标签:des style blog http color io os 使用 ar
一、SQLite简单使用
SQLite是遵循ACID的关系数据库管理系统,它的处理速度很快,
它的设计目标是嵌入式的,只需要几百K的内存就可以了。
1.下载SQLite
http://www.sqlite.org/download.html
sqlite-dll-win32-x86-201410071659.zip(294.11 KiB)
sqlite-shell-win32-x86-3080600.zip
解压在文件夹D:\Database\sqlite下,
得到文件sqlite3.dll,sqlite3.exe
参考:http://www.w3cschool.cc/sqlite/sqlite-installation.html
2.安装SQLite
写批处理文件z_sqlite.bat,内容是:
@echo d: cd D:\Database\sqlite cmd.exe
执行命令sqlite3,看到结果:
D:\Database\sqlite>sqlite3 SQLite version 3.8.6 2014-08-15 11:46:33 Enter ".help" for usage hints. Connected to a transient in-memory database. Use ".open FILENAME" to reopen on a persistent database. sqlite>
或是:
@echo PATH=%PATH%;D:\Database\sqlite cmd.exe
执行命令sqlite3,看到结果:
ECHO 处于打开状态。 D:\Database>PATH=C:\ProgramData\Oracle\Java\javapath;D:\Program_Files\oraclexe\app\oracle\product\10.2.0\server\bin;C:\P rogram Files\AMD APP\bin\x86;C:\Windows\system32;C:\Windows;C:\Windows\System32\Wbem;C:\Windows\System32\WindowsPowerShe ll\v1.0\;C:\Program Files\ATI Technologies\ATI.ACE\Core-Static;C:\Python27;C:\Program Files\MySQL\MySQL Server 5.5\bin;D :\Idea\config\apache-maven-3.2.3\bin;D:\Idea\config\apache-ant-1.9.4\bin;D:\Database\sqlite D:\Database>cmd.exe Microsoft Windows [版本 6.3.9600] (c) 2013 Microsoft Corporation。保留所有权利。 D:\Database>sqlite3 SQLite version 3.8.6 2014-08-15 11:46:33 Enter ".help" for usage hints. Connected to a transient in-memory database. Use ".open FILENAME" to reopen on a persistent database. sqlite>
表明sqlite已安装。
解释:不让bat文件运行命令结束后cmd窗口自动关闭,最后运行一下cmd.exe
更多疑问请参考:[SQLite 教程]:http://www.w3cschool.cc/sqlite/sqlite-installation.html
3.SQLite命令
.help 帮助
.show 显示各种设置的当前值
.schema 显示建表语句
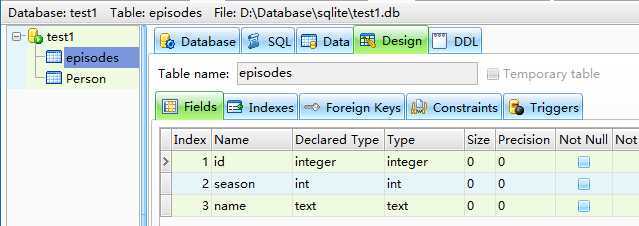
sqlite> .schema sqlite_master
create table episodes( id integer primary key, season int, name text );
其它的命令类似于一搬的sql语句
insert into episodes values(1, 1, ‘one‘);
select * from episodes;
4.SQLite管理工具:SQLiteExpert
下载:http://www.sqliteexpert.com/download.html
选择免费版:SQLite Expert Personal
下载的太慢了,可以选择以前的版本:
http://dl.dbank.com/c0sog1u0xb
创建db文件:
D:\Database\sqlite>sqlite3 test1.db
SQLite version 3.8.6 2014-08-15 11:46:33
Enter ".help" for usage hints.
sqlite> sqlite3 test1.db;
Error: near "sqlite3": syntax error
sqlite>
看到在D:\Database\sqlite目录下生成了一个test1.db的文件
File>OpenDatabase>选择刚刚生成的db文件>确定
看到数据库的文件已经导入: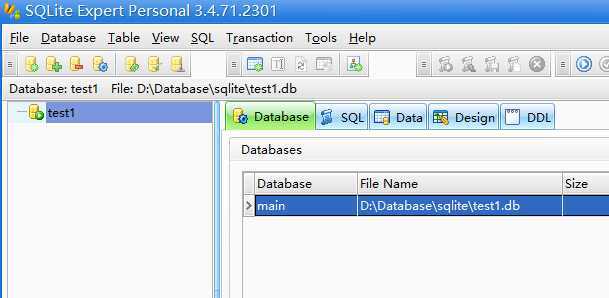
二、JPA介绍
Java Persistence API:简化现有的持久化开发工作和整合ORM技术
结束现在的Hibernate、TopLink、JDO等ORM框架各自为营的局面
面向Hibernate的API开发,会紧密的与Hibernate耦合
JPA规范是由Hibernate的作者制定的
ORM映射元数据: 描述对象与表之间的映射关系
Java持久化API: 执行CRUD操作
查询语言: JPQL,避免程序和SQL语句的紧密耦合
设置Maven4MyEclipse:MyEclipse>Maven4MyEclipse
Installation=D:\Idea\config\apache-maven-3.2.3
User Settings=D:\Idea\config\apache-maven-3.2.3\conf\settings.xml
Local Repository=D:\Idea\maven\repository
配置文件:META-INF/persistence.xml
D:\Idea\config\hibernate-release-4.3.6.Final\lib\jpa-metamodel-generator
/hibernate-jpamodelgen-4.3.6.Final.jar/persistence_2_1.xsd
配置数据库的方言,以及自动建表
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <persistence version="2.1" xmlns="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/persistence" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/persistence http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/persistence/persistence_2_1.xsd "> <persistence-unit name="module1" transaction-type="RESOURCE_LOCAL"> <properties> <property name="hibernate.hbm2ddl.auto" value="update" /> <property name="hibernate.show_sql" value="true" /> </properties> </persistence-unit> </persistence>
三、SQLite作为Hibernate的数据源
1.Maven配置文件:pom.xml
用MyEclipse新建一个Maven的模块app1.module1
配置它的pom文件:/module1/pom.xml
引入JPA的依赖:
http://hibernate.org/orm/downloads/
<!-- for JPA, use hibernate-entitymanager instead of hibernate-core -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.hibernate</groupId>
<artifactId>hibernate-entitymanager</artifactId>
<version>4.3.6.Final</version>
</dependency>
sqlite-jdbc
引入sqlite的依赖:http://www.mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.xerial/sqlite-jdbc/3.7.2
<dependency>
<groupId>org.xerial</groupId>
<artifactId>sqlite-jdbc</artifactId>
<version>3.7.2</version>
</dependency>
处理报错:ArtifactTransferException: Failure to transfer org.xerial:sqlite-jdbc:jar:3.7.2 from
