标签:ORC ports 存储 def 相机 几何 WebG 鼠标 事先
今天要把WebGL中一个非常重要的算法记录下来——raycaster射线法拾取模型。首先我们来了解一下为什么要做模型拾取,我们在做webgl场景交互的时候经常要选中场景中的某个模型,比如鼠标拖拽旋转,平移。为了能做到鼠标交互,就首先要能选中场景中的模型对象,这就要用到模型拾取算法,本文仅讨论射线法模型拾取raycaster。
所谓射线法就是利用一根射线去和场景中的模型进行碰撞,撞到的模型对象就是被拾取到的模型。请看下图
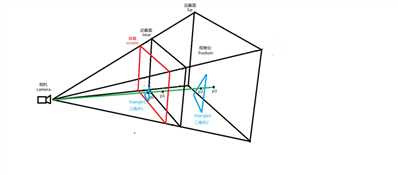
我逐个来解释一下上图中的元素。首先解释相机(camera),这就是人眼的抽象,代表用户在屏幕前的眼睛位置。人眼看到的世界是透视的(perspective),因此我们构造的视棱台(frustum)基于透视投影。整个视棱台区域介于场景近截面(near)和远截面(far)之间,这个区间内的空间就是我们可以看到的场景空间。需要说明一下,near近截面我们这里紧贴屏幕(screen),即距离很小约等于0.1,far远截面就是我们认为的视线最远能看到的距离,我们这里设置为1000。屏幕screen在近截面前0.1的位置上,也是离人眼最近的截面,也是鼠标交互的界面,这是要事先解释明白的。理解了这个空间结构以后我们就开始讲解raycaster的算法原理。
首先我们来看一下鼠标在屏幕上的位置点P0,我们可以看到P0点(鼠标),这个就是鼠标在屏幕上的位置。我们再来看看triangle1三角形1,这就是透视空间中triangle2三角形2在屏幕上的投影。我们可以明显看到鼠标位置P0点在屏幕triangle1三角形1内部,即鼠标点选中triangle1三角形1。这在屏幕上可以看的很清楚,但是问题来了,在空间中鼠标是没有深度概念的,即鼠标只有XY坐标,没有Z坐标,那我们在视棱台的空间坐标系中如何表示鼠标的三维空间位置呢,如果没有鼠标的3维空间坐标,如何判断在视棱台空间中鼠标是否选中triangle2三角形2这个模型对象呢?也许有同学会说,triangle1就是triangle2的投影嘛,选中投影就是选中模型了不是,我就这么说,非常正确,能说出这样的话就已经完全理解了模型在屏幕上的投影的原理,但是新的问题随之又来了,如何获取鼠标点选模型的坐标呢,即如何得到鼠标点在模型上的那个点的三维空间坐标呢,如果仅仅判断是否选中,那投影就够用了,但要计算鼠标点选模型上的点坐标,就远远不够用了。为了解决这个问题,raycaster算法应运而生。
raycaster顾名思义就是射线投射。他的原理其实非常简单,就是用一根射线去交有限平面,获得交点。射线是有起点的,起点就是我们的眼睛。我们做一根起于camera,通过鼠标在屏幕上的位置P0,继续延伸,交视棱台近截面于P1,继续延伸,交视棱台远截面于P3,射线截止,我们得到了一根线段P1-P3。这根线段P1-P3就是我们眼睛能看到的鼠标发出的射线在透视空间中的部分,凡是这根线段碰到的模型,都是鼠标点选中的空间模型。而这根线段和模型的交点就是鼠标点选模型的交点,这个交点坐标就是鼠标点选模型的交点空间三维坐标。这样就顺利解决了上面我们的问题,即求鼠标点选空间三维模型的交点坐标。在上图中我们看得很清楚,这个交点就是P2,接下来我们就来讲解怎么求这个P2的空间坐标。
做图形学的同学们都非常清楚。如何求线段和平面的交点,这里我截取一部分代码,以供叙述方便,以下就是求线段截取平面交点的函数。
/* */ let Intersector = require(‘./Intersector‘); let LineSegmentIntersection = require(‘./Intersection‘).LineSegmentIntersection; let Vec3 = require(‘./Vec3‘); let Mat4 = require(‘./Mat4‘); let Algorithm = require(‘./Algorithm‘); let LineSegmentIntersector = function () { Intersector.call(this); //原始的起始点和临界值,初始化设置的数据,保留作为参照,设置后不再变动 this._orginStart = Vec3.new();//线段起点 this._orginEnd = Vec3.new();//线段终点 this._orginThreshold = 0.0;//点和线求相交时的临界值,完全相交是很难求到的 //临时存储,每次求交都可能会变动的数据 //对于有变换的几何求交,不会变换几何顶点而是变换起始点和临界值 this._start = Vec3.new();//线段起点 this._end = Vec3.new();//线段终点 this._threshold = 0.0;//点和线求相交时的临界值,完全相交是很难求到的 this._direction = Vec3.new(); this._length = 0; this._inverseLength = 0; this._matrix = Mat4.new(); }; LineSegmentIntersector.prototype = Object.create(Intersector.prototype); LineSegmentIntersector.prototype.constructor = LineSegmentIntersector; Object.assign(LineSegmentIntersector.prototype, { init: function (start, end, threshold) { Vec3.copy(this._orginStart, start); Vec3.copy(this._orginEnd, end); Vec3.copy(this._start, start); Vec3.copy(this._end, end); if (threshold !== undefined) { this._orginThreshold = threshold; this._threshold = threshold; } }, intersect: function (drawable) { //先使用包围盒子 if (!drawable.getBoundingBox().intersectLineSegment(this._orginStart, this._orginEnd)) { return; } this._drawable = drawable; let geometry = drawable.getGeometry(); let vertexbuffer = geometry.getBufferArray(‘Vertex‘); this._vertices = vertexbuffer.getArrayBuffer(); //没有顶点数据不处理直接返回 if (!this._vertices) return; //没有图元不处理直接返回 let primitive = geometry.getPrimitive(); if (!primitive) return; //初始化求相交的各种数据 let matrix = drawable.getTransform(); if (this._transform !