pc" expression="execution(* aop.service.UserServiceImpl.*(..))"></aop:pointcut> <aop:aspect ref="myAdvice" > <!-- 指定名为before方法作为前置通知 --> <aop:before method="before" pointcut-ref="pc"></aop:before> <!-- 后置 --> <aop:after-returning method="afterReturning" pointcut-ref="pc"></aop:after-returning> <!-- 环绕通知 --> <aop:around method="around" pointcut-ref="pc" /> <!-- 异常拦截通知 --> <aop:after-throwing method="afterException" pointcut-ref="pc"></aop:after-throwing> <!-- 后置 --> <aop:after method="after" pointcut-ref="pc"></aop:after> </aop:aspect> </aop:config> </beans>
测试:
package aop; import aop.service.UserService; import org.junit.Test; import org.junit.runner.RunWith; import org.springframework.test.context.ContextConfiguration; import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringJUnit4ClassRunner; import javax.annotation.Resource; @RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class) @ContextConfiguration("classpath:/spring-config.xml") public class Demo { @Resource(name="userServiceTarget") private UserService us; @Test public void fun1(){ us.save(); } }
运行结果:
我是初始化方法这是前置通知!!
这是环绕通知之前的部分!!
保存用户!
这是后置通知(出现异常也会调用)!!
这是环绕通知之后的部分!!
这是后置通知(如果出现异常不会调用)!!
我是销毁方法
XML文件:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd"> <!--1、配置目标对象--> <bean name="userServiceTarget" class="aop.service.UserServiceImpl"></bean> <!--2、配置通知对象--> <bean name="myAdvice" class="aop.advice.MyAdvice2"></bean> <!-- 3.开启使用注解完成织入 --> <aop:aspectj-autoproxy></aop:aspectj-autoproxy> </beans>
通知:
package aop.advice; import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint; import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.*; //通知类 @Aspect //表示该类是一个通知类 public class MyAdvice2 { @Pointcut("execution(* aop.service.UserServiceImpl.*(..))") public void pc(){} //前置通知 //指定该方法是前置通知,并制定切入点 @Before("MyAdvice2.pc()") public void before(){ System.out.println("这是前置通知!!"); } //后置通知 @AfterReturning("execution(* aop.service.UserServiceImpl.*(..))") public void afterReturning(){ System.out.println("这是后置通知(如果出现异常不会调用)!!"); } //环绕通知 @Around("execution(* aop.service.UserServiceImpl.*(..))") public Object around(ProceedingJoinPoint pjp) throws Throwable { System.out.println("这是环绕通知之前的部分!!"); Object proceed = pjp.proceed();//调用目标方法 System.out.println("这是环绕通知之后的部分!!"); return proceed; } //异常通知 @AfterThrowing("execution(* aop.service.UserServiceImpl.*(..))") public void afterException(){ System.out.println("出事啦!出现异常了!!"); } //后置通知 @After("execution(* aop.service.UserServiceImpl.*(..))") public void after(){ System.out.println("这是后置通知(出现异常也会调用)!!"); } }
测试:
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class) @ContextConfiguration("classpath:/aop/advice/spring-config.xml") public class Demo { @Resource(name="userServiceTarget") private UserService us; @Test public void fun1(){ us.save(); } }
运行结果:
这是环绕通知之前的部分!!
这是前置通知!!
保存用户!
这是环绕通知之后的部分!!
这是后置通知(出现异常也会调用)!!
这是后置通知(如果出现异常不会调用)!!
