标签:解析 js代码 bubuko begin http 过程 scanf this for
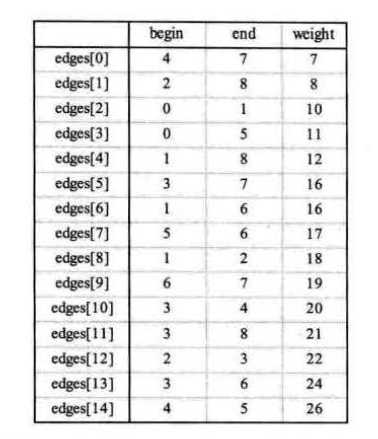
构造出所有边的集合 edges,从小到大,依次选出筛选边打印,遇到闭环(形成回路)时跳过。
JS代码:
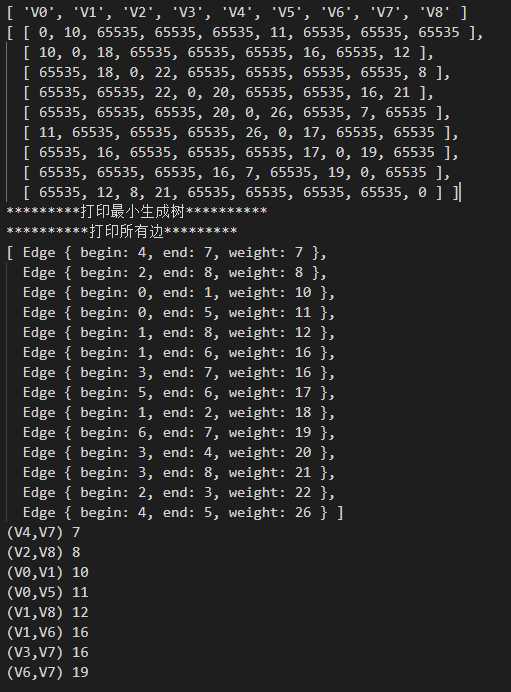
1 //定义邻接矩阵 2 let Arr2 = [ 3 [0, 10, 65535, 65535, 65535, 11, 65535, 65535, 65535], 4 [10, 0, 18, 65535, 65535, 65535, 16, 65535, 12], 5 [65535, 18, 0, 22, 65535, 65535, 65535, 65535, 8], 6 [65535, 65535, 22, 0, 20, 65535, 65535, 16, 21], 7 [65535, 65535, 65535, 20, 0, 26, 65535, 7, 65535], 8 [11, 65535, 65535, 65535, 26, 0, 17, 65535, 65535], 9 [65535, 16, 65535, 65535, 65535, 17, 0, 19, 65535], 10 [65535, 65535, 65535, 16, 7, 65535, 19, 0, 65535], 11 [65535, 12, 8, 21, 65535, 65535, 65535, 65535, 0], 12 ] 13 14 let numVertexes = 9, //定义顶点数 15 numEdges = 15; //定义边数 16 17 // 定义图结构 18 function MGraph() { 19 this.vexs = []; //顶点表 20 this.arc = []; // 邻接矩阵,可看作边表 21 this.numVertexes = null; //图中当前的顶点数 22 this.numEdges = null; //图中当前的边数 23 } 24 let G = new MGraph(); //创建图使用 25 26 //创建图 27 function createMGraph() { 28 G.numVertexes = numVertexes; //设置顶点数 29 G.numEdges = numEdges; //设置边数 30 31 //录入顶点信息 32 for (let i = 0; i < G.numVertexes; i++) { 33 G.vexs[i] = ‘V‘ + i; //scanf(‘%s‘); //ascii码转字符 //String.fromCharCode(i + 65); 34 } 35 console.log(G.vexs) //打印顶点 36 37 //邻接矩阵初始化 38 for (let i = 0; i < G.numVertexes; i++) { 39 G.arc[i] = []; 40 for (j = 0; j < G.numVertexes; j++) { 41 G.arc[i][j] = Arr2[i][j]; //INFINITY; 42 } 43 } 44 console.log(G.arc); //打印邻接矩阵 45 } 46 47 function Edge() { 