http://zhanghua.1199.blog.163.com/blog/static/464498072013529936189/
对于这个包从maven中心传输到本地仓库失败,决定不会重新尝试下载jar包,直到mavne再改更新索引,或强制更新。
实际的解决办法是:直接去本地仓库,把这个1.1.1的目录删除掉(因为包没有下载下来),再次刷新你的项目就中以了,
或者在你的项目上右击,选择maven--->update就可以了,让maven重新下载。
删除D:\Idea\maven\repository\org\xerial文件
/module1/pom.xml
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd"> <modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion> <groupId>yuki.jpa.hibernate.app1</groupId> <artifactId>module1</artifactId> <version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version> <packaging>jar</packaging> <name>module1</name> <url>http://maven.apache.org</url> <properties> <project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding> </properties> <dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>junit</groupId> <artifactId>junit</artifactId> <version>4.11</version> <scope>test</scope> </dependency> <!-- for JPA, use hibernate-entitymanager instead of hibernate-core --> <dependency> <groupId>org.hibernate</groupId> <artifactId>hibernate-entitymanager</artifactId> <version>4.3.6.Final</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.xerial</groupId> <artifactId>sqlite-jdbc</artifactId> <version>3.7.2</version> </dependency> </dependencies> </project>
2.JPA的配置文件:persistence.xml
D:\Workspaces\IntelliJ_IDEA\JavaEE_JPA\Module1\src\main\resources\META-INF\persistence.xml
在这里,需要配置数据源,数据源的位置是sqlite的db文件的位置
D:\Database\sqlite\test1.db
数据源的用户名和密码是空字符串就可以了
/module1/src/main/java/META-INF/persistence.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <persistence version="2.1" xmlns="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/persistence" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/persistence http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/persistence/persistence_2_1.xsd "> <persistence-unit name="module1" transaction-type="RESOURCE_LOCAL"> <class>yuki.jpa.hibernate.app1.module1.bean.Person</class> <properties> <property name="hibernate.dialect" value="com.applerao.hibernatesqlite.dialect.SQLiteDialect" /> <property name="hibernate.hbm2ddl.auto" value="update" /> <property name="hibernate.connection.driver_class" value="org.sqlite.JDBC" /> <property name="hibernate.connection.url" value="jdbc:sqlite://D:/Database/sqlite/test1.db" /> <property name="hibernate.connection.username" value="" /> <property name="hibernate.connection.password" value="" /> <property name="hibernate.show_sql" value="true" /> </properties> </persistence-unit> </persistence>
3.SQLite的hibernate方言
复制代码:https://code.google.com/p/hibernate-sqlite/source/browse/trunk/source/src/main/java/com/applerao/hibernatesqlite/dialect/SQLiteDialect.java?r=24
修改报错内容:http://www.myexception.cn/open-source/1120141.html
hibernate4 替代hibernate3 的Hibernate.INTEGER的用法
hibernate3 中没有了Hibernate.INTEGER的用法
在Hibernate4中使用的方法是 StandardBasicTypes.INTEGER用法
例如:sqlQuery.addScalar("id",StandardBasicTypes.INTEGER);
/module1/src/main/java/com/applerao/hibernatesqlite/dialect/SQLiteDialect.java
package com.applerao.hibernatesqlite.dialect; /** * https://code.google.com/p/hibernate-sqlite/source/browse/trunk/source/src/main/java/com/applerao/hibernatesqlite/dialect/SQLiteDialect.java?r=24 * http://www.myexception.cn/open-source/1120141.html * */ /* * The author disclaims copyright to this source code. In place of * a legal notice, here is a blessing: * * May you do good and not evil. * May you find forgiveness for yourself and forgive others. * May you share freely, never taking more than you give. * */ import java.sql.Types; import org.hibernate.dialect.Dialect; import org.hibernate.dialect.function.SQLFunctionTemplate; import org.hibernate.dialect.function.StandardSQLFunction; import org.hibernate.dialect.function.VarArgsSQLFunction; import org.hibernate.type.StandardBasicTypes; public class SQLiteDialect extends Dialect { public