Spring整合了一个可以操作数据库的对象JDBCTemplate(JBDC模板对象),该对象封装了jdbc技术,与DBUtils中的QueryRunner非常相似。
演示一下JDBCTemplate的使用:
//演示JDBC模板 public class Demo { @Test public void fun1() throws Exception { //0 准备连接池 ComboPooledDataSource dataSource = new ComboPooledDataSource(); dataSource.setDriverClass("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"); dataSource.setJdbcUrl("jdbc:mysql:///test"); dataSource.setUser("root"); dataSource.setPassword("666"); //1 创建JDBC模板对象 JdbcTemplate jt = new JdbcTemplate(); jt.setDataSource(dataSource); //2 书写sql,并执行 String sql = "insert into user values(null,‘long‘) "; jt.update(sql); } }
运行结果: 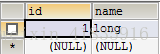
JDBCTemplate增删改查:
UserDao :
public interface UserDao { //增 void save(User u); //删 void delete(Integer id); //改 void update(User u); //查 User getById(Integer id); //查 int getTotalCount(); //查 List<User> getAll(); }
UserDaoImpl:
//使用JDBC模板实现增删改查 public class UserDaoImpl extends JdbcDaoSupport implements UserDao { @Override public void save(User u) { String sql = "insert into t_user values(null,?) "; super.getJdbcTemplate().update(sql, u.getName()); } @Override public void delete(Integer id) { String sql = "delete from t_user where id = ? "; super.getJdbcTemplate().update(sql,id); } @Override public void update(User u) { String sql = "update t_user set name = ? where id=? "; super.getJdbcTemplate().update(sql, u.getName(),u.getId()); } @Override public User getById(Integer id) { String sql = "select * from t_user where id = ? "; return super.getJdbcTemplate().queryForObject(sql,new RowMapper<User>(){ @Override public User mapRow(ResultSet rs, int arg1) throws SQLException { User u = new User(); u.setId(rs.getInt("id")); u.setName(rs.getString("name")); return u; }}, id); } @Override public int getTotalCount() { String sql = "select count(*) from t_user "; Integer count = super.getJdbcTemplate().queryForObject(sql, Integer.class); return count; } @Override public List<User> getAll() { String sql = "select * from t_user "; List<User> list = super.getJdbcTemplate().query(sql, new RowMapper<User>(){ @Override public User mapRow(ResultSet rs, int arg1) throws SQLException { User u = new User(); u.setId(rs.getInt("id")); u.setName(rs.getString("name")); return u; }}); return list; } }
将其配置到Spring容器中:
依赖关系: 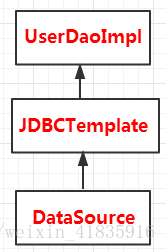
配置文件如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd"> <!-- 指定spring读取db.properties配置 --> <context:property-placeholder location="classpath:db.properties" /> <!-- 1.将连接池放入spring容器 --> <bean name="dataSource" class="com.mchange.v2.c3p0.ComboPooledDataSource" > <property name="jdbcUrl" value="${jdbc.jdbcUrl}" ></property> <property name="driverClass" value="${jdbc.driverClass}" ></property> <property name="user" value="${jdbc.user}" ></property> <property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}" ></property> </bean> <!-- 2.将JDBCTemplate放入spring容器 --> <bean name="jdbcTemplate" class="org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate" > <property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource" ></property> </bean> <!-- 3.将UserDao放入spring容器 --> <bean name="userDao" class="jdbcTemplate.UserDaoImpl" > <!-- <property name="jt" ref="jdbcTemplate" ></property> --> <property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource" ></property> </bean> </beans>
测试:
package jdbcTemplate; import com.mchange.v2.c3p0.ComboPooledDataSource; import org.junit.Test; import org.junit.runner.RunWith; import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate; import org.springframework.test.context.ContextConfiguration; import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringJUnit4ClassRunner; import javax.annotation.Resource; /** * Created by KPL on 2018/7/1. */ //演示JDBC模板 @RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class) @ContextConfiguration("classpath:spring-config.xml") public class Demo { @Resource(name="userDao") private UserDao ud; @Test public void fun2() throws Exception{ User u = new User(); u.setName("naruto"); ud.save(u); } @Test public void fun3() throws Exception{ User u = new User(); u.setId(2); u.setName("jack"); ud.update(u); } @Test public void fun4() throws Exception{ ud.delete(2); } @Test public void fun5() throws Exception{ System.out.println(ud.getTotalCount()); } @Test public void fun6() throws Exception{ System.out.println(ud.getById(1)); } @Test public void fun7() throws Exception{ System.out.println(ud.getAll()); } }
运行结果: 
public class UserDaoImpl extends JdbcDaoSupport继承了JdbcDaoSupport,Spring会根据连接池自动创建JDBC模板对象。也就是说不需要手动擦行间JBDC模板对象,从父类方法中直接获取即可。
String sql = "insert into t_user values(null,?) "; super.getJdbcTemplate().update(sql, u.getName());
此时,配置文件修改成如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd"> <!-- 指定spring读取db.properties配置 --> <context:property-placeholder location="classpath:db.properties" /> <!-- 1.将连接池放入spring容器 --> <bean name="dataSource" class="com.mchange.v2.c3p0.ComboPooledDataSource" > <property name="jdbcUrl" value="${jdbc.jdbcUrl}" ></property> <property name="driverClass" value="${jdbc.driverClass}" ></property> <property name="user" value="${jdbc.user}" ></property> <property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}" ></property> </bean> <!-- 3.将UserDao放入spring容器 --> <bean name="userDao" class="jdbcTemplate.UserDaoImpl" > <property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource" ></property> </bean> </beans>
1.1、事务概述
(1)什么是事务?
一件事情有n个组成单元 要不这n个组成单元同时成功,要不n个单元就同时失败
就将n个组成单元放到一个事务中。
(2)mysql的事务
默认的事务:一条sql语句就是一个事务 默认就开启事务并提交事务。sql执行完了之后自动提交了。
手动事务:
显示的开启一个事务:start transaction。
事务提交:commit代表从开启事务到事务提交,中间的所有的sql都认为有效真正的更新数据库。
事务的回滚:rollback代表事务的回滚从开启事务到事务回滚中间的所有的sql操作都认为无效数据库没有被更新。
1.2、JDBC事务操作
默认是自动事务:
执行sql语句:executeUpdate() —- 每执行一次executeUpdate方法代表事务自动提交。
通过jdbc的API手动事务:
开启事务:conn.setAutoComnmit(false);
提交事务:conn.commit();
回滚事务:conn.rollback();
注意:控制事务的connnection必须是同一个执行sql的connection与开启事务的connnection必须是同一个才能对事务进行控制。
1.3、DBUtils事务操作
QueryRunner
有参构造:QueryRunner runner = new QueryRunner(DataSource dataSource);
有参构造将数据源(连接池)作为参数传入QueryRunner,QueryRunner会从连接池中获得一个数据库连接资源操作数据库,所以直接使用无Connection参数的update方法即可操作数据库。不需要事务则采用此方法。
无参构造:QueryRunner runner = new QueryRunner();
无参的构造没有将数据源(连接池)作为参数传入QueryRunner,那么我们在使用QueryRunner对象操作数据库时要使用有Connection参数的方法。此方法能实现事务。
1.4、事务的特性ACID
(1)原子性(Atomicity)原子性是指事务是一个不可分割的工作单位,事务中的操作 要么都发生,要么都不发生。
(2)一致性(Consistency)一个事务中,事务前后数据的完整性必须保持一致。
(3)隔离性(Isolation)多个事务,事务的隔离性是指多个用户并发访问数据库时,一个用户的 事务不能被其它用户的事务所干扰,多个并发事务之间数据要相互隔离。
(4)持久性(Durability)持久性是指一个事务一旦被提交,它对数据库中数据的改变 就是永久性的,接下来即使数据库发生故障也不应该对其有任何影响。
五、事务的隔离
如果不考虑隔离性,事务存在3种并发访问问题。
脏读:B事务读取到了A事务尚未提交的数据 —— 要求B事务要读取A事务提交的数据
不可重复读:一个事务中 两次读取的数据的内容不一致 —– 要求的是一个事务中多次读取时数据是一致的 — unpdate
幻读/虚读:一个事务中 两次读取的数据的数量不一致 —– 要求在一个事务多 次读取的数据的数量是一致的 –insert delete
事务的隔离级别:
(1)read uncommitted : 读取尚未提交的数据 :哪个问题都不能解决
(2)read committed:读取已经提交的数据 :可以解决脏读 —- oracle默认的
(3)repeatable read:重读读取:可以解决脏读和不可重复读 —mysql默认的
(4)serializable:串行化:可以解决脏读不可重复读和虚读—相当于锁表