== matrix) {//如果不一样,需要计算新的起始点以及各种临时数据 this._transform = matrix; Mat4.invert(this._matrix, matrix); //根据矩阵计算新的临界值 if (this._orginThreshold > 0.0) { let tmp = this._start; Mat4.getScale(tmp, this._matrix); let x = tmp[0]; let y = tmp[1]; let z = tmp[2]; this._threshold = this._orginThreshold * (x > y ? (x > z ? x : z) : y > z ? y : z); } //根据矩阵计算新的起始点 Vec3.transformMat4(this._start, this._orginStart, this._matrix); Vec3.transformMat4(this._end, this._orginEnd, this._matrix); //根据新的起始点计算各种临时数据 Vec3.sub(this._direction, this._end, this._start); this._length = Vec3.length(this._direction);//长度 this._inverseLength = this._length <= Algorithm.EPSILON ? 0.0 : 1.0 / this._length; Vec3.scale(this._direction, this._direction, this._inverseLength);//求单位向量 }//如果变换与上次一样,直接使用上次的数据求相交 //求相交 primitive.operate(this); }, intersectPoint: function (vertex) { // https://www.geometrictools.com/GTEngine/Include/Mathematics/GteDistPointSegment.h //起点指向绘制点,向量M let m = Vec3.MemoryPool.alloc(); Vec3.sub(m, vertex, this._start); //起点指向终点,向量N let n = Vec3.MemoryPool.alloc(); Vec3.sub(n, this._end, this._start); //求M在N上的投影比例值 //|m|*|n|*cos / \n\*\n\ = |m|*cos/\n\ let r = Vec3.dot(m, n) * this._inverseLength * this._inverseLength; //计算绘制点到线段的距离 let sqrdist = 1.0; if (r < 0.0) {//夹角超过90度,绘制点在当前线段起点后面,求绘制点与起点的距离 sqrdist = Vec3.sqrLen(m); } else if (r > 1.0) {//绘制点在当前线段终点后面,求绘制点与终点的距离 sqrdist = Vec3.sqrDist(vertex, this._end); } else {//在0到1之间 //m - n * r 如果平行或者接近于平行,结果接近于0,相交 sqrdist = Vec3.sqrLen(Vec3.scaleAndAdd(m, m, n, -r)); } let intersection = undefined; if (sqrdist > this._threshold * this._threshold) {//超过了临界值,没有相交返回 } else { //相交 intersection = new LineSegmentIntersection(); //intersection._i1 = index; //intersection._r1 = 1.0; Vec3.scaleAndAdd(intersection._point, this._start, n, r); intersection._ratio = r; } Vec3.MemoryPool.free(m); Vec3.MemoryPool.free(n); return intersection; }, intersectLine: function (vertex0, vertex1) { // https://www.geometrictools.com/GTEngine/Samples/Geometrics/DistanceSegments3/DistanceSegments3.cpp //let epsilon = 0.00000001; //起点到终点的向量 let u = Vec3.MemoryPool.alloc(); Vec3.sub(u, vertex1, vertex0); let v = Vec3.MemoryPool.alloc(); Vec3.sub(v, this._end, this._start); let w = Vec3.MemoryPool.alloc(); Vec3.sub(w, vertex0, this._start); let a = Vec3.dot(u, u); let b = Vec3.dot(u, v); let c = Vec3.dot(v, v); let d = Vec3.dot(u, w); let e = Vec3.dot(v, w); let D = a * c - b * b; let sN; let tN; let sD = D; let tD = D; // compute the line parameters of the two closest points if (D < Algorithm.EPSILON) {//平行 // the lines are almost parallel sN = 0.0; // force using point P0 on segment S1 sD = 1.0; // to prevent possible division by 0.0 later tN = e; tD = c; } else { // get the closest points on the infinite lines sN = b * e - c * d; tN = a * e - b * d; if (sN < 0.0) { // sc < 0 => the s=0 edge is visible sN = 0.0; tN = e; tD = c; } else if (sN > sD) { // sc > 1 => the s=1 edge is visible sN = sD; tN = e + b; tD = c; } } if (tN < 0.0) { // tc < 0 => the t=0 edge is visible tN = 0.0; // recompute sc for this edge if (-d < 0.0) sN = 0.0; else if (-d > a) sN = sD; else { sN = -d; sD = a; } } else if (tN > tD) { // tc > 1 => the t=1 edge is visible tN = tD; // recompute sc for this edge if (-d + b < 0.0) sN = 0; else if (-d + b > a) sN = sD; else { sN = -d + b; sD = a; } } // finally do the division to get sc and tc let sc = Math.abs(sN) < Algorithm.EPSILON ? 