SQLiteDialect() { super(); registerColumnType(Types.BIT, "integer"); registerColumnType(Types.TINYINT, "tinyint"); registerColumnType(Types.SMALLINT, "smallint"); registerColumnType(Types.INTEGER, "integer"); registerColumnType(Types.BIGINT, "bigint"); registerColumnType(Types.FLOAT, "float"); registerColumnType(Types.REAL, "real"); registerColumnType(Types.DOUBLE, "double"); registerColumnType(Types.NUMERIC, "numeric"); registerColumnType(Types.DECIMAL, "decimal"); registerColumnType(Types.CHAR, "char"); registerColumnType(Types.VARCHAR, "varchar"); registerColumnType(Types.LONGVARCHAR, "longvarchar"); registerColumnType(Types.DATE, "date"); registerColumnType(Types.TIME, "time"); registerColumnType(Types.TIMESTAMP, "timestamp"); registerColumnType(Types.BINARY, "blob"); registerColumnType(Types.VARBINARY, "blob"); registerColumnType(Types.LONGVARBINARY, "blob"); // registerColumnType(Types.NULL, "null"); registerColumnType(Types.BLOB, "blob"); registerColumnType(Types.CLOB, "clob"); registerColumnType(Types.BOOLEAN, "integer"); registerFunction("concat", new VarArgsSQLFunction(StandardBasicTypes.STRING, "", "||", "")); registerFunction("mod", new SQLFunctionTemplate(StandardBasicTypes.INTEGER, "?1 % ?2")); registerFunction("substr", new StandardSQLFunction("substr", StandardBasicTypes.STRING)); registerFunction("substring", new StandardSQLFunction("substr", StandardBasicTypes.STRING)); } public boolean supportsIdentityColumns() { return true; } /* * public boolean supportsInsertSelectIdentity() { return true; // As * specify in NHibernate dialect } */ public boolean hasDataTypeInIdentityColumn() { return false; // As specify in NHibernate dialect } /* * public String appendIdentitySelectToInsert(String insertString) { return * new StringBuffer(insertString.length()+30). // As specify in NHibernate * dialect append(insertString). * append("; ").append(getIdentitySelectString()). toString(); } */ public String getIdentityColumnString() { // return "integer primary key autoincrement"; return "integer"; } public String getIdentitySelectString() { return "select last_insert_rowid()"; } public boolean supportsLimit() { return true; } public String getLimitString(String query, boolean hasOffset) { return new StringBuffer(query.length() + 20).append(query).append(hasOffset ? " limit ? offset ?" : " limit ?").toString(); } public boolean supportsTemporaryTables() { return true; } public String getCreateTemporaryTableString() { return "create temporary table if not exists"; } public boolean dropTemporaryTableAfterUse() { return false; } public boolean supportsCurrentTimestampSelection() { return true; } public boolean isCurrentTimestampSelectStringCallable() { return false; } public String getCurrentTimestampSelectString() { return "select current_timestamp"; } public boolean supportsUnionAll() { return true; } public boolean hasAlterTable() { return false; // As specify in NHibernate dialect } public boolean dropConstraints() { return false; } public String getAddColumnString() { return "add column"; } public String getForUpdateString() { return ""; } public boolean supportsOuterJoinForUpdate() { return false; } public String getDropForeignKeyString() { throw new UnsupportedOperationException("No drop foreign key syntax supported by SQLiteDialect"); } public String getAddForeignKeyConstraintString(String constraintName, String[] foreignKey, String referencedTable, String[] primaryKey, boolean referencesPrimaryKey) { throw new UnsupportedOperationException("No add foreign key syntax supported by SQLiteDialect"); } public String getAddPrimaryKeyConstraintString(String constraintName) { throw new UnsupportedOperationException("No add primary key syntax supported by SQLiteDialect"); } public boolean supportsIfExistsBeforeTableName() { return true; } public boolean supportsCascadeDelete() { return false; } }
4.设置
设置程序关联:控制面板\所有控制面板项\默认程序\设置默认程序\设置程序关联
设置XML格式化代码时不换行:
MyEclipse>FilesAndEditors>XML>XML Source>Linewidth=很大的值
设置JAVA格式化代码时不换行:
Java>CodeStyle>Formatter>New…>LineWrapping>
SettingsForAnnotation>选择上面的选项>LineWrapPolicy=DoNotWrap
5.异常处理
没有持久化的提供者
报错:javax.persistence.PersistenceException: No Persistence provider for EntityManager named module1
解决:http://stackoverflow.com/questions/21975553/javax-persistence-persistenceexception-no-persistence-provider-for-entitymanage
If you‘re doing this from a JUnit test, and using maven,
the persistence.xml should be located in src/test/resources/META-INF/persistence.xml
which will be put into the correct location at test execution time.
The file in src/main/resources/META-INF/ is not used as it is not in the test-jar‘s path.