注意:mysql数据库默认的隔离级别
查看mysql数据库默认的隔离级别:select @@tx_isolation
设置mysql的隔离级别:set session transaction isolation level 设置事务隔离级别
因为在不用平台,操纵事务的代码各不相同,于是Spring提供了一个接口PlatfromTransactionManager接口,针对不同的平台,提供不同的实现类。
***** 真正管理事务的对象 org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager //使用 SpringJDBC 或 iBatis 进行持久化数据时使用 org.springframework.orm.hibernate3.HibernateTransactionManager //使用Hibernate 版本进行持久化数据时使用
事务的传播行为:决定业务方法之间调用,事务应该如何处理。
//保证同一个事务中
PROPAGATION_REQUIRED 支持当前事务,如果不存在 就新建一个(默认)
PROPAGATION_SUPPORTS 支持当前事务,如果不存在,就不使用事务
PROPAGATION_MANDATORY 支持当前事务,如果不存在,抛出异常
//保证没有在同一个事务中
PROPAGATION_REQUIRES_NEW 如果有事务存在,挂起当前事务,创建一个新的事务
PROPAGATION_NOT_SUPPORTED 以非事务方式运行,如果有事务存在,挂起当前事务
PROPAGATION_NEVER 以非事务方式运行,如果有事务存在,抛出异常
PROPAGATION_NESTED 如果当前事务存在,则嵌套事务执行
演示一下Spring事务:
先完成基本的转账功能:
Dao:
package Transaction.dao; public interface AccountDao { //加钱 void increaseMoney(Integer id, Double money); //减钱 void decreaseMoney(Integer id, Double money); }
DaoImpl:
public class AccountDaoImpl extends JdbcDaoSupport implements AccountDao { @Override public void increaseMoney(Integer id, Double money) { getJdbcTemplate().update("update t_account set money = money+? where id = ? ", money,id); } @Override public void decreaseMoney(Integer id, Double money) { getJdbcTemplate().update("update t_account set money = money-? where id = ? ", money,id); } }
XML文件:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd"> <!-- 指定spring读取db.properties配置 --> <context:property-placeholder location="classpath:db.properties" /> <!-- 1.将连接池 --> <bean name="dataSource1" class="com.mchange.v2.c3p0.ComboPooledDataSource" > <property name="jdbcUrl" value="${jdbc.jdbcUrl}" ></property> <property name="driverClass" value="${jdbc.driverClass}" ></property> <property name="user" value="${jdbc.user}" ></property> <property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}" ></property> </bean> <!-- 2.Dao--> <bean name="accountDao" class="Transaction.dao.AccountDaoImpl" > <property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource1" ></property> </bean> <!-- 3.Service--> <bean name="accountService" class="Transaction.service.AccountServiceImpl" > <property name="ad" ref="accountDao" ></property> </bean> </beans>
测试类:
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class) @ContextConfiguration("classpath:spring-config2.xml") public class Demo { @Resource(name="accountService") private AccountService as; @Test public void fun1(){ as.transfer(1, 2, 100d); } }
运行结果: 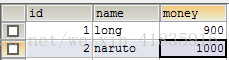
现在开始加事务:
Spring管理事务的方式:
编码式:(了解)
将核心事务管理器配置到Spring容器:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd"> <!-- 指定spring读取db.properties配置 --> <context:property-placeholder location="classpath:db.properties" /> <!-- 事务核心管理器,封装了所有事务操作. 依赖于连接池 --> <bean name="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager" > <property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource1" ></property> </bean> <!-- 事务模板对象 --> <bean name="transactionTemplate" class="org.springframework.transaction.support.TransactionTemplate" > <property name="transactionManager" ref="transactionManager" ></property> </bean> <!-- 1.将连接池 --> <bean name="dataSource1" class="com.mchange.v2.c3p0.ComboPooledDataSource" > <property name="jdbcUrl" value="${jdbc.jdbcUrl}" ></property> <property name="driverClass" value="${jdbc.driverClass}" ></property> <property name="user" value="${jdbc.user}" ></property> <property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}" ></property> </bean> <!-- 2.Dao--> <bean name="accountDao" class="Transaction.dao.AccountDaoImpl" > <property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource1" ></property> </bean> <!-- 3.Service--> <bean name="accountService" class="Transaction.service.AccountServiceImpl" > <property name="ad" ref="accountDao" ></property> <property name="tt" ref="transactionTemplate" ></property> </bean> </beans>