48 this.begin = 0; 49 this.end = 0; 50 this.weight = 0; 51 } 52 53 function Kruskal() { 54 let n, m; 55 let parent = []; //定义一数组用来判断边与边是否形成环路 56 let edges = []; //定义边集数组 57 58 for (let i = 0; i < G.numVertexes; i++) { 59 for (let j = i; j < G.numVertexes; j++) { //因为是无向图所以相同的边录入一次即可,若是有向图改为0 60 if (G.arc[i][j] != 0 && G.arc[i][j] != 65535) { 61 let edge = new Edge(); 62 edge.begin = i; 63 edge.end = j; 64 edge.weight = G.arc[i][j]; 65 edges.push(edge); 66 } 67 } 68 } 69 70 edges.sort((v1, v2) => { 71 return v1.weight - v2.weight 72 }); 73 74 console.log(‘**********打印所有边*********‘); 75 console.log(edges); 76 77 for (let i = 0; i < G.numVertexes; i++) { 78 parent[i] = 0; 79 } 80 81 for (let i = 0; i < edges.length; i++) { 82 n = Find(parent, edges[i].begin) 83 m = Find(parent, edges[i].end) 84 if (n != m) { //假如n与m不等,说明此边没有与现有生成树形成环路 85 parent[n] = m; 86 console.log("(%s,%s) %d", G.vexs[edges[i].begin], G.vexs[edges[i].end], edges[i].weight); 87 } 88 } 89 } 90 91 92 function Find(parent, f) { //查找连线顶点的尾部下标 93 while (parent[f] > 0) { 94 f = parent[f] 95 } 96 return f; 97 } 98 99 createMGraph(); 100 console.log(‘*********打印最小生成树**********‘) 101 Kruskal();
打印结果:
代码部分过程解析:
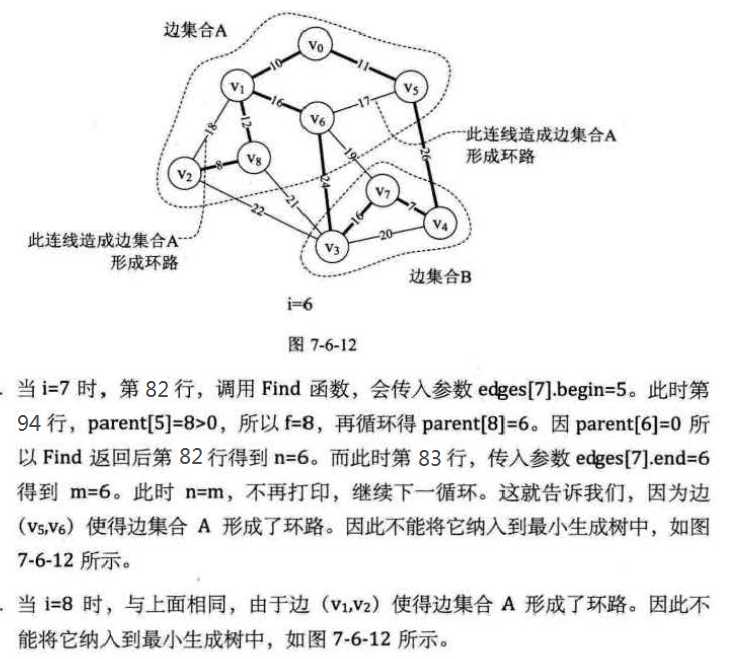
克鲁斯卡尔算法主要针对边展开,时间复杂度为 O(elog e),e为图的边数,普利姆算法的时间复杂度为O(n2),n为最小生成树的边数。所以,边数少(稀疏图)用克鲁斯卡尔算法,边数多(稠密图)用普利姆算法。
参考文献: 程杰老师的 《大话数据结构》
标签:解析 js代码 bubuko begin http 过程 scanf this for
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/xbblogs/p/9960255.html