执行maven clean之后
执行maven clean后会删除运行处的persistence.xml,可以删除再添加persistence.xml,来使persistence.xml在运行的文件夹下
四、JPA实体
1.自动建表
<property name="hibernate.hbm2ddl.auto" value="update" />
http://www.cnblogs.com/talo/articles/1662244.html
validate 加载hibernate时,验证创建数据库表结构
create 每次加载hibernate,重新创建数据库表结构,这就是导致数据库表数据丢失的原因。
create-drop 加载hibernate时创建,退出是删除表结构
update 加载hibernate自动更新数据库结构
需要建表的类Person.java
添加注解Entity,被 @Entity注解的类就是JPA的实体类,
主键注解 @Id, @GeneratedValue
http://andyj.iteye.com/blog/287827
IDENTITY: 表自增键字段,Oracle不支持这种方式
AUTO: JPA自动选择合适的策略,是默认选项
SEQUENCE: 通过序列产生主键,通过 @SequenceGenerator注解指定序列名,MySql不支持这种方式
TABLE: 通过表产生主键,框架借由表模拟序列产生主键,使用该策略可以使应用更易于数据库移植
/module1/src/main/java/yuki/jpa/hibernate/app1/module1/bean/person/Person1.txt
package yuki.jpa.hibernate.app1.module1.bean; import javax.persistence.Column; import javax.persistence.Entity; import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue; import javax.persistence.Id; @Entity public class Person { private Integer id; private String name; public Person() {} public Person(String name) { this.name = name; } @Id @GeneratedValue // @GeneratedValue (strategy=GenerationType.AUTO) public Integer getId() { return id; } public void setId(Integer id) { this.id = id; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } }
测试类PersonTest.java
获取实体管理器工厂,获取实体管理器,开启事务,保存,提交事务,关闭实体管理器,关闭实体管理器工厂
/module1/src/test/java/yuki/jpa/hibernate/app1/module1/bean/personTest/PersonTest1
package yuki.jpa.hibernate.app1.module1.bean; import javax.persistence.EntityManager; import javax.persistence.EntityManagerFactory; import javax.persistence.Persistence; import org.junit.Test; public class PersonTest { @Test public void save() { EntityManagerFactory factory = Persistence.createEntityManagerFactory("module1"); EntityManager manager = factory.createEntityManager(); manager.getTransaction().begin(); manager.persist(new Person("person1")); manager.getTransaction().commit(); manager.close(); factory.close(); } }
刷新SQliteExpert中的数据库,看到新建的表和保存的数据
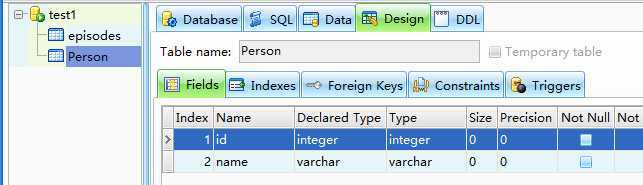
2.实体类的注解
自定义表名 @Table(name="xxxPerson")
自定义列的属性 @Column(length=10, nullable=false, name="personName")
/module1/src/main/java/yuki/jpa/hibernate/app1/module1/bean/person/Person2.txt
package yuki.jpa.hibernate.app1.module1.bean; import javax.persistence.Column; import javax.persistence.Entity; import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue; import javax.persistence.Id; import javax.persistence.Table; @Entity @Table(name="xxxPerson") public class Person { private Integer id; private String name; public Person() {} public Person(String name) { this.name = name; } @Id @GeneratedValue public Integer getId() { return id; } public void setId(Integer id) { this.id = id; } @Column(length=10, nullable=false, name="personName") public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } }
删除Person表,再次测试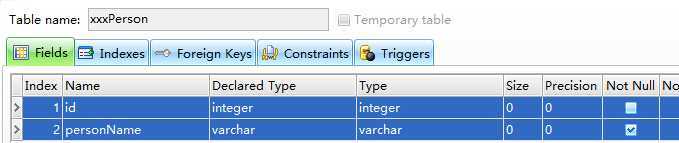
日期类型 @Temporal(TemporalType.DATE)
枚举类型 @Enumerated(EnumType.STRING)
/module1/src/main/java/yuki/jpa/hibernate/app1/module1/bean/person/Person3.txt
package yuki.jpa.hibernate.app1.module1.bean; import java.util.Date; import javax.persistence.Column; import javax.persistence.Entity; import javax.persistence.EnumType; import javax.persistence.Enumerated; import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue; import javax.persistence.Id; import javax.persistence.Temporal; import javax.persistence.TemporalType; @Entity public class Person { private Integer id; private String name; private Date birthday; //1987-12-10 private Gender gender = Gender.MAN; //默认值为MAN public Person() {} public Person(String name) { this.name = name; } @Id @GeneratedValue public Integer getId() { return id; } public void setId(Integer id) { this.id = id; } @Column(length=10, nullable=false) public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } @Temporal(TemporalType.DATE) public Date getBirthday() { return birthday; } public void setBirthday(Date birthday) { this.birthday = birthday; } @Enumerated(EnumType.STRING) @Column(length=5, nullable=false/*保存枚举值要设置数据库的字段不能为空*/) public Gender getGender() { return gender; } public void setGender(Gender gender) { this.gender = gender; } }
/module1/src/main/java/yuki/jpa/hibernate/app1/module1/bean/Gender.java
package yuki.jpa.hibernate.app1.module1.bean; public enum Gender { MAN,WOMEN }
删除Person表,再次测试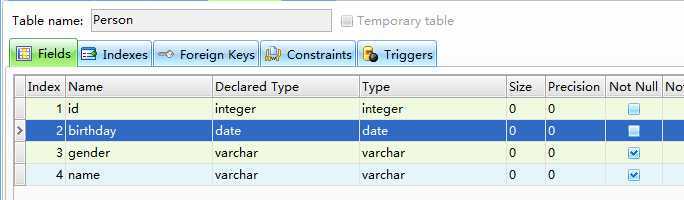
文件或大文本数据 @Lob
/module1/src/main/java/yuki/jpa/hibernate/app1/module1/bean/person/Person4.txt
package yuki.jpa.hibernate.app1.module1.bean; import java.util.Date; import javax.persistence.Column; import javax.persistence.Entity; import javax.persistence.EnumType; import javax.persistence.Enumerated; import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue; import javax.persistence.Id; import javax.persistence.Lob; import javax.persistence.Temporal; import javax.persistence.TemporalType; @Entity public class Person { private Integer id; private String name; private Date birthday; //1987-12-10 private Gender gender = Gender.MAN; //默认值为MAN private String info; //存放大文本数据 private byte[] file; //存放文件 public Person() {} public Person(String name) { this.name = name; } @Id @GeneratedValue public Integer getId() { return id; } public void setId(Integer id) { this.id = id; } @Column(length=10, nullable=false) public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } @Temporal(TemporalType.DATE) public Date getBirthday() { return birthday; } public void setBirthday(Date birthday) { this.birthday = birthday; } @Enumerated(EnumType.STRING) @Column(length=5, nullable=false/*保存枚举值要设置数据库的字段不能为空*/) public Gender getGender() { return gender; } public void setGender(Gender gender) { this.gender = gender; } @Lob public String getInfo() { return info; } public void setInfo(String info) { this.info = info; } @Lob public byte[] getFile() { return file; } public void setFile(byte[] file) { this.file = file; } }