ServiceImpl:
@Transactional(isolation=Isolation.REPEATABLE_READ,propagation=Propagation.REQUIRED,readOnly=true) public class AccountServiceImpl implements AccountService { private AccountDao ad ; private TransactionTemplate tt; @Override public void transfer(final Integer from,final Integer to,final Double money) { tt.execute(new TransactionCallbackWithoutResult() { @Override protected void doInTransactionWithoutResult(TransactionStatus arg0) { //减钱 ad.decreaseMoney(from, money); int i = 1/0; //加钱 ad.increaseMoney(to, money); } }); } public void setAd(AccountDao ad) { this.ad = ad; } public void setTt(TransactionTemplate tt) { this.tt = tt; } }
测试代码:
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class) @ContextConfiguration("classpath:spring-config2.xml") public class Demo { @Resource(name="accountService") private AccountService as; @Test public void fun1(){ as.transfer(1, 2, 100d); } }
运行结果,由于加入了事务,报错之后,钱并不会转过去: 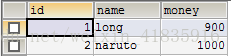
XML配置(aop)
Spring内部已经封装了事务通知方法,那么咱们只需要将它配置到业务处理上去就可以了。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop" xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.2.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-4.2.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-4.2.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx-4.2.xsd "> <!-- 指定spring读取db.properties配置 --> <context:property-placeholder location="classpath:db.properties" /> <!-- 事务核心管理器,封装了所有事务操作. 依赖于连接池 --> <bean name="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager" > <property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource" ></property> </bean> <!-- 事务模板对象 --> <bean name="transactionTemplate" class="org.springframework.transaction.support.TransactionTemplate" > <property name="transactionManager" ref="transactionManager" ></property> </bean> <!-- 配置事务通知 --> <tx:advice id="txAdvice" transaction-manager="transactionManager" > <tx:attributes> <!-- 以方法为单位,指定方法应用什么事务属性 isolation:隔离级别 propagation:传播行为 read-only:是否只读 --> <tx:method name="save*" isolation="REPEATABLE_READ" propagation="REQUIRED" read-only="false" /> <tx:method name="persist*" isolation="REPEATABLE_READ" propagation="REQUIRED" read-only="false" /> <tx:method name="update*" isolation="REPEATABLE_READ" propagation="REQUIRED" read-only="false" /> <tx:method name="modify*" isolation="REPEATABLE_READ" propagation="REQUIRED" read-only="false" /> <tx:method name="delete*" isolation="REPEATABLE_READ" propagation="REQUIRED" read-only="false" /> <tx:method name="remove*" isolation="REPEATABLE_READ" propagation="REQUIRED" read-only="false" /> <tx:method name="get*" isolation="REPEATABLE_READ" propagation="REQUIRED" read-only="true" /> <tx:method name="find*" isolation="REPEATABLE_READ" propagation="REQUIRED" read-only="true" /> <tx:method name="transfer" isolation="REPEATABLE_READ" propagation="REQUIRED" read-only="false" /> </tx:attributes> </tx:advice> <!-- 配置织入 --> <aop:config > <!-- 配置切点表达式 --> <aop:pointcut expression="execution(* Transaction.service.*ServiceImpl.*(..))" id="txPc"/> <!