0.0 : sN / sD; let tc = Math.abs(tN) < Algorithm.EPSILON ? 0.0 : tN / tD; // get the difference of the two closest points let closest0 = Vec3.MemoryPool.alloc(); let closest1 = Vec3.MemoryPool.alloc(); Vec3.scaleAndAdd(closest0, vertex0, u, sc); Vec3.scaleAndAdd(closest1, this._start, v, tc); let sqrDistance = Vec3.sqrDist(closest0, closest1); Vec3.MemoryPool.free(closest0); Vec3.MemoryPool.free(closest1); let intersection = undefined; if (sqrDistance > this._threshold * this._threshold) { } else { //相交 intersection = new LineSegmentIntersection(); // intersection._i1 = index0; // intersection._i2 = index1; // intersection._r1 = 1.0 - tc; // intersection._r2 = tc; Vec3.copy(intersection._point, closest1); intersection._ratio = tc; } Vec3.MemoryPool.free(u); Vec3.MemoryPool.free(v); Vec3.MemoryPool.free(w); return intersection; }, intersectTriangle: function (vertex0, vertex1, vertex2) { let e2 = Vec3.MemoryPool.alloc(); Vec3.sub(e2, vertex2, vertex0); let e1 = Vec3.MemoryPool.alloc(); Vec3.sub(e1, vertex1, vertex0); let pvec = Vec3.MemoryPool.alloc(); Vec3.cross(pvec, this._direction, e2); let intersection = undefined; //线段与三角面点积 let det = Vec3.dot(pvec, e1); //判断三角形所在的平面与线段是否平行,如果平行铁定不相交,面片没有厚度 if (Math.abs(det) < Algorithm.EPSILON) { //return undefined; }else{ let invDet = 1.0 / det; let tvec = Vec3.MemoryPool.alloc(); Vec3.sub(tvec, this._start, vertex0); let u = Vec3.dot(pvec, tvec) * invDet; //三角面超出了线段两个点范围外面,铁定不相交 if (u < 0.0 || u > 1.0) { //return undefined; }else{ let qvec = Vec3.MemoryPool.alloc(); Vec3.cross(qvec, tvec, e1); let v = Vec3.dot(qvec, this._direction) * invDet; // if (v < 0.0 || u + v > 1.0) { //return undefined; }else{ let t = Vec3.dot(qvec, e2) * invDet; if (t < Algorithm.EPSILON || t > this._length) { //return undefined; }else{ //相交 intersection = new LineSegmentIntersection(); //求相交点 let r0 = 1.0 - u - v; let r1 = u; let r2 = v; let r = t * this._inverseLength; let interX = vertex0[0] * r0 + vertex1[0] * r1 + vertex2[0] * r2; let interY = vertex0[1] * r0 + vertex1[1] * r1 + vertex2[1] * r2; let interZ = vertex0[2] * r0 + vertex1[2] * r1 + vertex2[2] * r2; // intersection._i1 = index0; // intersection._i2 = index1; // intersection._i3 = index2; // intersection._r1 = r0; // intersection._r2 = r1; // intersection._r3 = r2; //这里的点没有经过变换,不是真实的世界坐标点 Vec3.set(intersection._point, interX, interY, interZ); Vec3.transformMat4(intersection._point, intersection._point, this._transform); //求法向量,法向量未变换,如果有用途也要变换 let normal = intersection._normal; Vec3.cross(normal, e1, e2); Vec3.normalize(normal, normal); //比例,在相交线段上的比例,不需要变换 intersection._ratio = r; } } Vec3.MemoryPool.free(qvec); } Vec3.MemoryPool.free(tvec); } Vec3.MemoryPool.free(e1); Vec3.MemoryPool.free(e2); Vec3.MemoryPool.free(pvec); return intersection; // http://gamedev.stackexchange.com/questions/54505/negative-scale-in-matrix-4x4 // https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Determinant#Orientation_of_a_basis // you can‘t exactly extract scale of a matrix but the determinant will tell you // if the orientation is preserved //intersection._backface = mat4.determinant(intersection._matrix) * det < 0; }, intersectBoundingBox: function (box) { return box.intersectLineSegment(this._orginStart, this._orginEnd); }, }); module.exports = LineSegmentIntersector; // setDrawable: function (drawable) { // this._geometry = drawable.getGeometry(); // this._vertices = this._geometry.getBufferArray(‘Vertex‘); // // let matrix = drawable.getTransform(); // if (this._transform === matrix) {//如果与上次的一样,不再处理 // return; // } // // //如果不一样,需要计算新的起始点已经各种临时数据 // this._transform = matrix; // Mat4.invert(this._matrix, matrix); // // //根据矩阵计算新的临界值 // if (this._orginThreshold > 0.0) { // let tmp = this._start; // Mat4.getScale(tmp, this._matrix); // let x = tmp[0]; // let y = tmp[1]; // let z = tmp[2]; // this._threshold = this._orginThreshold * (x > y ? (x > z ? x : z) : y > z ? y : z); // } // //根据矩阵计算新的起始点 // Vec3.transformMat4(this._start, this._orginStart, this._matrix); // Vec3.transformMat4(this._end, this._orginEnd, this._matrix); // // //根据新的起始点计算各种临时数据 // Vec3.sub(this._direction, this._end, this._start); // this._length = Vec3.length(this._direction);//长度 // this._inverseLength = this._length <= Algorithm.EPSILON ? 1.0 / this._length : 0.0; // Vec3.scale(this._direction, this._direction, this._inverseLength);//求单位向量 // }, // setGeometry: function (geometry, matrix) { // Intersector.prototype.setGeometry.call(this, geometry, matrix); // // //如果不一样,需要计算新的起始点已经各种临时数据 // Mat4.invert(this._matrix, matrix); // // //根据矩阵计算新的临界值 // if (this._orginThreshold > 0.0) { // let tmp = this._start; // Mat4.getScale(tmp, this._matrix); // let x = tmp[0]; // let y = tmp[1]; // let z = tmp[2]; // this._threshold = this._orginThreshold * (x > y ? (x > z ? x : z) : y > z ? y : z); // } // //根据矩阵计算新的起始点 // Vec3.transformMat4(this._start, this._orginStart, this._matrix); // Vec3.transformMat4(this._end, this._orginEnd, this._matrix); // // //根据新的起始点计算各种临时数据 // Vec3.sub(this._direction, this._end, this._start); // this._length = Vec3.length(this._direction);//长度 // this._inverseLength = this._length <= Algorithm.EPSILON ? 1.0 / this._length : 0.0; // Vec3.scale(this._direction, this._direction, this._inverseLength);//求单位向量 // }, // setGeometry: function (geometry) { // //没有顶点数据不处理直接返回 // let vertexbuffer = geometry.getBufferArray(‘Vertex‘); // if(!vertexbuffer) return; // // //没有图元不处理直接返回 // let primitive = geometry.getPrimitive(); // if (primitive) // primitive.operate(this); // },
以上的LineSegmentIntersector就是计算线段和平面交点的类,具体算法不再赘述,请自行参考《WebGL编程指南》。好了,我们接下来就看一个项目中的具体案例,请看下图
我们在pick事件中使用了LineSegmentIntersector对场景中的包围盒和坐标系模型进行了raycaster射线碰撞检测,结果我们得到了一系列的返回对象,其中包括包围盒的2个面,坐标系的一根坐标轴的geometry,这就另我们觉得难办了,鼠标射线碰到了不止一个模型,我们该怎么办呢,这里就要说明一下,一般我们都取离near近截面最近的一个模型作为我们pick选中的模型,因为其他模型都被处于前方的该模型遮挡住了。
好了,今天对raycaster的解释就结束了,只是初步了解一下,raycaster还有很多应用场景,这里和我们的鼠标拾取不相关的就不介绍了,谢谢大家阅读,欢迎大家一起留言探讨,再次感谢。转载本文请注明出处:https://www.cnblogs.com/ccentry/p/9973165.html
标签:ORC ports 存储 def 相机 几何 WebG 鼠标 事先
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/ccentry/p/9973165.html