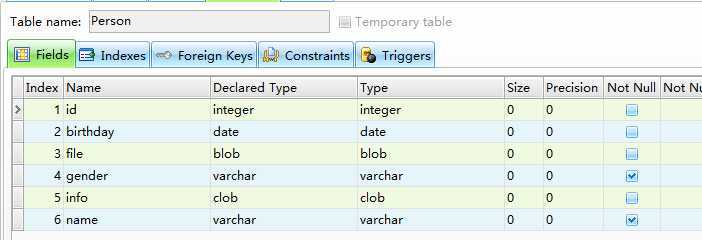
延迟加载 @Basic(fetch=FetchType.LAZY)
不持久化的字段 @Transient
/module1/src/main/java/yuki/jpa/hibernate/app1/module1/bean/person/Person5.txt
package yuki.jpa.hibernate.app1.module1.bean; import java.util.Date; import javax.persistence.Basic; import javax.persistence.Column; import javax.persistence.Entity; import javax.persistence.EnumType; import javax.persistence.Enumerated; import javax.persistence.FetchType; import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue; import javax.persistence.Id; import javax.persistence.Lob; import javax.persistence.Temporal; import javax.persistence.TemporalType; import javax.persistence.Transient; @Entity public class Person { private Integer id; private String name; private Date birthday; //1987-12-10 private Gender gender = Gender.MAN; //默认值为MAN private String info; //存放大文本 private byte[] file; //存放大文件,延迟加载 private String imagePath; //不持久化的字段 public Person() {} public Person(String name) { this.name = name; } @Id @GeneratedValue public Integer getId() { return id; } public void setId(Integer id) { this.id = id; } @Column(length=10, nullable=false) public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } @Temporal(TemporalType.DATE) public Date getBirthday() { return birthday; } public void setBirthday(Date birthday) { this.birthday = birthday; } @Enumerated(EnumType.STRING) @Column(length=5, nullable=false/*保存枚举值要设置数据库的字段不能为空*/) public Gender getGender() { return gender; } public void setGender(Gender gender) { this.gender = gender; } @Lob public String getInfo() { return info; } public void setInfo(String info) { this.info = info; } @Lob @Basic(fetch=FetchType.LAZY) //访问这个属性的时候才会加载进内存 public byte[] getFile() { return file; } public void setFile(byte[] file) { this.file = file; } @Transient public String getImagePath() { return imagePath; } public void setImagePath(String imagePath) { this.imagePath = imagePath; } }
下面使用的实体类
/module1/src/main/java/yuki/jpa/hibernate/app1/module1/bean/person/Person7
package yuki.jpa.hibernate.app1.module1.bean; import java.util.Date; import javax.persistence.Column; import javax.persistence.Entity; import javax.persistence.EnumType; import javax.persistence.Enumerated; import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue; import javax.persistence.Id; import javax.persistence.Temporal; import javax.persistence.TemporalType; import javax.persistence.Transient; @Entity public class Person { private Integer id; private String name; private Date birthday; //1987-12-10 private Gender gender = Gender.MAN; //默认值为MAN private String imagePath; //不持久化的字段 public Person() {} public Person(String name) { this.name = name; } @Id @GeneratedValue public Integer getId() { return id; } public void setId(Integer id) { this.id = id; } @Column(length=10, nullable=false) public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } @Temporal(TemporalType.DATE) public Date getBirthday() { return birthday; } public void setBirthday(Date birthday) { this.birthday = birthday; } @Enumerated(EnumType.STRING) @Column(length=5, nullable=false/*保存枚举值要设置数据库的字段不能为空*/) public Gender getGender() { return gender; } public void setGender(Gender gender) { this.gender = gender; } @Transient public String getImagePath() { return imagePath; } public void setImagePath(String imagePath) { this.imagePath = imagePath; } @Override public String toString() { return "Person [id=" + id + ", name=" + name + ", birthday=" + birthday + ", gender=" + gender + ", imagePath=" + imagePath + "]"; } }
3.对实体类的查找
/module1/src/test/java/yuki/jpa/hibernate/app1/module1/bean/personTest/PersonTest2
package yuki.jpa.hibernate.app1.module1.bean; import javax.persistence.EntityManager; import javax.persistence.EntityManagerFactory; import javax.persistence.Persistence; import org.junit.Test; public class PersonTest { @Test public void getPerson() { EntityManagerFactory factory = Persistence.createEntityManagerFactory("module1"); EntityManager em = factory.createEntityManager(); // em.getTransaction().begin(); Person person = em.find(Person.class, 1); System.out.println(person); // em.getTransaction().commit(); em.close(); factory.close(); } }
Hibernate: select person0_.id as id1_0_0_, person0_.birthday as birthday2_0_0_, person0_.gender as gender3_0_0_, person0_.name as name4_0_0_ from Person person0_ where person0_.id=? Person [id=1, name=person1, birthday=null, gender=MAN, imagePath=null]
.find和.getReference
/module1/src/test/java/yuki/jpa/hibernate/app1/module1/bean/personTest/PersonTest4