-- 配置切面 : 通知+切点 advice-ref:通知的名称 pointcut-ref:切点的名称 --> <aop:advisor advice-ref="txAdvice" pointcut-ref="txPc" /> </aop:config> <!-- 1.将连接池 --> <bean name="dataSource" class="com.mchange.v2.c3p0.ComboPooledDataSource" > <property name="jdbcUrl" value="${jdbc.jdbcUrl}" ></property> <property name="driverClass" value="${jdbc.driverClass}" ></property> <property name="user" value="${jdbc.user}" ></property> <property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}" ></property> </bean> <!-- 2.Dao--> <bean name="accountDao" class="Transaction.dao.AccountDaoImpl" > <property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource" ></property> </bean> <!-- 3.Service--> <bean name="accountService" class="Transaction.service.AccountServiceImpl" > <property name="ad" ref="accountDao" ></property> <property name="tt" ref="transactionTemplate" ></property> </bean> </beans>
注解配置(aop)
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop" xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.2.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-4.2.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-4.2.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx-4.2.xsd "> <!-- 指定spring读取db.properties配置 --> <context:property-placeholder location="classpath:db.properties" /> <!-- 事务核心管理器,封装了所有事务操作. 依赖于连接池 --> <bean name="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager" > <property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource" ></property> </bean> <!-- 事务模板对象 --> <bean name="transactionTemplate" class="org.springframework.transaction.support.TransactionTemplate" > <property name="transactionManager" ref="transactionManager" ></property> </bean> <!-- 开启使用注解管理aop事务 --> <tx:annotation-driven/> <!-- 1.将连接池 --> <bean name="dataSource" class="com.mchange.v2.c3p0.ComboPooledDataSource" > <property name="jdbcUrl" value="${jdbc.jdbcUrl}" ></property> <property name="driverClass" value="${jdbc.driverClass}" ></property> <property name="user" value="${jdbc.user}" ></property> <property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}" ></property> </bean> <!-- 2.Dao--> <bean name="accountDao" class="Transaction.dao.AccountDaoImpl" > <property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource" ></property> </bean> <!-- 3.Service--> <bean name="accountService" class="Transaction.service.AccountServiceImpl" > <property name="ad" ref="accountDao" ></property> <property name="tt" ref="transactionTemplate" ></property> </bean> </beans>
加入注解:
@Transactional(isolation= Isolation.REPEATABLE_READ,propagation= Propagation.REQUIRED,readOnly=true) public class AccountServiceImpl implements AccountService { private AccountDao ad ; private TransactionTemplate tt; @Override @Transactional(isolation=Isolation.REPEATABLE_READ,propagation=Propagation.REQUIRED,readOnly=false) public void transfer(final Integer from,final Integer to,final Double money) { //减钱 ad.decreaseMoney(from, money); int i = 1/0; //加钱 ad.increaseMoney(to, money); } public void setAd(AccountDao ad) { this.ad = ad; } public void setTt(TransactionTemplate tt) { this.tt = tt; } }
测试
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class) @ContextConfiguration("classpath:spring-config4.xml") public class Demo { @Resource(name="accountService") private AccountService as; @Test public void fun1(){ as.transfer(1, 2, 100d); } }
运行结果,由于出错,钱不会转过去:
标签:sele ica persist 持久 dea username this field col
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/wuluogan/p/9943304.html