package yuki.jpa.hibernate.app1.module1.bean; import javax.persistence.EntityManager; import javax.persistence.EntityManagerFactory; import javax.persistence.Persistence; import org.junit.Test; public class PersonTest { @Test public void getPerson() { EntityManagerFactory factory = Persistence.createEntityManagerFactory("module1"); EntityManager em = factory.createEntityManager(); // Person person = em.find(Person.class, 1); //相当于hibernate的get Person person = em.getReference(Person.class, 1); //相当于hibernate的load // load之后返回的是代理对象,使用的是cglib动态创建字节码的技术 // 如果不访问数据,是不回发生数据的加载行为的 // org.hibernate.LazyInitializationException: could not initialize proxy - no Session em.close(); System.out.println(person.getName()); factory.close(); } }
Tests run: 1, Failures: 0, Errors: 1, Skipped: 0, Time elapsed: 2.712 sec <<< FAILURE! getPerson(yuki.jpa.hibernate.app1.module1.bean.PersonTest) Time elapsed: 2.613 sec <<< ERROR! org.hibernate.LazyInitializationException: could not initialize proxy - no Session
异常在访问引用对象的属性时就会发生,即使实体管理器没有关闭
/module1/src/test/java/yuki/jpa/hibernate/app1/module1/bean/personTest/PersonTest5
package yuki.jpa.hibernate.app1.module1.bean; import javax.persistence.EntityManager; import javax.persistence.EntityManagerFactory; import javax.persistence.Persistence; import org.junit.Test; public class PersonTest { @Test public void getPerson() { EntityManagerFactory factory = Persistence.createEntityManagerFactory("module1"); EntityManager em = factory.createEntityManager(); /*Person person = em.find(Person.class, 2);//null Person person = em.getReference(Person.class, 2);//javax.persistence.EntityNotFoundException System.out.println(person);*/ Person person = em.getReference(Person.class, 2); System.out.println(person.getName()); //这里出现了异常 em.close(); factory.close(); } }
at yuki.jpa.hibernate.app1.module1.bean.Person_$$_jvst586_0.getName(Person_$$_jvst586_0.java)
at yuki.jpa.hibernate.app1.module1.bean.PersonTest.getPerson(PersonTest.java:19)
4.JPA实体的四种状态
new(新建)、managed(托管)、游离(脱管)、删除
当一个对象与事务关联且进入托管状态时
对属性进行更新,对应的数据就会同步到数据库
对象的属性发生更改后,会放进jdbc的批提交里去
/module1/src/test/java/yuki/jpa/hibernate/app1/module1/bean/personTest/PersonTest6
package yuki.jpa.hibernate.app1.module1.bean; import javax.persistence.EntityManager; import javax.persistence.EntityManagerFactory; import javax.persistence.Persistence; import org.junit.Test; public class PersonTest { @Test public void updatePerson() { EntityManagerFactory factory = Persistence.createEntityManagerFactory("module1"); EntityManager em = factory.createEntityManager(); em.getTransaction().begin(); Person person = em.find(Person.class, 2); person.setName("老张"); em.getTransaction().commit(); em.close(); factory.close(); /** * JPA对象的四种状态 * new(新建) * managed(托管) * 游离(脱管) * 删除 * * 当一个对象与事务关联且进入托管状态时, * 对属性进行更新,对应的数据就会同步到数据库 * 对象的属性发生更改后,会放进jdbc的批提交里去 * */ } }
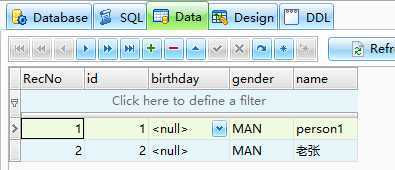
把实体管理器中的所有实体变成游离对象 .clear()
把游离对象同步回数据库 .merge(person)
/module1/src/test/java/yuki/jpa/hibernate/app1/module1/bean/personTest/PersonTest7
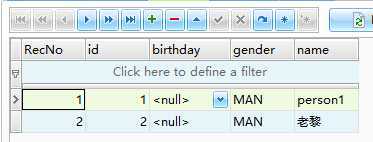
package yuki.jpa.hibernate.app1.module1.bean; import javax.persistence.EntityManager; import javax.persistence.EntityManagerFactory; import javax.persistence.Persistence; import org.junit.Test; public class PersonTest { @Test public void updatePerson() { EntityManagerFactory factory = Persistence.createEntityManagerFactory("module1"); EntityManager em = factory.createEntityManager(); em.getTransaction().begin(); Person person = em.find(Person.class, 2); em.clear(); //把实体管理器中的所有实体变成游离对象 person.setName("老黎"); em.merge(person); //把游离对象同步回数据库 em.getTransaction().commit(); em.close(); factory.close(); } }
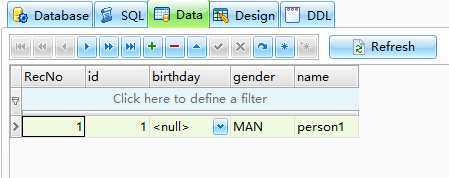
删除实体
/module1/src/test/java/yuki/jpa/hibernate/app1/module1/bean/personTest/PersonTest8
package yuki.jpa.hibernate.app1.module1.bean; import javax.persistence.EntityManager; import javax.persistence.EntityManagerFactory; import javax.persistence.Persistence; import org.junit.Test; public class PersonTest { @Test public void deletePerson() { EntityManagerFactory factory = Persistence.createEntityManagerFactory("module1"); EntityManager em = factory.createEntityManager(); em.getTransaction().begin(); Person person = em.find(Person.class, 2); em.remove(person); em.getTransaction().commit(); em.close(); factory.close(); } }
刷新实体
业务处理期间,有人修改了获取的数据,
这时,这个对象就不能拥有数据库中最新的数据
再次调用find方法也是不能获得最新数据的,
它会从EntityManager的一级缓存中获取刚才查询的对象
refresh可以刷新这个实体
/module1/src/test/java/yuki/jpa/hibernate/app1/module1/bean/personTest2/PersonTest4
package yuki.jpa.hibernate.app1.module1.bean; import javax.persistence.EntityManager; import javax.persistence.EntityManagerFactory; import javax.persistence.Persistence; import javax.persistence.Query; import org.junit.Test; public class PersonTest { @Test public void updateQuery() { EntityManagerFactory factory = Persistence.createEntityManagerFactory("module1"); EntityManager em = factory.createEntityManager(); em.getTransaction().begin(); Person person = em.find(Person.class, 3); /** * 业务处理期间,有人修改了获取的数据 * 这时,这个对象就不能拥有数据库中最新的数据 * 再次调用find方法也是不能获得最新数据的 * 它会从EntityManager的一级缓存中获取刚才查询的对象 * refresh可以刷新这个实体 */ em.refresh(person); System.out.println(person.getName()); em.getTransaction().commit(); em.close(); factory.close(); } }
Hibernate: select person0_.id as id1_0_0_, person0_.birthday as birthday2_0_0_, person0_.gender as gender3_0_0_, person0_.name as name4_0_0_ from Person person0_ where person0_.id=?
Hibernate: select person0_.id as id1_0_0_, person0_.birthday as birthday2_0_0_, person0_.gender as gender3_0_0_, person0_.name as name4_0_0_ from Person person0_ where person0_.id=?
person1
5.JPQL语句
用hibernate实现的JPA是可以不写select o的,建议写上select o,因为这是JPA的规范
写据查询语句参数的时候,不要把参数直接放进去
这样会造成字符串的组拼,delete from table_name会删除所有的表的数据
可以使用命名参数,比如:id;也可以使用位参,比如?;
位参可以设置编号,在问号后写1:?1,表示从1开始
/module1/src/test/java/yuki/jpa/hibernate/app1/module1/bean/personTest2/PersonTest1
package yuki.jpa.hibernate.app1.module1.bean; import java.util.List; import javax.persistence.EntityManager; import javax.persistence.EntityManagerFactory; import javax.persistence.Persistence; import javax.persistence.Query; import org.junit.Test; public class PersonTest { @Test public void queryPerson() { EntityManagerFactory factory = Persistence.createEntityManagerFactory("module1"); EntityManager em = factory.createEntityManager(); /** * 用hibernate实现的JPA是可以不写select o的 * 建议写上select o,因为这是JPA的规范 * * 写据查询语句参数的时候,不要把参数直接放进去 * 这样会造成字符串的组拼,delete from table_name会删除所有的表的数据 * 可以使用命名参数,比如:id;也可以使用位参,比如?; * 位参可以设置编号,在问号后写1:?1,表示从1开始 * */ // Query query = em.createQuery("select count(o) from Person o"); Query query = em.createQuery("select o from Person o where o.id=?1"); query.setParameter(1, 2); // Person person = (Person) query.getSingleResult(); // System.out.println(person.getName()); @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") List<Person> persons = query.getResultList(); for(Person p : persons) System.out.println(p.getName()); em.close(); factory.close(); } }
Hibernate: select person0_.id as id1_0_, person0_.birthday as birthday2_0_, person0_.gender as gender3_0_, person0_.name as name4_0_ from Person person0_ where person0_.id=?
person1
增删改操作需要开启事务,如果不开启会抛出异常
/module1/src/test/java/yuki/jpa/hibernate/app1/module1/bean/personTest2/PersonTest2
package yuki.jpa.hibernate.app1.module1.bean; import java.util.List; import javax.persistence.EntityManager; import javax.persistence.EntityManagerFactory; import javax.persistence.Persistence; import javax.persistence.Query; import org.junit.Test; public class PersonTest { @Test public void deleteQuery() { EntityManagerFactory factory = Persistence.createEntityManagerFactory("module1"); EntityManager em = factory.createEntityManager(); // 如果不开启事务 // javax.persistence.TransactionRequiredException: Executing an update/delete query em.getTransaction().begin(); Query query = em.createQuery("delete from Person o where o.id=?1"); query.setParameter(1, 2); query.executeUpdate(); em.getTransaction().commit(); em.close(); factory.close(); } }
javax.persistence.TransactionRequiredException: Executing an update/delete query /module1/src/test/java/yuki/jpa/hibernate/app1/module1/bean/personTest2/PersonTest2 Hibernate: delete from Person where id=?
/module1/src/test/java/yuki/jpa/hibernate/app1/module1/bean/personTest2/PersonTest3
package yuki.jpa.hibernate.app1.module1.bean; import javax.persistence.EntityManager; import javax.persistence.EntityManagerFactory; import javax.persistence.Persistence; import javax.persistence.Query; import org.junit.Test; public class PersonTest { @Test public void updateQuery() { EntityManagerFactory factory = Persistence.createEntityManagerFactory("module1"); EntityManager em = factory.createEntityManager(); // 如果不开启事务 // javax.persistence.TransactionRequiredException: Executing an update/delete query em.getTransaction().begin(); Query query = em.createQuery("update Person o set o.name=:name where o.id=:id"); query.setParameter("name", "name3"); query.setParameter("id", 3); query.executeUpdate(); em.getTransaction().commit(); em.close(); factory.close(); } }
/module1/src/test/java/yuki/jpa/hibernate/app1/module1/bean/personTest2/PersonTest3
Hibernate: update Person set name=? where id=?
五、"JPA并不依赖于某一个持久化产品"的解释
创建实体管理工厂:Persistence.createEntityManagerFactory
寻找类路径下所有的持久化驱动类,JPA并不依赖于某一个持久化产品
如何与持久化产品进行对接,使用的是类似于JDBC驱动的一个类
这个类在jdbc里叫做jdbc驱动,在持久化里叫做持久化驱动类
/META-INF/services/下寻找:javax.persistence.spi.PersistenceProvider
找到指定的持久化驱动,这个文件起到了桥梁的作用
org.hibernate.jpa.HibernatePersistenceProvider
# The deprecated provider, logs warnings when used.
org.hibernate.ejb.HibernatePersistence
遍历所有的驱动,具体使用哪一个具有随机性
如果创建出了EntityManagerFactory对象,就跳出循环
/module1/src/test/java/yuki/jpa/hibernate/app1/module1/bean/persistence/Persistence.java
/* * Copyright (c) 2008, 2009, 2011 Oracle, Inc. All rights reserved. * * This program and the accompanying materials are made available under the * terms of the Eclipse Public License v1.0 and Eclipse Distribution License v. 1.0 * which accompanies this distribution. The Eclipse Public License is available * at http://www.eclipse.org/legal/epl-v10.html and the Eclipse Distribution License * is available at http://www.eclipse.org/org/documents/edl-v10.php. */ //package javax.persistence; package yuki.jpa.hibernate.app1.module1.bean.persistence; import java.util.HashSet; import java.util.List; import java.util.Map; import java.util.Set; import javax.persistence.EntityManagerFactory; import javax.persistence.PersistenceException; import javax.persistence.PersistenceUtil; import javax.persistence.spi.LoadState; import javax.persistence.spi.PersistenceProvider; import javax.persistence.spi.PersistenceProviderResolverHolder; /** * Bootstrap class that provides access to an EntityManagerFactory. */ public class Persistence { @Deprecated public static final String PERSISTENCE_PROVIDER = "javax.persistence.spi.PeristenceProvider"; @Deprecated protected static final Set<PersistenceProvider> providers = new HashSet<PersistenceProvider>(); /** * Create and return an EntityManagerFactory for the named persistence unit. * * @param persistenceUnitName The name of the persistence unit * * @return The factory that creates EntityManagers configured according to the specified persistence unit */ /// 一开始调用的方法 public static EntityManagerFactory createEntityManagerFactory(String persistenceUnitName) { return createEntityManagerFactory( persistenceUnitName, null ); } /** * Create and return an EntityManagerFactory for the named persistence unit using the given properties. * * @param persistenceUnitName The name of the persistence unit * @param properties Additional properties to use when creating the factory. The values of these properties override * any values that may have been configured elsewhere * * @return The factory that creates EntityManagers configured according to the specified persistence unit */ // 被一开始调用的方法指向的方法 public static EntityManagerFactory createEntityManagerFactory(String persistenceUnitName, @SuppressWarnings("rawtypes") Map properties) { EntityManagerFactory emf = null; /** * 寻找类路径下所有的持久化驱动类,JPA并不依赖于某一个持久化产品 * 如何与持久化产品进行对接,使用的是类似于JDBC驱动的一个类 * 这个类在jdbc里叫做jdbc驱动,在持久化里叫做持久化驱动类 * * D:\Idea\maven\repository\org\hibernate\hibernate-entitymanager\4.3.6.Final\hibernate-entitymanager-4.3.6.Final.jar * 寻找hibernate-entitymanager-4.3.6.Final.jar/META-INF/services/javax.persistence.spi.PersistenceProvider // org.hibernate.jpa.HibernatePersistenceProvider // # The deprecated provider, logs warnings when used. // org.hibernate.ejb.HibernatePersistence * 找到指定的持久化驱动,这个文件起到了桥梁的作用 * */ List<PersistenceProvider> providers = getProviders(); /** * 遍历所有的驱动,具体使用哪一个具有随机性 * 如果创建出了EntityManagerFactory对象,就跳出循环 */ for ( PersistenceProvider provider : providers ) { emf = provider.createEntityManagerFactory( persistenceUnitName, properties ); if ( emf != null ) { break; } } if ( emf == null ) { throw new PersistenceException( "No Persistence provider for EntityManager named " + persistenceUnitName ); } return emf; } private static List<PersistenceProvider> getProviders() { return PersistenceProviderResolverHolder .getPersistenceProviderResolver() .getPersistenceProviders(); } /** * Create database schemas and/or tables and/or create DDL scripts as determined by the supplied properties * * Called when schema generation is to occur as a separate phase from creation of the entity manager factory. * * @param persistenceUnitName the name of the persistence unit * @param properties properties for schema generation; these may also contain provider-specific properties. The * values of these properties override any values that may have been configured elsewhere. * * @throws PersistenceException if insufficient or inconsistent configuration information is provided or if schema * generation otherwise fails. */ public static void generateSchema(String persistenceUnitName, @SuppressWarnings("rawtypes") Map properties) { List<PersistenceProvider> providers = getProviders(); for ( PersistenceProvider provider : providers ) { final boolean generated = provider.generateSchema( persistenceUnitName, properties ); if ( generated ) { return; } } throw new PersistenceException( "No persistence provider found for schema generation for persistence-unit named " + persistenceUnitName ); } /** * @return Returns a <code>PersistenceUtil</code> instance. */ public static PersistenceUtil getPersistenceUtil() { return util; } private static PersistenceUtil util = //TODO add an Hibernate specific optimization new PersistenceUtil() { public boolean isLoaded(Object entity, String attributeName) { List<PersistenceProvider> providers = Persistence.getProviders(); for ( PersistenceProvider provider : providers ) { final LoadState state = provider.getProviderUtil().isLoadedWithoutReference( entity, attributeName ); if ( state == LoadState.UNKNOWN ) continue; return state == LoadState.LOADED; } for ( PersistenceProvider provider : providers ) { final LoadState state = provider.getProviderUtil().isLoadedWithReference( entity, attributeName ); if ( state == LoadState.UNKNOWN ) continue; return state == LoadState.LOADED; } return true; } public boolean isLoaded(Object object) { List<PersistenceProvider> providers = Persistence.getProviders(); for ( PersistenceProvider provider : providers ) { final LoadState state = provider.getProviderUtil().isLoaded( object ); if ( state == LoadState.UNKNOWN ) continue; return state == LoadState.LOADED; } return true; } }; }
目录结构:
更多详情请参考[黎活明JPA教程]:http://www.itcast.cn/news/c8cd98d0/3d09/443f/a189/904fccafbd72.shtml
更多好文请关注:http://www.cnblogs.com/kodoyang/
请点击下方红色的" 关注我 ",关注我吧!
孔東陽
2014/10/12
标签:des style blog http color io os 使用 ar
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/kodoyang/p/JavaEE_JPA_Hibernate_SQLite.html